How to Write Effective Facebook Ad Copy A Comprehensive Guide
How to write effective Facebook ad copy is crucial for any business looking to reach their target audience. This guide dives deep into the strategies, techniques, and best practices to create compelling ads that drive conversions. From understanding your objectives to crafting captivating headlines, we’ll explore everything you need to know to maximize your Facebook ad performance.
We’ll examine different ad objectives, like website clicks, app installs, and lead generation, and show you how to align your copy with those goals. Learning to target the right audience with tailored messaging, creating compelling headlines, and crafting persuasive body copy will also be discussed. We’ll also touch on the importance of high-quality visuals and concise language, and finish with essential testing and optimization strategies for continuous improvement.
Understanding Facebook Ad Copy Goals
Crafting effective Facebook ad copy starts with a clear understanding of your campaign objectives. Knowing what you want users to do is paramount to creating compelling messaging. This understanding translates directly into more targeted ads and ultimately, higher conversion rates. Your ad copy should be meticulously designed to achieve specific results, whether it’s driving website traffic, boosting app downloads, or collecting leads.Effective ad copy directly aligns with the specific objectives set for the Facebook ad campaign.
The ad copy’s job is to motivate the target audience to take the desired action. This involves a deep understanding of your target audience and their needs. The more accurately you can anticipate their desires and motivations, the more effective your ad copy will be.
Facebook Ad Objectives and Their Importance
Understanding the different Facebook ad objectives is crucial for crafting effective copy. These objectives range from simple website clicks to complex lead generation campaigns. Matching the ad copy to the specific objective is vital. A call to action (CTA) that encourages website clicks will differ significantly from one aimed at driving app installations.
Examples of Facebook Ad Objectives
- Website clicks: This objective aims to drive traffic to a specific webpage. Examples include promoting a new product launch, highlighting a special offer, or driving awareness about a new blog post.
- App installs: This objective is designed to encourage users to download and install a mobile application. The ad copy should highlight the key benefits of the app, such as its unique features or ease of use.
- Lead generation: This objective focuses on collecting contact information from potential customers. This could involve forms for sign-ups, email subscriptions, or requests for a consultation. This objective is vital for building a database and nurturing potential clients.
- Video views: This objective is centered on increasing the number of views for a particular video. The ad copy should entice users to watch the video, highlighting the value proposition and potential entertainment or educational content.
Aligning Ad Copy with Objectives
The success of your Facebook ad campaign hinges on the alignment between your ad copy and the desired objective. If your goal is to drive website clicks, the ad copy must clearly and concisely communicate the reason for visiting the website. The same principle applies to other objectives.
Identifying the Ideal Action for Your Target Audience, How to write effective facebook ad copy
Understanding your target audience is crucial. Knowing their pain points, desires, and motivations allows you to craft ad copy that resonates deeply. Consider what problems your product or service solves and how you can communicate this clearly and effectively. This understanding will shape your calls to action (CTAs) and the entire ad copy strategy. For example, if you’re targeting busy professionals, your ad copy should emphasize time-saving features.
Crafting Compelling Calls to Action (CTAs)
CTAs are the heart of effective Facebook ad copy. They are the clear instructions you give to your target audience on what action to take. A strong CTA will translate your ad’s message into a tangible result.
Table of Ad Objectives and Optimal CTA Examples
| Ad Objective | Optimal CTA Example |
|---|---|
| Website Clicks | “Shop Now,” “Learn More,” “Visit Our Website” |
| App Installs | “Download Now,” “Get the App,” “Install Today” |
| Lead Generation | “Request a Demo,” “Sign Up Today,” “Get a Free Consultation” |
| Video Views | “Watch Now,” “See What We’re Up To,” “Learn More in the Video” |
Targeting the Right Audience
Crafting effective Facebook ad copy hinges on understanding your target audience. Simply creating compelling ads isn’t enough; you need to speak directly to the specific needs and desires of the people most likely to convert. This involves more than just demographics; it’s about understanding their interests, behaviors, and the language they use. A well-targeted ad resonates, generating higher engagement and conversion rates.Understanding your audience goes beyond basic categorization.
Crafting compelling Facebook ad copy hinges on understanding your audience. A strong ad needs to grab attention, clearly communicate value, and motivate action. To achieve this, a crucial step is analyzing your target audience’s online behavior, which often aligns with SEO best practices. Knowing how to leverage this data, like through a comprehensive SEO website analysis , helps you tailor your ad copy to resonate with them on a deeper level, resulting in a more effective campaign overall.
Ultimately, effective Facebook ad copy is about understanding your customers, and a deep dive into their online presence is key.
It requires delving into their motivations, pain points, and aspirations. This knowledge allows you to craft messaging that connects on a deeper level, making your ad copy more persuasive and impactful. This targeted approach is crucial for maximizing ROI and achieving your ad campaign objectives.
Tailoring Ad Copy to Specific Demographics
Knowing your audience’s demographics—age, gender, location, and income—is a fundamental step in tailoring your ad copy. Different age groups, for instance, may respond differently to the same message. Consider using language and imagery that resonate with the specific age group.
Effective Language Choices for Different Audience Segments
The language you use in your ad copy should reflect the specific interests and values of your target audience. Millennials, for example, are often drawn to brands that champion social responsibility and sustainability. Their language preferences often lean towards authenticity, relatability, and humor. Gen Z, on the other hand, might respond more favorably to concise, visually engaging content with a modern aesthetic.
The key is to understand the cultural nuances and trends relevant to each segment.
- For a luxury skincare product aimed at affluent women in their 40s and 50s, you might use sophisticated language and highlight the product’s prestige. Emphasize results-oriented benefits and timeless elegance.
- When targeting young professionals (25-35) interested in career advancement, use professional but approachable language, highlighting the practical benefits of the product or service.
- If your product is geared towards teenagers, use contemporary slang and emojis to connect with their interests and communication style. Emphasize social acceptance and trendy aspects of the product.
Using Audience Insights to Inform Ad Copy
Facebook’s advertising platform provides valuable audience insights. Utilize these insights to understand your target audience’s interests, behaviors, and preferences. This data can inform your ad copy, ensuring it resonates with the audience’s needs and desires. This data can be used to create targeted campaigns, improve ad relevance, and optimize for better conversion rates.
Comparing Ad Copy for Various Demographic Segments
| Demographic Segment | Ad Copy Focus | Language Tone | Visual Style |
|---|---|---|---|
| Millennials (25-40) | Social impact, career advancement, experiences | Authentic, relatable, humorous | Modern, diverse imagery |
| Gen Z (16-24) | Community, social media trends, individuality | Concise, trendy, engaging | Visually appealing, vibrant, bold colors |
| Baby Boomers (65+) | Health, security, comfort | Respectful, reassuring, straightforward | Familiar, trustworthy imagery |
Crafting Compelling Headlines
Facebook ad headlines are your first and oftenonly* chance to capture a user’s attention in a crowded newsfeed. A weak headline means your ad, no matter how well-targeted or visually appealing, will likely be skipped. A compelling headline, on the other hand, can draw users in, spark their curiosity, and ultimately drive conversions.Crafting a compelling headline requires a strategic approach, focusing on what makes your ad stand out from the rest.
This involves understanding the psychology of grabbing attention, incorporating strong elements, and tailoring your approach to your target audience.
The Power of Attention-Grabbing Headlines
A strong headline is more than just a few words; it’s a concise summary of the value proposition of your ad. It’s the hook that draws the reader into the rest of your ad copy. A poorly written headline can result in wasted ad spend and missed opportunities. Effectively crafting a headline is critical for maximizing the impact of your Facebook ad campaign.
Strategies for Writing Attention-Grabbing Headlines
Several strategies can significantly improve your headline’s effectiveness. Understanding these strategies will help you write headlines that capture attention and compel users to click.
- Pique Curiosity: Formulate headlines that pose a question, offer a surprising revelation, or hint at something intriguing. This creates a sense of anticipation and encourages users to learn more.
- Use Strong Verbs: Action-oriented verbs can convey a sense of urgency and excitement. Words like “achieve,” “discover,” “unlock,” and “transform” can make a headline more engaging than passive phrases.
- Incorporate Numbers: Statistics and quantifiable results often resonate with readers. Headlines that use numbers like “5 Ways to…” or “7 Steps to…” can provide a sense of structure and authority. For example, “Unlock 10 Ways to Boost Facebook Ad Engagement” is far more compelling than “Boost Facebook Ad Engagement.”
- Employ Curiosity and Intrigue: Pose a problem, introduce a mystery, or hint at a solution in your headline. This can trigger a desire to learn more and click through to your ad.
Headline Styles and Their Impact
Different headline styles can evoke different responses. The right choice depends on your specific campaign goals and target audience.
| Headline Style | Description | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Question-Based | Posing a question directly to the reader | Engages curiosity, encourages interaction |
| Benefit-Driven | Highlighting the benefits of using your product/service | Appeals to the reader’s self-interest |
| Problem-Solution | Presenting a problem and offering a solution | Addresses a reader’s pain point, showcases value |
| Intriguing/Mysterious | Creating intrigue and hinting at a valuable reward | Creates a sense of anticipation, drives curiosity |
Writing Persuasive Body Copy
Crafting compelling Facebook ad copy goes beyond catchy headlines. The body copy is where you truly connect with your audience and convert them into customers. It’s the heart of your ad, explaining your product or service, building trust, and ultimately driving action. This section delves into the structure and techniques for crafting persuasive body copy that resonates with your target audience.Effective body copy isn’t just about listing features; it’s about showcasing the value your product or service brings to the user’s life.
Crafting compelling Facebook ad copy is key to grabbing attention and driving conversions. Think about your target audience and what motivates them. Knowing the potential costs of a data breach, like those detailed in this insightful report on data breach cost , underscores the importance of robust security measures, and ultimately, influences your ad copy’s tone and focus.
Ultimately, clear and persuasive language will boost your ad campaign’s effectiveness.
It needs to be engaging, concise, and focused on delivering a clear and compelling message that motivates the reader to take the desired action.
Structure of Effective Body Copy
The structure of your Facebook ad body copy is crucial for capturing attention and driving conversions. A well-structured body copy clearly presents your value proposition, addresses customer concerns, and encourages immediate action. Begin by immediately establishing the problem your product or service solves, and then transition seamlessly to a solution. Concisely highlight key benefits, use strong verbs, and end with a clear call to action.
Storytelling for Connection
Using storytelling in your body copy can create a powerful emotional connection with your audience. By sharing relatable experiences or narratives, you humanize your brand and make your product or service more relatable.
- Example: Instead of simply stating “Our software streamlines your workflow,” you could tell a story about a small business owner who struggled with inefficient processes and how your software helped them reclaim their time and focus on growing their business.
- Example: If you sell a fitness tracker, instead of listing features, describe the emotional journey of a customer who used the tracker to achieve their fitness goals and improve their overall well-being.
Leveraging Social Proof and Testimonials
Social proof and testimonials are powerful tools for building trust and credibility. When potential customers see that others are satisfied with your product or service, they are more likely to consider it for themselves.
- Incorporating testimonials: Include direct quotes from satisfied customers in your ad copy, highlighting specific benefits they experienced. For example, “I was skeptical at first, but after using this product for a week, I’m already seeing results.” Include photos or videos to add visual appeal and credibility.
- Showcase reviews and ratings: Display star ratings or positive reviews from reputable platforms directly within your ad copy to reinforce your product’s quality and reputation.
Creating Urgency and Scarcity
A sense of urgency and scarcity can be powerful motivators for immediate action. Limited-time offers, exclusive discounts, or promotions can incentivize potential customers to act quickly.
- Limited-time offers: Clearly state the expiration date of a promotion or offer. “This offer ends on [date], so act now!”
- Limited quantities: If your product or service is in limited supply, mention it directly in your ad copy. “Only [number] units left! Don’t miss out!”
Presenting Value Propositions
Effectively communicate the value your product or service offers. Clearly define what problem you solve and how it improves the customer’s life.
- Focus on benefits, not features: Instead of listing technical specifications, highlight the positive outcomes that result from using your product or service. How does it save time? Improve efficiency? Enhance productivity? These are the benefits that resonate with the audience.
- Quantify the value: Use numbers and statistics to demonstrate the impact of your product or service. For example, “Save up to 30% on your energy bill” or “Increase your sales by 20% in the first month.”
Utilizing Visuals Effectively: How To Write Effective Facebook Ad Copy

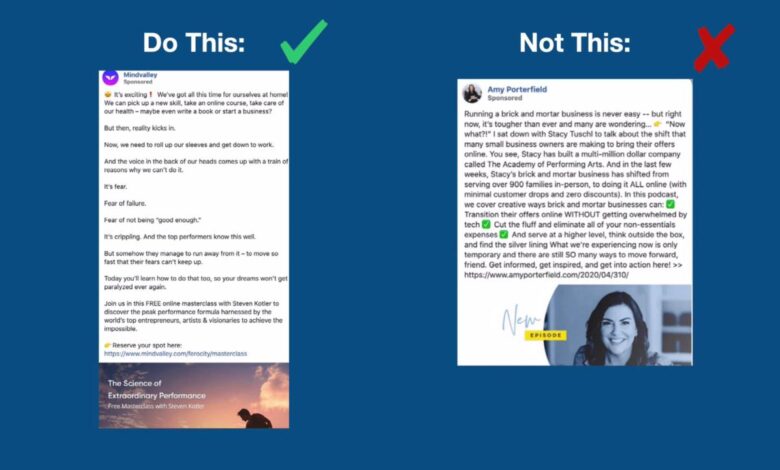
A compelling Facebook ad isn’t just about words; it’s about a captivating visual experience. High-quality visuals are crucial for grabbing attention, conveying your message effectively, and ultimately driving conversions. They act as a silent salesperson, instantly communicating value and fostering trust with your target audience. A well-chosen image or video can significantly improve click-through rates and ultimately impact your campaign’s overall success.Visuals are more than just pretty pictures; they’re an integral part of the overall ad strategy.
Crafting compelling Facebook ad copy is key to grabbing attention. Knowing your target audience is crucial, and a strong call to action is essential. For example, Ryan Markiewicz, a marketing specialist at Logistics Plus, ryan markiewicz marketing specialist logisitcs plus , has a proven track record of success in creating effective ads. Ultimately, focusing on clear messaging and compelling visuals will lead to higher engagement and conversions in your Facebook ads.
They need to seamlessly complement your copy, reinforcing the message and creating a cohesive, memorable experience for the viewer. This section delves into the art of selecting, designing, and integrating visuals that work in perfect harmony with your ad copy.
Importance of High-Quality Visuals
High-quality visuals are paramount in Facebook ads because they are the first point of contact for potential customers. A professional-looking image or video can significantly enhance your ad’s credibility and attract viewers. Poor-quality visuals, on the other hand, can quickly deter potential customers and negatively impact your ad’s performance. This visual impression plays a vital role in establishing trust and influencing purchase decisions.
Choosing Visuals that Resonate
Understanding your target audience is key to choosing visuals that resonate with them. Consider their demographics, interests, and pain points. What kind of imagery would speak to their needs and aspirations? For example, if you’re targeting young professionals, vibrant and modern imagery might be more effective than a classic or outdated aesthetic. Images should align with the overall tone and message of your brand.
Incorporating Visuals that Enhance Copy
Visuals should amplify your ad copy, not compete with it. A good visual complements the message in the copy, reinforcing the core benefit or value proposition. For example, if your ad copy emphasizes speed and efficiency, a dynamic graphic showcasing a fast-paced process or a product in motion would be highly effective. Choose visuals that add context and interest to your copy.
Ensuring Visuals Complement Ad Copy Style
Visuals should be consistent with the overall style and tone of your ad copy. If your copy is playful and humorous, the visuals should reflect that. Conversely, if your copy is serious and professional, the visuals should match that tone. Consistency builds brand recognition and creates a cohesive brand experience.
Visual Styles and Product/Service Effectiveness
The table below illustrates how different visual styles can be tailored to various product/service categories, ensuring a strong connection with the target audience and maximizing ad effectiveness.
| Visual Style | Product/Service Category | Effectiveness |
|---|---|---|
| High-Quality Product Shots | Electronics, Fashion, Furniture | Builds trust and showcases product details effectively. |
| Lifestyle Imagery | Travel, Fitness, Wellness | Connects with aspirations and evokes emotions related to the product/service. |
| Problem/Solution Visuals | Software, Tools, Home Improvement | Visually demonstrates how the product/service solves a specific problem. |
| Before & After Comparisons | Beauty products, Weight loss programs, Home renovation | Clearly illustrates the benefits and transformation achieved by the product/service. |
| User Testimonials | Services, Customer Support | Builds trust by showcasing real-life experiences and positive feedback. |
Ensuring Clarity and Conciseness
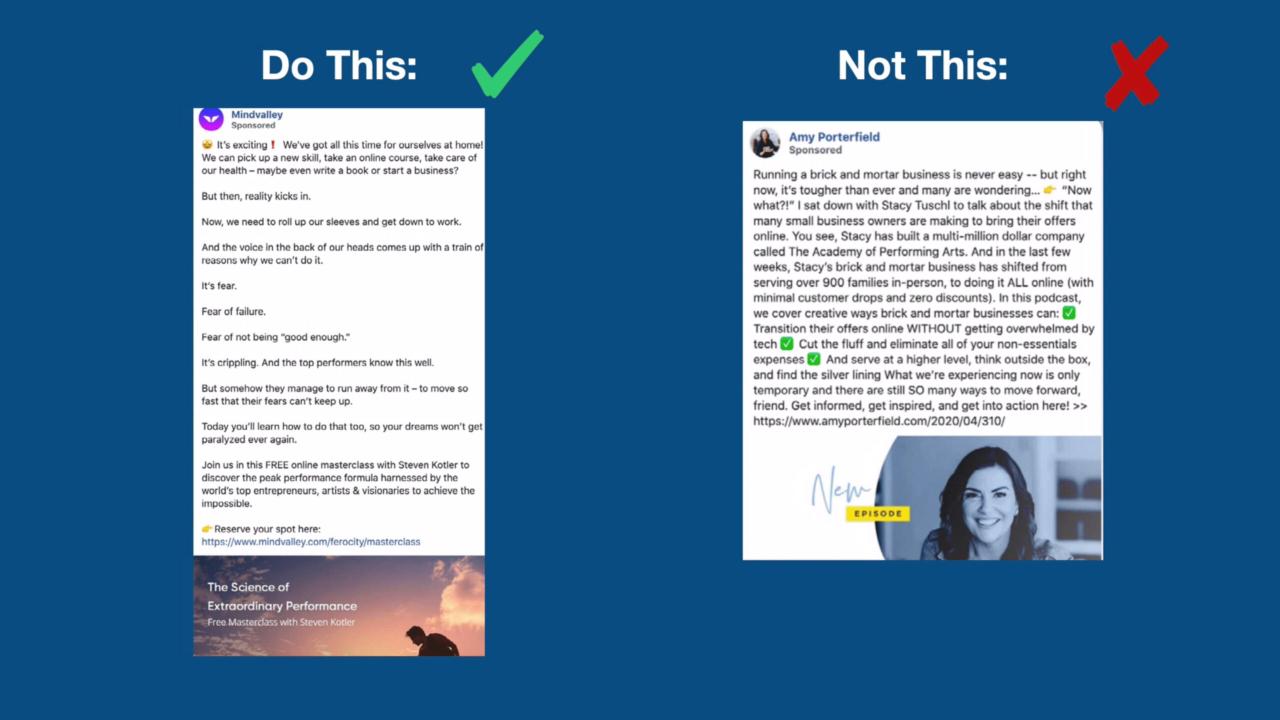
Crafting compelling Facebook ad copy isn’t just about snappy headlines and eye-catching visuals; it’s also about clear communication. Your audience needs to quickly grasp the value proposition of your product or service. Vague language and overly technical terms can lead to confusion and lost conversions. Effective ad copy, therefore, prioritizes clarity and conciseness, ensuring your message resonates with your target audience.Clear and concise language in your ad copy is crucial for capturing attention and driving conversions.
A well-crafted message is easily understood, leaving a lasting impression on the reader. This contrasts with overly complex language that might confuse or alienate potential customers.
Avoiding Jargon and Technical Terms
Technical jargon, while understandable within a specific industry, can be confusing for a wider audience. Avoid using terms that your target demographic may not readily comprehend. Instead, opt for plain language that conveys the core message effectively. For instance, instead of “proprietary algorithm,” use “advanced technology.” This approach ensures broader appeal and avoids alienating potential customers who might not be familiar with the specific terminology.
Simplifying Complex Information
Sometimes, your product or service involves intricate details. Break down complex information into digestible chunks, focusing on the key benefits and advantages. Use simple, everyday language to explain complex concepts. For example, if your software uses complex data analysis, explain how it simplifies a task for the user. Focus on the “what” and “why” rather than the “how.” The “how” is often secondary to the benefits and ease of use.
Short Sentences and Paragraphs
Short sentences and paragraphs enhance readability and comprehension. Break down long, complex thoughts into smaller, manageable units. This approach makes your ad copy scannable and easier to process for the reader. Avoid overly lengthy paragraphs that might lose the reader’s attention. Keep your copy brief, impactful, and easy to follow.
A well-structured ad with short, clear sentences can significantly increase engagement.
Common Pitfalls and How to Avoid Them
- Using overly complex sentence structures. Use simple, direct language that avoids convoluted sentence structures. Keep sentences concise and to the point.
- Employing industry jargon. Replace industry-specific jargon with plain language. Focus on terms your target audience will understand.
- Presenting information in an overwhelming manner. Break down complex information into smaller, more manageable pieces. Focus on highlighting key benefits and advantages.
- Including unnecessary details. Keep the ad focused on the most important information. Avoid including details that aren’t crucial to the conversion process.
- Using passive voice. Use active voice for a more direct and engaging tone. This makes your message clear and easy to follow.
- Writing long, rambling paragraphs. Break down paragraphs into shorter, more manageable units to improve readability. This helps your ad copy maintain engagement and clarity.
By avoiding these common pitfalls, you’ll create Facebook ad copy that is clear, concise, and persuasive, ultimately leading to better engagement and conversions.
Testing and Optimizing Ad Copy
Fine-tuning your Facebook ad copy isn’t a one-and-done affair. It’s a continuous process of experimentation, analysis, and adjustment. Understanding what resonates with your target audience takes time and effort. A/B testing is crucial for uncovering the most effective messaging, ensuring your budget is spent wisely, and ultimately driving the best possible results.Effective Facebook ad copy isn’t static.
What works today might not work tomorrow. The ever-changing digital landscape demands ongoing optimization. By meticulously testing and refining your ad copy, you can ensure your ads remain highly relevant and impactful, maximizing your return on investment (ROI).
Importance of A/B Testing
A/B testing is a cornerstone of successful ad copy optimization. It allows you to compare different versions of your ad copy to identify which performs best. This data-driven approach enables you to identify what resonates with your target audience, leading to higher conversion rates and better ROI. It’s an essential strategy for refining your ad copy and ensuring your ads are as effective as possible.
Tracking Key Metrics
Several key metrics can help you measure ad performance. Crucial to monitoring is click-through rate (CTR), which indicates how often people click on your ad after seeing it. Conversion rate, another critical metric, measures the percentage of people who complete a desired action (e.g., making a purchase) after clicking on your ad. Cost per click (CPC) and cost per conversion (CPC) are equally important in assessing the cost-effectiveness of your campaigns.
Understanding these metrics provides crucial insights into what works and what needs improvement.
Examples of Using Data to Refine Copy
Let’s say an ad with the headline “Get 20% Off Your First Order” has a CTR of 2%, while another ad with the headline “Limited-Time Offer: 20% Off + Free Shipping” has a CTR of 4%. The data clearly indicates that the second headline, highlighting the free shipping benefit, is more compelling to potential customers, driving higher engagement. This is a simple example, but the principles are consistent.
Data-driven analysis leads to optimized copy that better meets user needs and expectations.
Ongoing Monitoring and Adjustments
Regular monitoring of ad performance is paramount. Ad copy effectiveness can fluctuate based on several factors, including seasonality, audience engagement, and market trends. Adapting your copy in response to these changes is essential for maintaining a high level of engagement. By constantly reviewing and adjusting your ads, you can ensure they remain relevant and impactful.
Step-by-Step Guide for A/B Testing
- Define your goal: Clearly articulate the desired outcome of your A/B test. Are you aiming to increase clicks, conversions, or both? This clarity guides your testing strategy.
- Identify variables: Select the specific elements of your ad copy to test. This might include headlines, body copy, call-to-actions (CTAs), or images.
- Create variations: Develop two or more versions of your ad copy, each focusing on one specific variable. Ensure these variations are significantly different to accurately gauge the impact of the change.
- Run the test: Use Facebook’s built-in A/B testing tools to display both variations to a segment of your target audience. Ensure the test group is large enough to yield statistically significant results.
- Monitor results: Track key metrics like CTR and conversion rate for each variation. Pay close attention to the difference in performance between variations.
- Analyze and optimize: Compare the performance of each variation. Identify which version performed best and implement the winning variation for wider use. If no significant difference is observed, refine your test parameters.
- Repeat the process: Continue A/B testing to further refine your ad copy and optimize your campaign. This iterative approach ensures your ads stay relevant and effective over time.
Conclusion
In conclusion, crafting effective Facebook ad copy is a multi-faceted process requiring a deep understanding of your audience, your goals, and the platform itself. By mastering the principles Artikeld in this guide, you can create ads that not only capture attention but also convert prospects into customers. Remember, ongoing testing and optimization are key to achieving the best results.