How to Audit Your Site for Google Page Experience
How to audit your site for the Google Page Experience update is crucial for maintaining a strong online presence. This comprehensive guide dives deep into the specifics of Google’s Page Experience signals, exploring everything from Core Web Vitals to mobile-friendliness and HTTPS security. We’ll dissect the key factors impacting user experience and search rankings, providing actionable strategies to optimize your site for better performance and visibility.
Understanding these factors is essential for ensuring your website meets Google’s evolving standards. This update isn’t just about technical tweaks; it’s about creating a seamless and enjoyable experience for your users, which directly correlates with improved search rankings.
Understanding the Google Page Experience Update
The Google Page Experience Update isn’t just another algorithm tweak; it’s a significant shift in how Google evaluates websites. It prioritizes user experience, recognizing that a positive experience directly correlates with a better search result. This update isn’t about penalizing sites; it’s about rewarding those that prioritize user-friendliness. Google wants to ensure searchers find what they need quickly and easily, leading to a more satisfying online experience.This update fundamentally changes how search engine optimization () is approached.
It moves beyond simply optimizing for s and technical elements to encompass the holistic user experience. By prioritizing user experience, Google is aiming to deliver the most relevant and helpful results to users, improving their overall satisfaction with search.
Core Principles of Page Experience
Google’s Page Experience update emphasizes user-centric design principles. It recognizes that a fast, mobile-friendly, secure, and accessible website contributes significantly to a positive user experience. A positive experience, in turn, fosters trust and encourages repeat visits, ultimately driving more engagement and loyalty.
Key Factors Contributing to a Positive Page Experience
Several factors contribute to a positive page experience, each crucial in determining how Google ranks websites.
- Core Web Vitals: These metrics assess how quickly a page loads, how stable it is while loading, and how easy it is to interact with. Page loading speed, visual stability, and user interaction are critical for a seamless user experience. For example, a website that takes too long to load or experiences frequent visual shifts during loading will likely receive a lower score in this category.
Conversely, a website that loads quickly and displays content without significant shifts is more likely to be well-received by users and Google.
- Mobile-Friendliness: With mobile browsing becoming increasingly prevalent, a website must be optimized for various screen sizes and devices. This involves responsive design, ensuring the website displays correctly and functions smoothly on smartphones and tablets. Mobile-friendliness isn’t just about visual appeal; it’s about ensuring users can easily access and navigate content on their devices. For example, a website that requires excessive scrolling or zooming on a mobile device is less user-friendly and likely to be penalized.
- HTTPS Security: A secure connection (HTTPS) is now a critical aspect of page experience. This ensures the security of user data and builds trust. Google prioritizes secure websites as they protect user information, preventing data breaches and creating a more trustworthy environment for users.
- Accessibility: Websites must be accessible to users with disabilities. This involves using appropriate color contrasts, providing alternative text for images, and ensuring keyboard navigation is possible. This ensures that all users can access and interact with the website content.
Metrics Used to Assess Page Experience
Google uses specific metrics to evaluate a website’s page experience.
- Core Web Vitals: These are crucial metrics that evaluate loading performance, stability, and interactivity. They include metrics like Largest Contentful Paint (LCP), First Input Delay (FID), and Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS).
- Mobile-Friendliness: Google’s mobile-friendly test assesses how well a website adapts to different screen sizes and devices.
- HTTPS Security: Google checks for the presence of an HTTPS connection to evaluate the website’s security.
Comparing and Contrasting Factors
Each factor contributing to a positive page experience plays a unique role, but they’re interconnected. Core Web Vitals directly impact user experience, ensuring fast loading and stable interactions. Mobile-friendliness ensures accessibility on various devices. HTTPS security fosters trust and protects user data. While all are important, the relative importance can vary depending on the specific context and user needs.
Impact on Search Rankings and Visibility
The Google Page Experience Update significantly impacts search rankings. Websites with exceptional page experience tend to rank higher in search results, improving their visibility and attracting more organic traffic. Conversely, websites with poor page experience may see a decline in their rankings. This prioritization of user experience positions websites that prioritize user needs at the forefront of search results, ultimately benefiting users and driving organic growth for websites.
Assessing Core Web Vitals
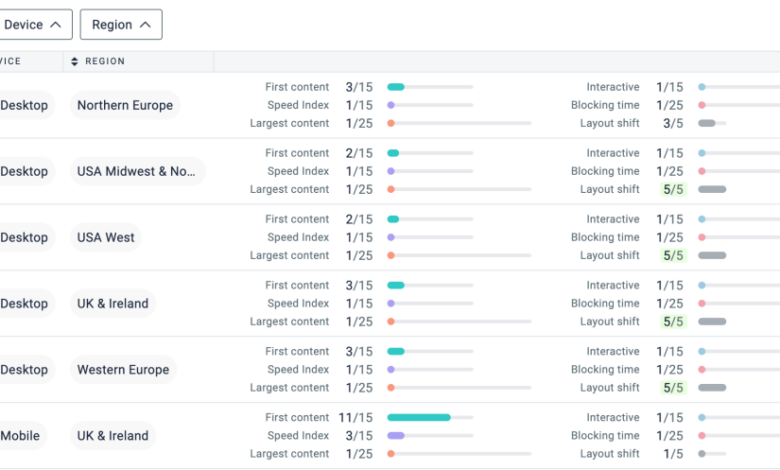
The Google Page Experience Update emphasizes user experience as a critical ranking factor. A key component of this update revolves around Core Web Vitals, which measure key aspects of site performance. Understanding these metrics allows you to optimize your site for better user engagement and search engine rankings.Core Web Vitals provide insights into how quickly and smoothly users can interact with your website.
This translates directly into user satisfaction and, ultimately, into better search engine rankings. Poor Core Web Vital scores can lead to a less enjoyable user experience, potentially resulting in higher bounce rates and lower engagement.
Defining Core Web Vitals
Core Web Vitals are three crucial metrics that evaluate the loading performance and responsiveness of your website. These include Largest Contentful Paint (LCP), First Input Delay (FID), and Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS). Understanding how each of these affects user experience is vital for optimizing your site.
Largest Contentful Paint (LCP)
Largest Contentful Paint (LCP) measures the time it takes for the largest image or text block to load. A faster LCP indicates a more responsive and user-friendly website.
Want to nail your site’s Google Page Experience score? First, you need to understand how Google’s algorithms are changing. While exciting new ad formats like the 3D ads featured in google swirl 3d ads ignite friday are emerging, focusing on core web vitals and mobile-friendliness is key. Tools like Google Search Console can help you identify areas needing improvement.
Ultimately, a robust audit will ensure your site is optimized for a seamless user experience.
- Definition: LCP signifies the time taken for the most visually impactful element on a page to load. It’s a crucial indicator of initial load performance. It’s essentially the point where a user can first perceive the page’s main content.
- Impact on Users: A slow LCP results in users waiting longer to see the core content of the page. This can lead to frustration and potentially drive them away from the site. Users prefer quick loading times, as this signifies a responsive website.
- Metrics: The metric for LCP is measured in milliseconds. Ideal LCP times are under 2.5 seconds. Any time beyond this threshold can negatively impact the user experience.
- Tools to Measure: Tools like Google PageSpeed Insights, Lighthouse, and Chrome DevTools provide comprehensive data on LCP performance.
Example: A good LCP performance would be under 1.5 seconds, where users see the page’s main content quickly. A poor LCP score, exceeding 4 seconds, would result in users waiting a considerable time before seeing the core content, impacting the user experience negatively.
First Input Delay (FID)
First Input Delay (FID) measures the time it takes for the browser to respond to a user’s first interaction with the page. A lower FID signifies a more responsive website, enabling users to interact promptly with the site’s elements.
- Definition: FID quantifies the delay between a user’s initial interaction (like clicking a button or scrolling) and the browser’s ability to process that interaction.
- Impact on Users: A high FID value suggests a sluggish response time, hindering user interaction. Users want a website that feels quick and responsive to their input, otherwise, they may abandon the page.
- Metrics: FID is measured in milliseconds. An FID value below 100 milliseconds is generally considered good performance. Higher values indicate a slower response.
- Tools to Measure: Google PageSpeed Insights, Lighthouse, and Chrome DevTools provide comprehensive data on FID performance.
Example: A good FID score is under 100 milliseconds, allowing users to interact promptly with page elements. A poor FID, exceeding 300 milliseconds, results in a noticeable delay between user input and browser response, negatively impacting the user experience.
Figuring out how to audit your site for Google’s Page Experience Update is crucial for ranking. Beyond technical checks, consider your ad strategies; optimizing for user experience often ties into effective value based bidding strategies. Ultimately, a comprehensive audit needs to evaluate both technical elements and user engagement for the best results.
Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS)
Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS) measures unexpected layout shifts on a page. A lower CLS score indicates a more stable and predictable layout, enhancing the user experience.
- Definition: CLS quantifies the cumulative visual instability caused by unexpected layout shifts on a page, such as elements moving or changing position after the initial load.
- Impact on Users: Unexpected layout shifts can disrupt the user’s flow and comprehension of the page, leading to a frustrating experience. Users expect a stable and predictable layout.
- Metrics: CLS is measured in a unit called a “score” or “value”. A CLS score of 0.1 or less is considered good performance.
- Tools to Measure: Google PageSpeed Insights, Lighthouse, and Chrome DevTools provide comprehensive data on CLS performance.
Example: A good CLS score is under 0.1, maintaining a stable layout and ensuring that content remains in its expected location. A poor CLS score exceeding 0.2 indicates significant layout shifts that can disorient users and reduce their confidence in the site’s stability.
Measuring Core Web Vitals
Various tools provide comprehensive data on Core Web Vitals performance. Utilizing these resources is crucial for identifying areas needing optimization.
| Core Web Vital | Definition | Impact on Users | Metrics | Tools to Measure |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LCP | Time for largest contentful element to load. | Impacts initial load perception. | Milliseconds (under 2.5s ideal) | PageSpeed Insights, Lighthouse, Chrome DevTools |
| FID | Delay between user interaction and browser response. | Impacts responsiveness. | Milliseconds (under 100ms ideal) | PageSpeed Insights, Lighthouse, Chrome DevTools |
| CLS | Cumulative visual instability from layout shifts. | Impacts user experience stability. | Score (0.1 or less ideal) | PageSpeed Insights, Lighthouse, Chrome DevTools |
Evaluating Mobile-Friendliness
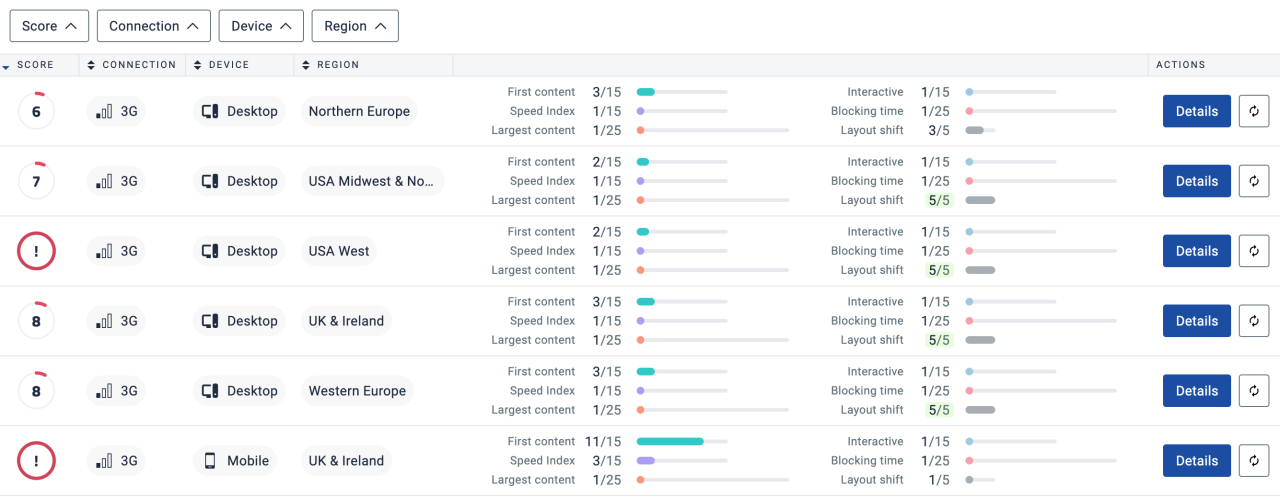
Your website’s mobile experience is crucial for user satisfaction and search engine rankings. Google’s mobile-first indexing prioritizes websites optimized for mobile devices. A seamless mobile experience keeps visitors engaged, encouraging them to explore your site and potentially convert. This section dives into mobile-friendliness best practices, testing methods, and the impact on your overall online presence.Mobile-friendliness isn’t just about having a website that displays on a smartphone; it’s about providing a user-friendly interface and experience tailored to the smaller screen size.
A responsive design adapts to various screen sizes, ensuring optimal readability and navigation across all devices. This adaptability is vital for maintaining user engagement and avoiding frustration.
Mobile-Friendliness Best Practices
Following best practices for mobile design ensures a positive user experience. This involves optimizing images for faster loading, using a clean layout that’s easy to navigate on smaller screens, and employing clear and concise text. Effective mobile design prioritizes intuitive navigation, avoiding complex interactions that can hinder the user’s journey.
Responsive Design for Various Screen Sizes, How to audit your site for the google page experience update
Responsive design is the cornerstone of mobile-friendliness. It’s a web development approach that adapts website layouts and content to fit different screen sizes and resolutions. This ensures consistent readability and usability across desktops, laptops, tablets, and smartphones. A well-executed responsive design seamlessly transitions from one screen size to another, providing a consistent and enjoyable user experience. Elements like images and text adjust dynamically to the viewport, preventing content from being cut off or rendered illegibly.
Testing Mobile-Friendliness Using Online Tools
Several online tools can assess your website’s mobile-friendliness. Google’s Mobile-Friendly Test is a free and readily available tool that analyzes your site’s structure and design for mobile compliance. It provides specific feedback on areas needing improvement, such as issues with text size, button placement, or image optimization. Other valuable tools, like those from various web development and testing services, also offer similar analyses and pinpoint areas requiring adjustment.
The output from these tools provides concrete recommendations to address identified weaknesses.
Impact of Mobile-Friendliness on User Experience and Search Rankings
Mobile-friendliness directly impacts user experience. A site that’s optimized for mobile devices is easier to navigate, read, and use, leading to higher user satisfaction. This positive user experience contributes to improved search rankings. Google’s algorithm prioritizes mobile-friendly sites, giving them a higher position in search results. A site that’s cumbersome or difficult to use on mobile devices can significantly hinder engagement and rankings.
Different Aspects of Mobile-Friendliness Testing and Optimization
Mobile-friendliness optimization encompasses several crucial aspects. Firstly, ensuring that text and images are properly scaled and displayed on various screen sizes is vital. Secondly, effective navigation is critical, ensuring that menus, buttons, and other interactive elements are easily accessible and intuitive. Finally, efficient loading times are essential. Optimizing images, compressing files, and minimizing HTTP requests contribute to a faster loading experience.
These three aspects collectively form the core of a well-optimized mobile website.
Analyzing HTTPS Security
Securing your website is paramount in today’s digital landscape. Beyond basic functionality, trust and security are crucial for user experience and search engine rankings. A significant aspect of this is implementing HTTPS. This protocol, the secure version of HTTP, encrypts communication between your website and users’ browsers, protecting sensitive data like passwords and credit card information.Understanding HTTPS is not just about technical details; it’s about building a trustworthy online presence.
Users are increasingly aware of security risks, and a lack of HTTPS can significantly impact user confidence and, ultimately, your website’s success.
Significance of HTTPS for Website Security and User Trust
HTTPS establishes a secure connection between your website and users’ browsers. This encrypted connection prevents eavesdropping and tampering with data during transmission. Protecting sensitive information is critical, as a breach can lead to significant reputational damage and financial losses. This strong security foundation directly fosters user trust, encouraging visitors to engage with your website without fear of their data being compromised.
Users are more likely to complete transactions and return to sites they perceive as secure.
Benefits of Using HTTPS
Implementing HTTPS provides numerous advantages beyond enhanced security. Search engines, like Google, prioritize HTTPS websites, often reflecting this in search rankings. This visibility boost can lead to increased traffic and greater discoverability. Furthermore, HTTPS demonstrates a commitment to user privacy and security, which can be a powerful marketing tool, attracting users and building a strong reputation.
Implementing HTTPS on Your Website
Implementing HTTPS involves configuring your web server to use SSL/TLS certificates. These certificates establish the secure connection. You’ll need a trusted Certificate Authority (CA) to issue these certificates. Common providers include Let’s Encrypt, Comodo, and DigiCert.
Common HTTPS Implementation Errors
Several common errors can hinder a successful HTTPS implementation. Misconfigurations of the SSL/TLS certificate can lead to connection errors, and failure to redirect all HTTP traffic to HTTPS can leave users vulnerable. Furthermore, outdated certificates or improperly installed certificates can compromise security. Incorrect configurations can also result in mixed content issues, where parts of the site use HTTP while others use HTTPS, hindering the security benefits.
Step-by-Step Guide on Configuring HTTPS
The process of configuring HTTPS varies depending on your web server (Apache, Nginx, etc.). However, the fundamental steps are generally similar.
Figuring out how your site stacks up against Google’s Page Experience Update can feel overwhelming. A great starting point is to use tools like Google Search Console. To really dig deep and understand the data, you can leverage Google Data Studio google data studio to visualize the insights gleaned from your site audits. This allows you to easily spot trends and areas needing improvement.
Ultimately, consistent audits and data analysis are key to achieving optimal Page Experience scores.
- Obtain an SSL/TLS certificate from a trusted Certificate Authority (CA). Let’s Encrypt offers free certificates, which are a great option for many users.
- Configure your web server to use the certificate. This involves specifying the certificate file and key file within the server’s configuration.
- Configure your server to redirect all HTTP requests to HTTPS. This is crucial to ensure that users are automatically redirected to the secure version of your site.
- Test the HTTPS implementation thoroughly. Use browser developer tools and security testing tools to validate the connection and identify any potential issues.
- Ensure that all assets (images, scripts, stylesheets) are served over HTTPS. Mixed content issues can arise if some resources are still served over HTTP.
Investigating Content Quality and Accessibility
High-quality content is the lifeblood of any successful website. It’s not just about having words on a page; it’s about providing value to your visitors, keeping them engaged, and ultimately, helping them achieve their goals. This is directly reflected in search engine rankings, as Google prioritizes sites that offer a positive user experience. Poorly written, inaccessible, or unengaging content can lead to high bounce rates and a decline in organic traffic.Strong content, therefore, is crucial for establishing authority, building trust, and driving conversions.
It’s a fundamental aspect of and a critical element in the broader Google Page Experience Update, ensuring your website not only looks good but also functions well and provides valuable information to users.
Significance of High-Quality Content
High-quality content is paramount for user engagement and search engine rankings. It provides valuable information, addresses user needs, and keeps visitors coming back for more. This is directly correlated with search engine optimization () as search engines reward websites that offer informative and engaging content. Websites with high-quality content tend to rank higher in search results, leading to increased visibility and organic traffic.
This ultimately translates into more opportunities for conversions and revenue generation.
Best Practices for Creating Informative and Engaging Content
Creating informative and engaging content requires a multi-faceted approach. First, understand your target audience and tailor your content to their specific needs and interests. Conduct thorough research to gather accurate and up-to-date information. Use clear and concise language, avoiding jargon or overly technical terms. Organize your content logically with headings, subheadings, bullet points, and visuals to enhance readability.
Incorporate multimedia elements like images, videos, and infographics to break up text and keep visitors engaged. Encourage interaction through comments, polls, and Q&A sections. Finally, always proofread and edit your content for clarity, grammar, and spelling errors.
Ensuring Accessibility for Users with Disabilities
Ensuring content accessibility is vital for inclusivity. This involves making your website usable for users with disabilities, such as visual, auditory, motor, or cognitive impairments. Key aspects include providing alternative text for images, using sufficient color contrast between text and background, and ensuring keyboard navigation is possible. Using ARIA attributes for interactive elements is also critical. By incorporating these practices, you create a more inclusive website experience for everyone.
Improving Readability and Understandability
Improving readability and understandability involves focusing on factors that make your content easy to digest. This includes using clear and concise language, breaking up large blocks of text with headings, subheadings, and bullet points. Use short paragraphs and sentences to avoid overwhelming users. Maintaining a consistent font size and style throughout the website is also crucial. Consider using visual aids such as charts, graphs, and images to illustrate complex information and make it easier to understand.
Prioritize using headings and subheadings for clear structure and navigation.
Content Quality Checks and Accessibility Guidelines
| Aspect | Checkpoints | Accessibility Guideline |
|---|---|---|
| Content Accuracy | Verify information through multiple reliable sources. | Accuracy and reliability are essential for credibility. |
| Clarity and Conciseness | Avoid jargon and overly technical terms. | Ensure clear and concise language for better comprehension. |
| Readability | Use headings, subheadings, bullet points, and visuals. | Optimize readability for ease of understanding. |
| Accessibility | Use alternative text for images, sufficient color contrast, keyboard navigation. | Ensure website usability for users with disabilities. |
| Engagement | Incorporate multimedia, interactive elements. | Keep users engaged with interesting and interactive content. |
| Organization | Logical structure, proper use of headings. | Well-structured content aids navigation and comprehension. |
Identifying and Fixing Performance Issues
A lightning-fast website is crucial for a positive user experience and strong search engine rankings. Slow loading times frustrate visitors and can lead to lost conversions. Optimizing your website’s performance is an essential step in achieving the Google Page Experience update’s core web vitals goals.Identifying and resolving performance bottlenecks is a multifaceted process that requires a systematic approach.
Understanding the various factors that contribute to page speed is the first step towards creating a more responsive and efficient online presence.
Performance Factors Impacting Page Speed
Several factors significantly influence a website’s loading time. These include the size of HTML, CSS, and JavaScript files, the number of HTTP requests, the server response time, and the network connection speed. Additionally, the size and optimization of images and other assets play a critical role. These factors combine to create a comprehensive picture of the performance characteristics of a website.
Common Performance Bottlenecks
Several issues frequently hinder website performance. Large image files, inefficient code, excessive HTTP requests, and slow server response times are common culprits. A lack of caching mechanisms can also dramatically affect loading times, leading to poor user experience. Identifying and resolving these bottlenecks is key to improving overall site performance.
- Large Image Files: Unoptimized images contribute substantially to slow loading times. High-resolution images, especially those not appropriately compressed, can significantly increase page load times, negatively impacting the user experience. A crucial optimization step involves compressing images without sacrificing quality.
- Inefficient Code: Unnecessarily complex or poorly structured code can significantly slow down a website. Redundant code, unused libraries, and inefficiently written JavaScript functions can lead to substantial delays. Employing proper coding practices and minimizing the codebase is essential for improving page load times.
- Excessive HTTP Requests: Each file requested from a server contributes to the loading time. Excessive requests can dramatically increase page load time. Minimizing the number of external resources a page needs to load is crucial for improving performance.
- Slow Server Response Time: If the server hosting the website takes a long time to respond to requests, it directly impacts page load time. Slow server response time is a significant contributor to poor user experience. Employing strategies for faster server response times, such as optimizing the server-side code, is essential.
- Lack of Caching: Caching mechanisms store frequently accessed content, allowing for faster retrieval. Without appropriate caching, each user request has to retrieve the content from the server, leading to slow page load times. Implementing caching mechanisms, such as browser caching and server-side caching, is vital for optimal performance.
Optimizing Images and Assets
Image optimization is crucial for improving website performance. Appropriate compression techniques can significantly reduce file sizes without compromising visual quality. Using optimized formats, like WebP, can lead to smaller file sizes compared to JPEG or PNG. Proper image sizing based on the intended display area can also contribute to performance gains.
Optimizing Website Code and Reducing HTTP Requests
Website code optimization involves minimizing unnecessary elements and optimizing the structure for better performance. Using CSS sprites, combining JavaScript files, and leveraging browser caching can reduce the number of HTTP requests. These techniques can reduce the time needed to load a page.
Flowchart for Identifying and Fixing Performance Issues
A flowchart illustrating the process for identifying and resolving performance issues would typically start with measuring current page speed. This step involves using tools like Google PageSpeed Insights or GTmetrix. Analyzing the results would lead to identifying areas for optimization, such as image optimization, code improvements, and reducing HTTP requests. The flowchart would then guide users through specific optimization techniques for each area, leading to iterative improvements in website performance.
Implementing Optimization Strategies
Optimizing your website for the Google Page Experience Update is crucial for improving user experience and search engine rankings. This involves a multi-faceted approach focusing on various aspects of your site, from page load speed to mobile-friendliness and content quality. Effective optimization strategies are vital for maintaining a competitive edge in today’s digital landscape.A comprehensive optimization strategy addresses not only immediate performance improvements but also anticipates future algorithm changes and evolving user expectations.
This proactive approach builds a resilient and user-friendly website that is well-positioned for sustained success.
Actionable Steps for Website Optimization
Implementing specific, actionable steps is key to achieving tangible results. This involves a structured process that prioritizes tasks based on their impact and feasibility. Prioritization ensures that the most impactful changes are addressed first, maximizing the return on investment for your optimization efforts.
- Optimize Images: Compressing images without sacrificing quality is crucial for reducing page load times. Tools like TinyPNG and ImageOptim can significantly compress images, resulting in faster loading times. This is a high-impact, relatively low-effort optimization that can quickly improve Core Web Vitals.
- Minimize HTTP Requests: Fewer HTTP requests translate to faster page load times. Combine CSS and JavaScript files, use image sprites, and leverage browser caching to minimize the number of requests your site makes.
- Enable Browser Caching: Enabling browser caching allows users’ browsers to store static resources (images, CSS, JavaScript) locally. This significantly speeds up subsequent visits, as the browser retrieves these resources from the cache instead of making requests to the server.
- Leverage a Content Delivery Network (CDN): A CDN distributes your website’s static content across various servers globally. This reduces latency for users located in different geographical areas, leading to faster load times. Consider CDNs like Cloudflare or Akamai for broader coverage and performance improvements.
Prioritizing Tasks Based on Impact and Feasibility
Prioritization ensures that the most impactful changes are addressed first, maximizing the return on investment for your optimization efforts. This involves evaluating the potential impact of each optimization task and its associated effort. High-impact, low-effort tasks should be prioritized over low-impact, high-effort tasks.
- Assess Current Performance Metrics: Analyze your site’s current Core Web Vitals, mobile-friendliness, and HTTPS security to pinpoint areas needing immediate attention. Tools like Google PageSpeed Insights and Lighthouse provide valuable data for this assessment.
- Prioritize Optimization Tasks: Organize the identified optimization tasks based on their potential impact on Core Web Vitals. For example, optimizing images generally has a higher impact than minor code adjustments. This allows you to focus on high-leverage changes first.
- Estimate Time and Resources: Determine the estimated time and resources required for each optimization task. This helps in realistic planning and resource allocation.
Examples of Successful Website Optimizations
Successful website optimizations often involve a combination of strategies. For example, a company that reduced its page load time by 50% through image optimization and CDN implementation saw a corresponding increase in user engagement and conversion rates.
- E-commerce sites frequently optimize product images to reduce page load times and improve user experience, leading to higher conversion rates.
- News websites optimize images and leverage CDNs to ensure fast loading times, which keeps users engaged.
Detailed Checklist for Auditing Site Optimization
A checklist ensures that all crucial aspects are considered during the optimization process. This comprehensive approach systematically addresses each element of the Google Page Experience Update, guaranteeing a comprehensive review.
- Review Core Web Vitals metrics (LCP, FID, CLS).
- Analyze mobile-friendliness using Google’s Mobile-Friendly Test.
- Verify HTTPS security and certificate validity.
- Evaluate content quality and accessibility.
- Assess page load speed using tools like Google PageSpeed Insights.
- Identify and address any performance issues.
Comparing Optimization Strategies and Effectiveness
A comparison of various optimization strategies provides insights into their effectiveness. This analysis considers the impact on Core Web Vitals and the effort required for implementation.
| Optimization Strategy | Impact on Core Web Vitals | Effort Level |
|---|---|---|
| Image Optimization | High | Medium |
| Browser Caching | Medium | Low |
| Content Delivery Network (CDN) | High | Medium |
| Code Optimization | Medium | High |
Monitoring and Tracking Progress: How To Audit Your Site For The Google Page Experience Update
Optimizing your website for the Google Page Experience Update is a continuous process. Simply implementing changes isn’t enough; you need to track their impact to ensure you’re achieving your goals. This involves understanding how your improvements affect user experience and website performance. Regular monitoring provides insights into what’s working, what needs adjustment, and allows for proactive problem-solving.
Importance of Post-Optimization Monitoring
Monitoring website performance after implementing optimization strategies is crucial for several reasons. It allows you to assess the effectiveness of your changes and identify any unforeseen negative consequences. It also helps you understand how your improvements affect user experience, such as page load speed and overall navigation. This feedback loop allows for proactive adjustments to maintain and further enhance your website’s performance.
Tools and Methods for Tracking Progress
Various tools and methods are available to track your website’s progress against your goals. Google Search Console, for example, provides valuable data on Core Web Vitals, mobile-friendliness, and security issues. Third-party analytics platforms, such as Google Analytics, offer detailed insights into user behavior and website performance metrics. These platforms offer data visualization tools that help in understanding the trends and patterns in your website’s performance.
Regularly reviewing these reports is essential for identifying potential issues and making informed decisions.
Analyzing Data to Identify Areas Needing Improvement
Analyzing data from monitoring tools is vital to pinpoint areas requiring further attention. Trends and patterns in Core Web Vitals, like increased loading times or high bounce rates, signal potential problems. By carefully examining the data, you can pinpoint specific pages or sections of your website that are underperforming. This detailed analysis allows you to prioritize improvements and allocate resources effectively.
For example, if you notice a significant drop in mobile-friendliness scores for a particular page, you can investigate the cause and implement the necessary fixes.
Setting Up Alerts for Critical Performance Issues
Setting up alerts for critical performance issues is a proactive approach to maintaining website health. By configuring alerts in your monitoring tools, you can be notified immediately if key metrics fall below predefined thresholds. This allows you to address problems promptly, preventing negative impacts on user experience and search rankings. These alerts are essential for maintaining a high level of performance and keeping your website running smoothly.
Sample Dashboard for Tracking Key Metrics
A sample dashboard for tracking Core Web Vitals, mobile-friendliness, and HTTPS security could include the following elements:
| Metric | Target | Current Value | Trend |
|---|---|---|---|
| Largest Contentful Paint (LCP) | 2.5 seconds | 2.8 seconds | Increasing |
| Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS) | 0.1 | 0.2 | Increasing |
| First Input Delay (FID) | 100ms | 150ms | Increasing |
| Mobile-friendliness | Excellent | Good | Stable |
| HTTPS Security | Secure | Secure | Stable |
This dashboard provides a quick overview of the key performance indicators. Visual representations of the data, such as charts and graphs, enhance the understanding of trends. Color-coded indicators (e.g., green for good, yellow for warning, red for critical) help quickly identify areas requiring immediate attention. Regular review and analysis of this dashboard are vital to maintaining a high level of website performance.
Last Point
In conclusion, auditing your website for Google Page Experience signals is a vital step in optimizing your site for success. By meticulously evaluating Core Web Vitals, mobile-friendliness, HTTPS security, and content quality, you’ll be well-equipped to enhance user experience and achieve higher search rankings. This guide has provided a roadmap for understanding and implementing the necessary changes, empowering you to adapt and succeed in the ever-evolving digital landscape.