Google Data Studio Your Data Visualization Hub
Google Data Studio sets the stage for insightful data visualization. This comprehensive guide delves into the world of data analysis, exploring the powerful features and functionalities of Google Data Studio. From connecting various data sources to creating interactive dashboards, we’ll uncover the secrets to transforming raw data into actionable insights. Learn how to effectively visualize your data, uncover hidden patterns, and make data-driven decisions.
This guide covers everything from basic setup and data connection to advanced techniques like calculated fields and data blending. We’ll also explore troubleshooting common issues and showcase real-world case studies. Whether you’re a seasoned data analyst or just starting your data journey, this resource will empower you to leverage Google Data Studio to its fullest potential.
Introduction to Google Data Studio
Google Data Studio is a powerful, user-friendly business intelligence tool designed for creating interactive dashboards and reports. It allows users to connect to various data sources, visualize data in compelling ways, and share insights with stakeholders. Data Studio streamlines the process of transforming raw data into actionable insights, empowering businesses to make data-driven decisions.Data Studio excels at consolidating data from diverse sources, offering a comprehensive view of performance metrics.
Its intuitive interface makes it easy for both technical and non-technical users to create and share informative reports, facilitating collaboration and data-driven decision-making across organizations.
Core Functionalities of Google Data Studio
Data Studio’s core functionalities are centered around data visualization and reporting. It allows users to connect to various data sources, transform data into meaningful visualizations, and present these insights in interactive dashboards. This enables users to identify trends, patterns, and anomalies in data, leading to better informed business decisions. The core functionalities include: data source connection, data transformation, visualization creation, dashboard design, and report sharing.
Data Sources Supported by Google Data Studio
Data Studio supports a wide range of data sources, enabling users to integrate data from diverse platforms and applications. This flexibility is crucial for creating comprehensive and accurate reports. These include:
- Google Sheets: A widely used spreadsheet application that provides a simple way to input and organize data. This allows users to quickly import and visualize data stored in spreadsheets.
- Google Analytics: A powerful web analytics tool providing insights into website traffic, user behavior, and conversion rates. Connecting Google Analytics data allows users to track key website performance metrics.
- BigQuery: A fully managed, serverless data warehouse service. This robust platform allows users to process massive datasets and generate reports on complex analytics.
- Salesforce: A cloud-based customer relationship management (CRM) platform. Integrating with Salesforce allows users to track sales performance, customer interactions, and other key metrics.
- Other Data Sources: Data Studio also supports various other data sources like SQL databases, cloud storage services, and more, demonstrating its adaptability for different business needs.
Creating a Data Visualization Report in Google Data Studio
Creating a data visualization report in Google Data Studio involves several steps. This process is designed to be user-friendly and accessible to individuals with varying technical backgrounds. A typical workflow includes:
- Data Connection: Connect to the desired data source. This might involve authenticating with the data source and selecting the specific data sets to be used.
- Data Transformation: Transform the data into a suitable format for visualization. This step might involve creating calculated fields, modifying data types, or filtering data.
- Visualization Selection: Choose appropriate visualizations (charts, graphs, tables) to effectively display the data. Consider the type of data and the message you want to convey.
- Dashboard Design: Arrange the visualizations on a dashboard to create a cohesive and informative presentation. Consider the flow and hierarchy of information.
- Report Sharing: Share the report with relevant stakeholders to facilitate data-driven decision-making. Sharing can be done through various methods and with varying levels of access.
Benefits of Using Google Data Studio
The use of Google Data Studio provides significant advantages for organizations seeking to extract insights from their data. These advantages include:
- Improved Decision Making: Data visualization allows users to identify trends, patterns, and anomalies in data, leading to more informed business decisions.
- Enhanced Collaboration: Sharing reports with stakeholders facilitates communication and collaboration across teams, fostering a data-driven culture.
- Time Savings: Automating data collection and analysis saves significant time compared to manual processes.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Data Studio is a cloud-based platform, making it accessible and cost-effective compared to traditional BI tools.
- Accessibility and Simplicity: The user-friendly interface makes it accessible to users with varying technical backgrounds.
Data Connection and Preparation
Connecting and preparing data is crucial for insightful visualizations in Google Data Studio. This involves selecting the right data sources, cleansing the data to eliminate errors, and transforming it to align with the intended visualizations. Effective data preparation ensures accurate and reliable insights.
Connecting Data Sources
Data Studio supports a wide range of data sources, including Google Sheets, Google Analytics, BigQuery, and many more. The connection process generally involves authenticating with the source and specifying the data you wish to import. Each data source has its own connection method. For example, connecting to Google Sheets is straightforward, while connecting to a database might require a specific connector or API key.
Google Data Studio is a fantastic tool for visualizing data, but sometimes you need a deeper understanding of the market forces at play. Take a look at how Jesse Semchuck, director of acquisition at Traeger Grills ( jesse semchuck director acquisition traeger grills ), is shaping the barbecue industry. Ultimately, using data like this helps us build better dashboards in Google Data Studio.
Data Preparation Techniques
Preparing data for visualization involves cleaning, transforming, and shaping the data to ensure accuracy and consistency. This stage is critical for obtaining reliable insights. Cleaning involves handling missing values, correcting errors, and standardizing formats. Transformations involve calculations, aggregations, and restructuring the data to suit the visualizations. For example, converting a date field to a specific format or calculating a new metric.
Data preparation is an iterative process, often requiring several rounds of cleaning and transformation to achieve the desired outcome.
Google Data Studio is fantastic for visualizing data, but did you know repurposing your insights can supercharge your SEO? By taking existing data visualizations and transforming them into different formats like blog posts or infographics, you can significantly increase the value of your content. Check out this helpful guide on repurpose content boost seo value for actionable strategies.
Ultimately, this repurposing process can make your Google Data Studio dashboards even more powerful by extending their reach and driving more organic traffic to your website.
Data Cleaning in Data Studio
Data cleaning techniques are vital for removing errors and inconsistencies in data. These techniques include handling missing values (imputing with mean, median, or constant), removing duplicates, and correcting data entry errors. Using formulas and filters in Data Studio allows you to pinpoint and fix issues. For example, a formula could identify and correct inconsistent date formats within a dataset.
Data Transformation for Visualization
Data transformation is essential to tailor the data to specific visualization needs. This involves creating calculated fields, aggregating data, and pivoting tables. Calculated fields allow for the creation of new metrics or dimensions from existing data. Aggregation groups data based on specified criteria. For example, you might aggregate sales data by region to understand regional performance.
Transformations in Data Studio can involve creating new columns, calculating ratios, or grouping values for more meaningful visualization.
Importing and Preparing Data – Step-by-Step Guide
This guide Artikels the process of importing and preparing data for use in Google Data Studio.
- Choose the Data Source: Identify the relevant data source (e.g., Google Sheets, Google Analytics). Select the dataset and desired fields to import.
- Connect to the Data Source: Follow the instructions for connecting to your chosen data source. This might involve entering credentials or selecting a specific dataset within the source.
- Preview the Data: Review the imported data to ensure it’s accurate and complete. Verify data types, formats, and values.
- Clean the Data: Identify and address any missing values, errors, or inconsistencies. Use Data Studio’s built-in tools for cleaning, or use scripting tools for complex tasks.
- Transform the Data: Create calculated fields, aggregate data, or reshape tables to meet your visualization needs. This stage might involve creating new metrics or pivoting tables.
- Visualize and Analyze: Build your visualizations using the prepared data and explore the insights.
Data Source Connection Steps
The following table Artikels the steps for connecting to different data sources in Google Data Studio.
| Data Source | Connection Steps |
|---|---|
| Google Sheets | Select “Google Sheets” as the data source. Authenticate with your Google account and select the desired sheet. |
| Google Analytics | Select “Google Analytics” as the data source. Authenticate with your Google account and select the desired view. |
| BigQuery | Select “BigQuery” as the data source. Authenticate with your Google account and select the desired project and dataset. |
| CSV/Excel | Import the CSV/Excel file. Specify the delimiter (e.g., comma, tab) and data types. |
Dashboard Creation and Customization: Google Data Studio
Crafting compelling and insightful dashboards in Google Data Studio is a crucial step in effectively communicating data-driven insights. This involves more than just arranging charts; it’s about strategically organizing information to tell a story and empower informed decision-making. A well-designed dashboard serves as a central hub for data visualization, allowing users to explore trends, identify patterns, and understand key performance indicators (KPIs) at a glance.Creating a dashboard in Data Studio is a process of layering data visualizations, arranging them strategically, and customizing the look and feel to enhance user engagement and comprehension.
It’s not just about putting data on a screen; it’s about presenting it in a way that fosters understanding and actionable insights.
Structured Approach to Dashboard Creation
A systematic approach to dashboard creation in Data Studio is vital for building effective and user-friendly visualizations. Start by defining the objectives of the dashboard. What key insights are you trying to communicate? Who is the intended audience? These questions will guide the design process.
Next, select the relevant data sources and create the necessary connections. Identify the key metrics and dimensions that will be used in the visualizations. Finally, plan the layout and arrangement of the dashboard elements to ensure clarity and ease of navigation.
Customizing Dashboard Elements and Layouts
Data Studio provides a range of tools for customizing dashboard elements and layouts. These customizations include adjusting chart types, colors, fonts, and labels to align with the overall aesthetic and branding guidelines. Users can also customize chart parameters like data ranges, aggregations, and filters. These customizations enhance the visual appeal and allow users to focus on specific data points of interest.
Personalizing Dashboards
Personalization is key to user engagement. Users can be given the option to filter or customize views of the dashboard to align with their specific needs and priorities. For example, a sales manager might want to see a dashboard focusing on regional sales performance, while a marketing analyst might prioritize customer acquisition trends. These personalized views can be implemented through interactive filters and custom dashboards.
Clear Labeling and Data Context
Clear and concise labeling is critical for effective dashboard communication. Labels should accurately reflect the data presented and be easily understood by the intended audience. Data context is equally important. Providing context, such as units of measurement, time periods, and data sources, helps users interpret the data accurately. This approach reduces ambiguity and increases user trust in the dashboard’s insights.
Adding Interactive Elements
Interactive elements significantly enhance user engagement and data exploration. Features like clickable charts, drill-down capabilities, and interactive filters allow users to delve deeper into specific data points and uncover hidden trends. Adding interactivity enables users to explore data from various perspectives, fostering a deeper understanding of the information presented.
Dashboard Layout Options
| Layout Option | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Single Column | Simple and straightforward, ideal for a small number of visualizations. | A dashboard presenting key sales metrics across different regions in a single column. |
| Multiple Columns | Effective for displaying multiple visualizations simultaneously, facilitating comparisons and analyses. | A dashboard showing website traffic, conversion rates, and bounce rates in different columns. |
| Modular | Utilizes modular panels for organizing visualizations, offering a flexible and customizable approach. | A dashboard segmented into panels for different sales teams, each displaying relevant performance metrics. |
| Grid | Employs a grid-based structure for presenting a balanced distribution of charts. | A dashboard visualizing marketing campaign performance metrics across various channels in a grid layout. |
Dashboards should be designed with the user in mind. A well-structured and visually appealing dashboard fosters a deeper understanding of the data and empowers users to make data-driven decisions.
Advanced Features and Applications
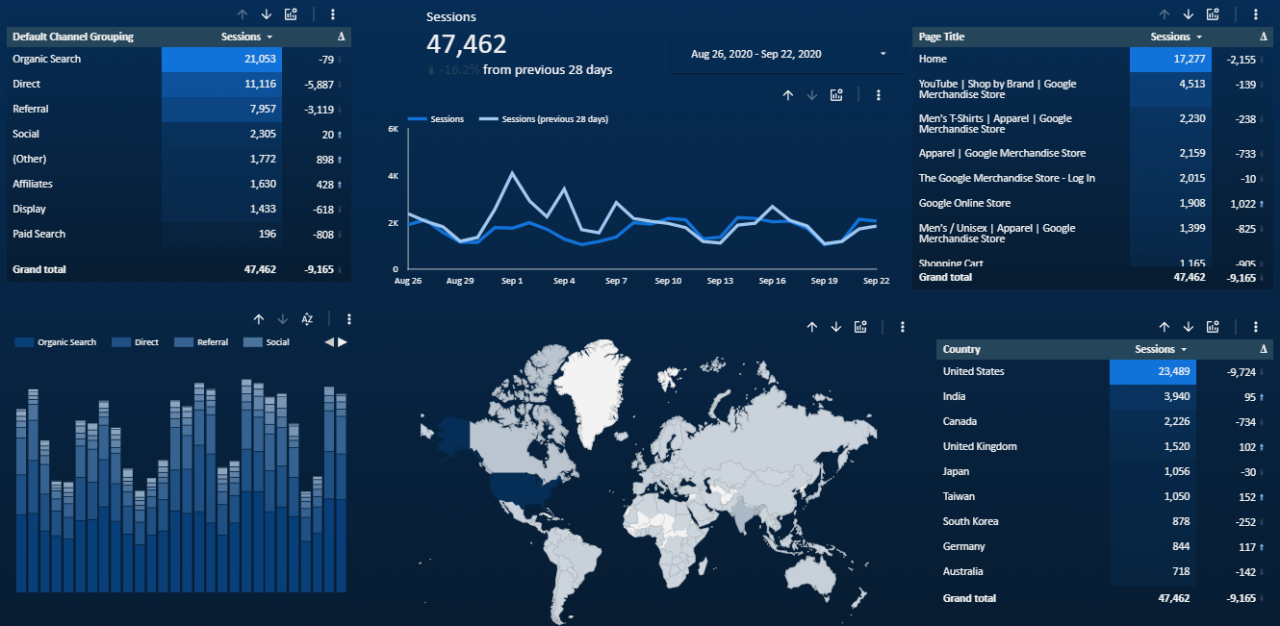
Google Data Studio, while powerful for basic reporting, truly shines when leveraging its advanced features. These features allow users to perform complex analysis, create dynamic dashboards, and go beyond simple visualizations to uncover deeper insights. This section dives into calculated fields, data blending, and other techniques to unlock the full potential of Data Studio.Data Studio’s strength lies in its ability to transform raw data into actionable insights.
By understanding and implementing its advanced functionalities, you can move beyond summarizing data and start predicting trends, identifying patterns, and building more comprehensive narratives from your data.
Calculated Fields
Calculated fields in Data Studio enable users to create new metrics and dimensions directly within the platform. This empowers you to perform complex calculations and derive new insights from your existing data. For instance, you can calculate customer lifetime value, calculate the percentage change in sales, or derive a new metric for engagement by combining existing fields. The possibilities are vast.Calculated fields are particularly beneficial when you need to create custom metrics that aren’t readily available in your source data.
This allows for a highly personalized approach to analysis, tailored specifically to your business needs. Formulas can be straightforward or quite intricate, depending on the desired outcome. Examples include calculating the average order value, finding the difference in revenue between two periods, or deriving a customer churn rate.
Example: To calculate the average order value, you might use a formula like `SUM(Order Value) / COUNT(Orders)`.
Data Blending
Data blending allows Data Studio to combine data from multiple sources into a single view. This is crucial for creating comprehensive analyses when your insights need data from disparate sources. Imagine analyzing sales data with website traffic or customer demographics. Data blending seamlessly integrates this information, enabling a holistic understanding of your business. The process is straightforward, enabling the creation of interconnected dashboards that provide a more detailed and insightful picture.
Advanced Data Studio Applications, Google data studio
Beyond standard reporting, Data Studio is exceptionally useful in a variety of scenarios:
- Predictive Analysis: Data Studio can be utilized to forecast future trends by integrating data with predictive models. For instance, you can use historical sales data and economic indicators to predict future sales patterns.
- Customer Segmentation: By blending customer data with transaction data, you can segment customers based on their purchasing behavior. This allows for targeted marketing campaigns and personalized recommendations, leading to increased customer satisfaction.
- Performance Tracking: Data Studio facilitates comprehensive performance monitoring across multiple departments or teams. This real-time view of performance enables informed decision-making, leading to continuous improvement.
- Market Analysis: By incorporating external data sources like industry reports or competitor information, you can gain a broader perspective on market trends and analyze your position in relation to the competition.
Dynamic Dashboards
Dynamic dashboards react to user interactions, providing a more interactive and personalized experience. This can include features like filters, drill-downs, and parameters. For example, users can filter data by region or product type to focus on specific aspects of their analysis. Furthermore, parameters enable users to customize their views with specific inputs, such as selecting a specific year or a particular product category.
Google Data Studio is a fantastic tool for visualizing data, but to really get the most out of it, you need a strong internal linking structure on your website. A well-structured site, with links strategically placed throughout, is key to SEO success. For example, if you’re creating reports in Google Data Studio that analyze sales performance, linking those reports to related product pages or blog posts on your site will improve user experience and help search engines understand the context of your data.
This thoughtful internal linking structure, as detailed in our guide on internal linking structure seo , ultimately boosts your Google Data Studio dashboards’ visibility and helps you reach a wider audience. Proper internal linking enhances the overall effectiveness of your Google Data Studio strategy.
Data Studio Versions Comparison
| Feature | Data Studio Version 1 | Data Studio Version 2 | Data Studio Version 3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Calculated Fields | Basic | Enhanced | Advanced |
| Data Blending | Limited | Supported | Improved with more sources |
| Interactive Features | Basic | Intermediate | Extensive |
| Data Source Support | Few | More | Many |
Note: This table provides a simplified comparison and specific features and capabilities may vary depending on the particular version and its functionalities.
Troubleshooting and Common Issues
Navigating the complexities of data visualization tools can sometimes lead to frustrating roadblocks. Google Data Studio, while powerful, is not immune to hiccups. This section dives into common issues encountered during the Data Studio journey, offering practical solutions and preventive measures. Understanding these challenges beforehand empowers you to confidently troubleshoot and refine your dashboards.
Data Connection Problems
Data connection failures are frequent hurdles. Issues can arise from various sources, including network problems, incorrect data source configurations, or authentication issues. Troubleshooting requires a systematic approach.
- Verify Network Connectivity: Ensure a stable internet connection. Temporarily disable any network proxies or firewalls that might interfere with the data source connection. Testing basic web browsing can help rule out wider network problems.
- Check Data Source Credentials: Double-check the credentials you’ve provided for the data source. Incorrect user IDs, passwords, or API keys can block the connection. Ensure that the correct authentication methods are employed for your chosen data source (e.g., Google Sheets, BigQuery). Confirm the data source’s availability and accessibility.
- Examine Data Source Configuration: Verify the data source’s settings and availability. Review whether the dataset you’re targeting is accessible and if it’s configured properly within Data Studio. If using a third-party API, confirm the API key or authentication tokens are valid.
Visualization Errors
Visualization errors often stem from issues with data formatting, incompatible data types, or misconfigured chart settings. A methodical approach can help resolve these problems.
- Data Type Mismatches: Ensure that the data types in your data source align with the expected types for the visualizations you’re trying to create. For example, a column intended for numerical values should not contain text strings or dates.
- Data Formatting Errors: Data Studio often requires specific formatting for date, time, and currency values. Check the data source to verify proper formatting or adjust the formatting within Data Studio’s configuration. A missing or incorrect separator (e.g., commas in numbers) can cause problems.
- Chart Configuration Errors: Ensure the chart settings (e.g., dimensions, metrics, filters) are correctly configured to produce the desired output. Verify the correct selections for each chart element and ensure data sources match.
Data Import Problems
Data import problems can be perplexing. Troubleshooting this often involves systematically checking each step of the import process.
- Verify Data Source Compatibility: Ensure the data source you’re connecting to is compatible with Data Studio. Review Data Studio’s supported data sources to ensure compatibility.
- Inspect Data Structure: Analyze the structure of the data to identify any inconsistencies or errors. Check for missing values, incorrect data types, or duplicated entries. Consider using tools within the data source (e.g., Google Sheets’ Data Validation) to identify and fix potential issues.
- Check for Data Integrity: Confirm the data in your source file is accurate and consistent. Look for any obvious errors, inconsistencies, or missing values in the imported data.
- Review Import Settings: Double-check the import settings in Data Studio to ensure they are correct and compatible with the data source. Check for delimiters, data types, and other configuration settings.
Best Practices for Preventing Common Errors
Proactive steps can prevent many issues.
- Data Validation: Validate your data source before importing into Data Studio. Check for data integrity and quality.
- Data Cleaning: Clean and prepare your data before connecting it to Data Studio. Correct any formatting errors, handle missing values, and ensure data consistency.
- Testing: Test your visualizations and data connections before deploying to ensure everything functions as expected. Use sample data to validate functionality.
Case Studies and Examples
Data visualization is not just about pretty charts; it’s about transforming raw data into actionable insights. Google Data Studio, with its user-friendly interface and robust features, empowers businesses to derive meaningful conclusions from their data. Real-world examples demonstrate how effectively utilizing Google Data Studio can lead to significant improvements in decision-making and ultimately, business outcomes.Data visualization, facilitated by platforms like Google Data Studio, is crucial for understanding complex datasets.
Presenting data in a visual format allows stakeholders to quickly grasp trends, patterns, and anomalies that might be missed in a spreadsheet. This improved understanding leads to better strategic decisions and informed actions.
Real-World Google Data Studio Implementations
Successful data visualization projects often involve a clear understanding of the business objectives and the data available. Data Studio dashboards should directly address key questions and provide actionable insights. Choosing the right metrics and visualizations is essential for effective communication and decision-making.
Examples Across Industries
Data Studio’s versatility is evident in its application across various industries. Retailers can track sales performance across different channels, identify high-performing products, and optimize inventory management. E-commerce businesses can monitor website traffic, customer behavior, and conversion rates to improve marketing campaigns and sales strategies. Healthcare organizations can use Data Studio to monitor patient outcomes, track resource utilization, and identify areas for improvement.
Impact on Decision-Making
“Data visualization enables faster and more informed decisions by quickly highlighting key trends and patterns.”
Data Studio’s dashboards can provide a comprehensive overview of key performance indicators (KPIs). This allows stakeholders to make timely and data-driven decisions, leading to improved operational efficiency and strategic planning. For example, a marketing team can analyze campaign performance metrics in real-time, adjusting their strategies to maximize return on investment (ROI).
Impact on Business Outcomes
The impact of data visualization on business outcomes can be significant. By identifying areas for improvement and optimizing processes, companies can increase revenue, reduce costs, and enhance customer satisfaction. For instance, a retail business using Data Studio to monitor inventory levels can prevent stockouts, optimize pricing strategies, and enhance customer experience. A healthcare organization, by visualizing patient outcomes, can identify trends that lead to better treatment plans and improved patient health.
Table of Data Visualization Dashboard Examples
| Industry | Dashboard Purpose | Key Metrics Visualized | Example Visualization |
|---|---|---|---|
| Retail | Track sales performance across different channels | Sales revenue, profit margin, conversion rate, customer acquisition cost | Bar charts comparing sales by region, line graphs showing sales trends over time, and scatter plots correlating product popularity with price. |
| E-commerce | Monitor website traffic and customer behavior | Website traffic, bounce rate, conversion rate, average order value | Donut charts showing traffic sources, heatmaps illustrating user engagement on product pages, and line graphs depicting conversion rates over different marketing campaigns. |
| Healthcare | Monitor patient outcomes and resource utilization | Patient satisfaction scores, readmission rates, average length of stay, hospital resources utilization | Scatter plots showing correlations between patient demographics and treatment outcomes, line graphs depicting trends in hospital readmission rates, and bar charts highlighting resource utilization by department. |
Summary
In conclusion, Google Data Studio empowers users to transform complex data into compelling visuals. This exploration of its functionalities, techniques, and applications demonstrates the tool’s versatility and value across diverse industries. By mastering the art of data visualization, you can unlock the full potential of your data and make informed decisions. This guide serves as your comprehensive resource to get started with Google Data Studio.
