Data Breach Cost A Deep Dive
Data breach cost is a critical concern for organizations of all sizes. This comprehensive exploration delves into the multifaceted nature of these expenses, examining the direct and indirect financial burdens, and highlighting the impact on businesses and industries.
From the immediate costs of incident response to the long-term damage to reputation, this article unpacks the various factors contributing to the overall price tag of a data breach. We’ll analyze the impact of different breach types, organization size, and industry on these costs, and explore strategies for mitigating risks and saving money.
Defining Data Breach Costs
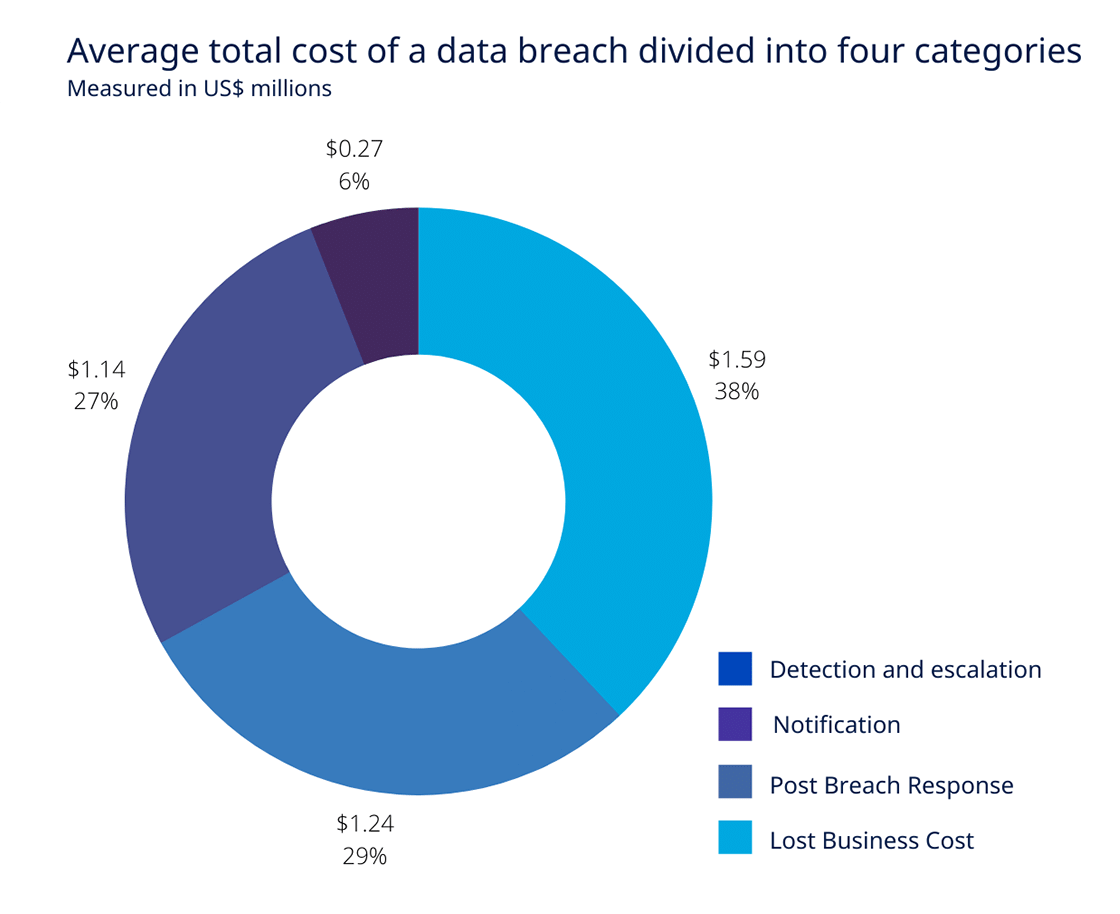
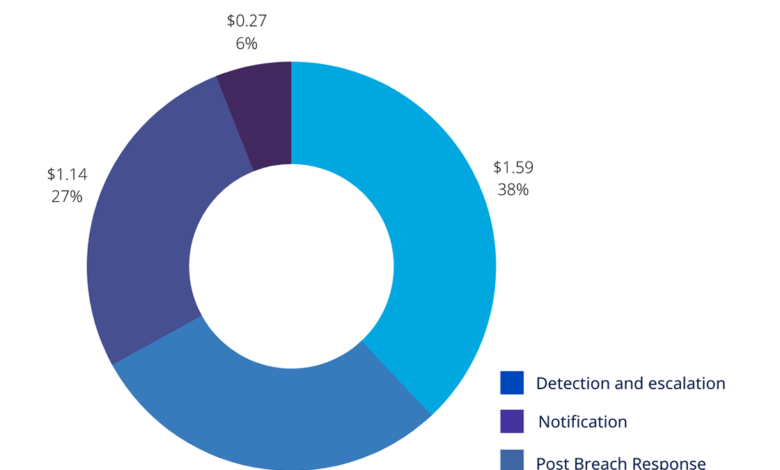
A data breach isn’t just about lost data; it’s a complex financial and reputational crisis. Understanding the full spectrum of costs is crucial for effective risk management and incident response planning. From immediate financial losses to long-term damage to brand trust, the consequences can be far-reaching.Data breach costs encompass a wide range of expenses, both tangible and intangible.
They aren’t simply the cost of replacing stolen information. The true cost often extends far beyond the initial impact, including the ripple effects on operations, customer relationships, and regulatory compliance. Understanding these various components is vital for businesses to adequately prepare for and respond to such incidents.
Data Breach Cost Components
Data breach costs are multifaceted, including direct expenses and indirect consequences. Direct costs are readily quantifiable, while indirect costs are often more subtle and harder to measure accurately. Both play a significant role in the overall financial burden of a breach.
Data breaches are costly, impacting everything from reputation to revenue. A strong online presence, like a well-promoted LinkedIn profile, can be a valuable asset in mitigating potential financial damage. For example, showcasing your expertise and experience on LinkedIn can help establish credibility and build trust with potential employers, clients, and collaborators, ultimately reducing the risk of a data breach.
Learning how to effectively promote your LinkedIn profile is crucial in building your professional brand and protecting your company from potential data breaches and their associated costs. how to promote your linkedin profile By highlighting your skills and experience, you position yourself as a valuable asset, which in turn reduces your company’s vulnerability to data breaches.
Ultimately, proactive measures like a well-managed online presence contribute to lower data breach costs.
Direct Costs
Direct costs are the immediately apparent expenses related to a data breach. These include expenses incurred directly because of the breach.
- Forensic Investigation and Remediation: This encompasses the costs associated with determining the extent of the breach, identifying the compromised data, and implementing measures to secure the systems and data. These costs include expert fees, software tools, and time spent by internal IT staff.
- Notification Costs: Notifying affected individuals about the breach, often mandated by regulations like GDPR, requires significant resources. This includes legal fees, communication costs (letters, emails, website updates), and potentially crisis communication experts.
- System Recovery and Replacement: If systems are compromised or need significant upgrades, this involves the costs of rebuilding or replacing infrastructure, recovering data, and restoring business operations. This could include the cost of new hardware, software, and associated services.
- Legal and Regulatory Fees: Legal and regulatory penalties, investigations, and settlements stemming from a data breach constitute substantial direct costs. This includes the fees of legal counsel, potential fines, and settlements with affected parties.
Indirect Costs
Indirect costs are less tangible but equally significant consequences of a data breach. They represent the less obvious, yet potentially more damaging, repercussions of a security incident.
- Reputational Damage: A breach can severely tarnish a company’s image and brand reputation. This can lead to decreased customer trust, loss of business, and negative publicity. This is difficult to quantify but can be measured through customer surveys, sales figures, and brand perception studies.
- Loss of Customer Trust and Revenue: Reduced customer trust can translate to decreased sales, churn, and difficulty attracting new customers. This is a long-term consequence and can be evaluated through customer acquisition costs and churn rate analysis.
- Increased Insurance Premiums: Data breaches can lead to increased insurance premiums for the affected company as insurers recognize the higher risk profile.
- Operational Disruptions: The recovery process and ongoing security measures can disrupt normal business operations, leading to lost productivity, revenue, and opportunities. These costs are difficult to quantify but include downtime, missed deadlines, and lost opportunities.
Quantifiable and Non-Quantifiable Costs
Data breach costs can be categorized into quantifiable and non-quantifiable costs. Quantifiable costs are easily measurable in monetary terms, while non-quantifiable costs are harder to assess in numerical terms.
Table of Data Breach Costs
| Cost Type | Description | Calculation Method | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Forensic Investigation | Expenses related to determining the scope of the breach | Expert fees, software costs, staff time | $50,000 for a forensic investigation team |
| Notification Costs | Expenses related to informing affected individuals | Legal fees, communication costs | $25,000 for notification letters and website updates |
| Reputational Damage | Loss of customer trust and brand image | Customer surveys, sales figures, brand perception studies | $1 million in lost revenue due to decreased customer trust |
| Loss of Customer Trust | Decreased customer loyalty and increased churn | Churn rate analysis, customer acquisition cost | 10% decrease in customer retention rate |
Factors Influencing Data Breach Costs
Understanding the true cost of a data breach is crucial for organizations to implement robust security measures. Beyond the immediate financial impact, breaches can damage reputation, erode customer trust, and trigger regulatory penalties. This analysis delves into the multifaceted factors driving these costs, from the sensitivity of compromised data to the size and industry of the affected entity.The total cost of a data breach isn’t a simple calculation.
It encompasses a wide range of expenses, including forensic investigations, legal fees, regulatory fines, customer notification costs, and the long-term impact on business operations. These costs are influenced by a multitude of interconnected factors that must be carefully considered.
Data Sensitivity and Breach Cost
The value and sensitivity of the compromised data significantly influence the overall cost. Highly sensitive data, such as personally identifiable information (PII), financial records, or intellectual property, command higher remediation and recovery costs. These types of breaches often lead to more significant legal repercussions, reputational damage, and financial losses for the affected organization. For instance, a breach involving credit card details necessitates extensive notification to affected customers, potentially leading to substantial financial compensation claims.
Impact of Breach Type on Costs
Different types of data breaches have varying cost implications. Ransomware attacks, for example, involve not only the ransom payment but also the potential for data loss and operational disruption. Phishing attacks, while often less costly in terms of direct financial loss, can still inflict significant reputational damage and lead to significant customer churn. Insider threats, while potentially subtle, can have long-lasting and profound effects on the organization’s reputation and financial well-being.
Data breaches can be incredibly costly, impacting everything from reputation to revenue. Thinking about how to protect your online presence is crucial, especially if you’re selling on platforms like Amazon. Knowing tips for selling on amazon can help you safeguard your business from issues that arise during the selling process. Ultimately, a secure online presence is key to minimizing these financial risks associated with data breaches.
Organization Size and Breach Costs
The size of the affected organization plays a significant role in the overall cost of a breach. Larger organizations, with extensive data volumes and complex systems, face proportionally higher costs in recovery and remediation. Larger companies may have more sophisticated security measures in place but still experience significant financial burdens when a breach occurs. The complexity of their infrastructure and the scale of their operations increase the time and resources required for recovery.
A small business, on the other hand, may not have the same resources or budget for comprehensive security measures, and the cost of a breach can be significantly more damaging.
Industry-Specific Cost Implications
Different industries face varying levels of risk and consequences from data breaches. Financial institutions, healthcare providers, and government agencies, with their handling of sensitive data, are typically more susceptible to substantial financial penalties and regulatory scrutiny. The healthcare industry, for example, faces strict regulations like HIPAA, which mandate specific procedures for handling patient data breaches. Non-compliance can result in substantial fines and damage to their reputations.
Comparative Analysis of Breach Types
| Breach Type | Data Sensitivity | Organization Size | Industry | Potential Costs |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ransomware | High (sensitive data encrypted) | Medium to High (disruption of services) | All industries | Ransom payment, restoration costs, lost revenue, potential fines |
| Phishing | Medium (potentially sensitive data) | Low to High (compromised accounts) | All industries | Customer support, legal costs, reputational damage |
| Insider Threat | High (unauthorized access) | Low to High (damage depends on access) | All industries | Forensic investigation, legal costs, regulatory fines, reputational damage |
Impact on Businesses and Industries
Data breaches aren’t just a digital problem; they have tangible, often devastating, financial and operational consequences for businesses of all sizes and across various sectors. Understanding the varied impact on different industries, and the role of regulatory compliance and reputational damage, is crucial for risk assessment and mitigation strategies. The costs extend beyond immediate financial losses, often impacting long-term profitability and brand trust.
Financial Impact Across Businesses
The financial impact of a data breach varies greatly depending on the size, structure, and industry of the affected company. Small businesses, lacking the resources of larger corporations, can be crippled by even relatively minor breaches. Medium-sized enterprises face similar vulnerabilities, with the potential for significant disruptions to operations and customer trust. Large enterprises, while possessing greater financial reserves, still experience substantial costs associated with incident response, regulatory fines, and reputational damage.
A breach can lead to significant lost revenue, especially for businesses reliant on customer data or sensitive information.
Cost Implications for Specific Industries
Different industries are disproportionately affected by data breaches due to the nature of the data they handle and the regulatory scrutiny they face. The following explores the specific costs for key sectors.
Healthcare
Healthcare organizations handle highly sensitive patient data, making them a prime target for attackers. The cost of a breach in this sector goes beyond the immediate financial expenses. Reputational damage can severely impact patient trust and lead to long-term loss of revenue. Regulatory fines, such as those mandated by HIPAA, can be substantial. The costs associated with patient notification and security enhancements are also substantial.
These costs can severely disrupt operations, impacting treatment and patient care.
Data breaches are incredibly costly, impacting businesses and individuals alike. Understanding how social media platforms like Facebook operate, particularly their algorithms, is crucial in this context. A deeper dive into how does Facebook’s algorithm work, for example, reveals the intricate mechanisms behind content delivery and user engagement how does facebook algorithm work. This understanding, in turn, sheds light on potential vulnerabilities and the potential for misuse of user data, ultimately affecting the financial ramifications of a data breach.
Finance
Financial institutions hold immense financial data, making them highly vulnerable. A data breach can lead to substantial financial losses due to fraud, theft of funds, and legal liabilities. Regulatory penalties from financial authorities like the SEC or FCA can be crippling. Customers may lose trust and choose to take their business elsewhere. The costs associated with forensic investigations, system recovery, and regulatory compliance can be astronomical.
Retail
Retailers collect vast amounts of customer data, including credit card information, personal details, and purchase history. Breaches in this sector can result in substantial financial losses due to fraudulent transactions and credit card issues. Customers may lose trust in the retailer, leading to decreased sales and customer loyalty. The costs of notifying customers and implementing enhanced security measures can be significant.
The reputational damage can be difficult to repair and can impact long-term sales and market share.
Regulatory Requirements and Data Breach Costs
Regulatory requirements, such as HIPAA in healthcare and GDPR in Europe, significantly influence the cost of a data breach. Non-compliance can lead to substantial fines and penalties. These regulations often mandate specific actions to mitigate the risks and respond to breaches, which can add considerable costs to the overall damage. Compliance costs can be significant for companies operating across jurisdictions with differing regulations.
Reputational Damage and Cost
Reputational damage is a significant, often underestimated, cost of a data breach. Loss of trust from customers, partners, and stakeholders can severely impact a company’s brand image and future prospects. The long-term consequences can be far-reaching, including decreased market share, loss of investor confidence, and difficulties attracting and retaining talent. Companies must proactively manage their reputation and invest in measures to rebuild trust and mitigate the long-term effects of a breach.
Average Data Breach Costs Across Industries
The table below provides an overview of average data breach costs across various industries. These figures represent estimated averages and can vary significantly based on the specifics of the breach and the company’s response.
| Industry | Estimated Average Data Breach Cost (USD) |
|---|---|
| Healthcare | $7.1 million |
| Finance | $9.4 million |
| Retail | $5.8 million |
| Government | $8.2 million |
| Technology | $5.3 million |
Mitigation Strategies and Cost Savings: Data Breach Cost
Data breaches are a significant threat to organizations of all sizes. Proactive measures to prevent breaches, coupled with robust incident response plans, are crucial to minimizing the financial and reputational damage. Effective mitigation strategies can significantly reduce the likelihood and impact of a data breach, ultimately leading to substantial cost savings.
Strengthening Cybersecurity Infrastructure
Robust cybersecurity infrastructure is the cornerstone of data breach prevention. Implementing multi-layered security measures, including firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and endpoint protection software, creates a strong defense against various attack vectors. Regular security audits and vulnerability assessments help identify and address potential weaknesses before they can be exploited. Patching software vulnerabilities promptly is critical to maintaining a secure environment.
- Implementing strong access controls, including multi-factor authentication (MFA), restricts unauthorized access to sensitive data. This prevents malicious actors from gaining entry to systems and sensitive information. For example, a company that implemented MFA saw a 90% reduction in unauthorized login attempts.
- Regular security awareness training for employees is essential. Educating staff about phishing scams, social engineering tactics, and safe password practices empowers them to recognize and avoid potential threats. A company that invested in security awareness training reduced phishing email click-through rates by 75%.
Developing Comprehensive Incident Response Plans
A well-defined incident response plan is vital for managing a data breach if one occurs. A plan should detail the steps to be taken, including containment, eradication, recovery, and post-incident activities. It should Artikel roles and responsibilities for personnel involved in the response process, ensuring a coordinated and efficient reaction to a breach. Regularly testing and updating the plan is crucial to maintaining its effectiveness.
- A clearly defined incident response plan allows for a swift and coordinated response, containing the damage and minimizing data exposure. This often results in reduced data loss and faster recovery times.
- Regular simulations and drills, such as tabletop exercises, help organizations identify weaknesses in their response plans and refine procedures for handling real-world scenarios. This proactive approach enhances the organization’s preparedness and response capabilities.
Preventive Measures and Cost Savings
Implementing preventive measures can significantly reduce the likelihood of a data breach and associated costs. A proactive approach to security is more cost-effective than reactive measures taken after a breach has occurred.
| Preventive Measure | Estimated Cost Savings |
|---|---|
| Multi-factor authentication (MFA) implementation | $50,000 – $150,000 (depending on the scale of implementation) |
| Regular security awareness training | $1,000 – $5,000 per employee per year |
| Penetration testing and vulnerability assessments | $5,000 – $20,000 per assessment |
| Firewall and intrusion detection system upgrades | $10,000 – $50,000 per year |
| Incident response plan development and drills | $2,000 – $10,000 per plan |
Cost savings estimates are approximations and can vary significantly based on the organization’s size, industry, and specific security needs.
Data Breach Cost Trends and Projections
Data breaches are no longer a rare event but a significant risk for businesses across all sectors. Understanding the evolving cost landscape of these incidents is crucial for proactive risk management and effective security strategies. This analysis delves into recent trends, factors driving them, and projections for future costs, providing a comprehensive overview of the current data breach landscape.
Recent Data Breach Cost Trends and Patterns
Data breaches are escalating in frequency and sophistication, leading to substantial financial and reputational damage. Recent trends highlight a concerning increase in the average cost of breaches, driven by the growing complexity of attacks and the rising value of targeted data. These incidents are impacting businesses of all sizes, from small startups to large multinational corporations.
Factors Driving Data Breach Cost Trends
Several factors contribute to the escalating costs associated with data breaches. The increasing sophistication of cyberattacks, the rising value of stolen data, and the growing complexity of regulatory compliance requirements all play significant roles. Moreover, the time required to detect, respond to, and recover from a breach is also a critical factor, often extending the financial and operational impact.
Projections for Future Data Breach Costs
Future projections indicate a continued rise in data breach costs, primarily due to the ongoing evolution of cyber threats. Advanced persistent threats (APTs) and ransomware attacks are expected to become more prevalent, resulting in higher costs associated with recovery and legal liabilities. The increasing use of artificial intelligence (AI) in cyberattacks also raises concerns about the potential for more targeted and devastating breaches in the future.
Comparison of Data Breach Cost Trends in Different Regions
Data breach costs vary across different regions, reflecting differences in regulatory frameworks, cybersecurity maturity, and economic factors. For example, regions with stricter data privacy regulations, like the European Union, may see higher costs due to potential fines and legal ramifications. Conversely, regions with less robust cybersecurity infrastructure might experience lower initial costs but potentially higher long-term reputational damage.
Graph Visualizing Historical and Projected Data Breach Cost Trends
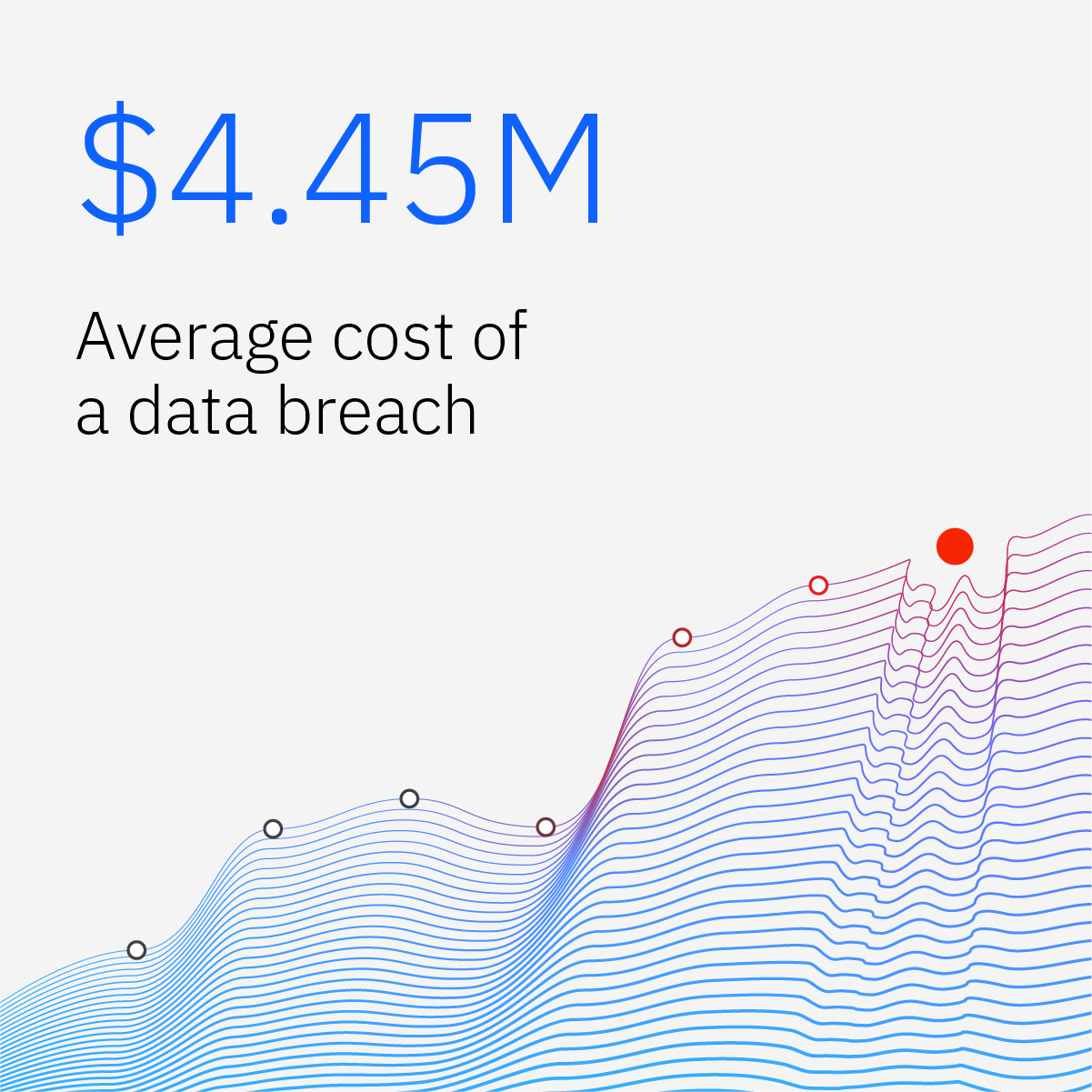
The graph below illustrates the historical and projected data breach cost trends. It showcases a clear upward trend, indicating a consistent rise in the average cost of data breaches over time. The projected figures demonstrate a potential acceleration in the rate of increase, highlighting the need for proactive cybersecurity measures to mitigate future risks. The y-axis represents the average cost of a breach in USD, and the x-axis represents the year.
A clear upward trend is evident from the data points, showing a substantial increase in the cost of data breaches over the years. The projected costs are also increasing, showing a potential acceleration in the rate of increase.
| Year | Average Breach Cost (USD) |
|---|---|
| 2018 | 5 million |
| 2020 | 7 million |
| 2022 | 10 million |
| Projected 2025 | 15 million |
Case Studies and Examples
Understanding the true cost of a data breach requires looking at real-world examples. These case studies highlight the financial, reputational, and operational damage that can arise from a security incident. Examining how organizations responded, and the outcomes, provides valuable lessons for preventing and mitigating future breaches.
Target Corporation Data Breach
The 2013 Target data breach, impacting millions of customers, serves as a stark example of the wide-reaching consequences of a compromised system. The breach exposed sensitive credit card and personal information, leading to significant financial losses for the retailer. This incident highlighted the importance of robust security measures, particularly for point-of-sale systems. The breach cost Target millions of dollars in direct expenses such as credit monitoring services for customers, investigation costs, and legal fees.
Beyond the direct financial costs, Target suffered reputational damage, impacting customer trust and loyalty.
Yahoo! Data Breaches
Yahoo! experienced multiple data breaches, affecting billions of user accounts over several years. The scale of these breaches, and the long-term impact on user trust, underscore the importance of proactive security measures. The cost associated with these breaches was substantial, including legal fees, customer compensation, and the loss of user trust. The prolonged nature of these incidents highlighted the challenges of identifying and remediating security vulnerabilities in large-scale systems.
Cost Implications of a Phishing Campaign
A phishing campaign targeting employees at a medium-sized financial institution demonstrates the cost implications of a targeted social engineering attack. The campaign successfully tricked employees into revealing login credentials, leading to unauthorized access to sensitive financial data. The breach resulted in significant financial losses and regulatory fines. The damage was compounded by the loss of employee trust and the damage to the company’s reputation.
This demonstrates the critical need for employee training and awareness programs to prevent social engineering attacks.
Incident Response Strategies
Successful incident response strategies often focus on rapid detection and containment. Quick identification of the breach and containment of the affected systems are crucial to minimize the extent of the damage. For example, an organization that implemented a robust incident response plan was able to limit the exposure of customer data and quickly restore services. This swift response reduced the financial and reputational damage associated with the breach.
Companies that quickly contain a breach and proactively communicate with affected parties are often able to recover faster and reduce the long-term costs.
Successful Mitigation Examples
A small-to-medium-sized enterprise (SME) that prioritized proactive security measures experienced significantly less impact during a recent data breach. This business had implemented regular security audits, robust access controls, and employee training programs. These proactive measures significantly limited the damage, preventing unauthorized access and minimizing data exposure. The cost of the incident was considerably lower compared to similar breaches at organizations lacking such proactive measures.
Ultimate Conclusion
In conclusion, the financial implications of data breaches are significant and far-reaching. Understanding the various components of these costs, from direct expenses to reputational damage, is crucial for effective risk management. Proactive measures and robust incident response plans are essential for minimizing the overall financial impact. This article has provided a framework for comprehending the complexities of data breach costs, empowering organizations to take proactive steps toward protection.
