What is Canonicalization? How to Use Canonical Tags
What is canonicalization how to use canonical tags? This guide dives deep into the world of search engine optimization (), revealing how canonicalization can save your website from duplicate content issues and boost your search rankings. We’ll explore everything from the basics of canonicalization to advanced strategies for handling multiple domains and mobile versions. Get ready to master the art of canonical tags and optimize your site for maximum visibility.
Understanding how to implement canonical tags correctly is vital for any website owner serious about . This isn’t just about avoiding penalties; it’s about ensuring search engines understand your content and its intended audience. This article provides practical examples and actionable steps to help you implement these tags effectively.
Understanding Canonicalization
Canonicalization is a crucial aspect of website management, especially for search engine optimization (). It’s the process of designating a single, definitive version of a web page to avoid duplicate content issues. This single version is known as the canonical URL. Understanding and implementing canonicalization effectively can significantly improve a website’s ranking in search engine results pages (SERPs) and enhance user experience.Canonicalization, in essence, tells search engines which version of a page is the primary one.
This helps prevent search engines from indexing multiple versions of the same content, which can dilute the page’s authority and potentially harm its ranking. By designating a single canonical URL, websites ensure that search engines only index and rank the designated version, optimizing their performance.
Importance for
Duplicate content can severely impact a website’s . Search engines often struggle to determine which version of a page is the most relevant and authoritative. Canonicalization resolves this ambiguity by clearly specifying the preferred version, helping search engines prioritize and index the correct page, leading to improved search engine rankings.
Implementation Methods
Several methods exist for implementing canonicalization on a website. The most common and effective method involves using the ` ` tag within the `
` section of a web page. This tag provides a clear signal to search engines about the canonical URL. Alternatively, a 301 redirect can be used to permanently redirect duplicate URLs to the canonical URL. This approach effectively instructs search engines to treat the duplicate page as a redirect to the canonical version. Using the correct HTTP status codes (e.g., 301 for permanent redirects) is critical for a smooth transition. Proper implementation ensures that search engines understand the intended canonical version of the content.Crucial Scenarios
Canonicalization is essential in various website scenarios. For instance, it’s critical when dealing with pages generated dynamically by content management systems (CMS). Such systems can create multiple versions of a page based on different parameters, making canonicalization necessary to ensure a single version is prioritized. It’s equally crucial for e-commerce sites with product pages that may appear in different variations or filters.
The correct implementation of canonicalization can prevent duplicate content issues and ensure the best possible performance.
Understanding canonicalization and using canonical tags correctly is crucial for SEO, especially in a digital PR campaign. It helps search engines understand which version of a page is the main one, preventing duplicate content issues. A well-structured digital PR campaign, like the ones offered by JAR Digital , often involves multiple touchpoints and variations of content. This makes proper canonicalization even more important to ensure search engines don’t get confused, and your hard work is rewarded.
By correctly using canonical tags, you steer search engines to the intended page and boost your overall SEO.
Benefits and Drawbacks of Canonicalization
| Benefits of Using Canonical Tags | Potential Drawbacks of Not Using Them | Practical Examples | Explanation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Improved Search Engine Rankings | Reduced Search Engine Ranking | A blog post published on multiple platforms (e.g., website, social media) | Using canonical tags ensures that search engines index the main blog post version, leading to better rankings |
| Reduced Duplicate Content Issues | Duplicate Content Penalties from Search Engines | A product page with variations like color and size | Canonical tags prevent search engines from treating different variations as separate pages, avoiding duplicate content issues. |
| Enhanced User Experience | Confusing Search Engine Crawlers | A website with multiple URLs leading to the same content | Users are directed to the correct version of the page, leading to a better experience. |
| Increased Website Authority | Diluted Website Authority | A website with dynamically generated pages (e.g., a news site) | Search engines prioritize the canonical version, increasing the website’s authority. |
Identifying Duplicate Content Issues
Duplicate content is a significant hurdle for website owners aiming for high search engine rankings. It essentially means presenting the same or near-identical text across multiple pages on your site, or even on other websites. This redundancy confuses search engines, potentially leading to lower rankings and decreased organic traffic. Understanding the nuances of duplicate content is crucial for maintaining a healthy online presence.Duplicate content negatively impacts search engine optimization () by diluting the site’s overall authority and relevance.
Search engines struggle to determine which version of the content is the most authoritative and representative of the site’s overall value. This uncertainty can lead to poor search engine rankings, hindering your website’s visibility to potential customers.
Different Types of Duplicate Content
Duplicate content can manifest in several ways. It’s not just about identical paragraphs; slight variations, or even different presentation formats of the same information, can trigger issues.
- Exact Duplicates: Identical text appearing on multiple pages. This is the most straightforward form of duplicate content, often stemming from unintentional copying or content scraping. For instance, a product description repeated across multiple product pages, or a blog post published on multiple platforms without modification, could cause this problem.
- Near-Duplicate Content: Content with high similarity, but not identical. This often occurs when content is rewritten or paraphrased without significant changes, or when similar content is generated automatically.
- Content Syndication Issues: If your content is republished on other websites without proper attribution or canonicalization, search engines may view it as duplicate content, diluting the original source’s authority.
- Dynamically Generated Content: Websites using parameters or filters to generate content, such as product variations or search results pages, might create duplicate content. For example, a clothing store’s website might generate many pages for different sizes and colors of a particular garment. If these are not handled appropriately, they become duplicate content.
- Mirrored Sites: If a website has identical or very similar content on different domain names, this creates duplicate content problems, confusing search engines.
Negative Impacts of Duplicate Content on
Duplicate content can severely harm your website’s search engine rankings. Search engines, primarily Google, aim to provide users with the most relevant and unique information. When they encounter duplicate content, they might penalize the site, resulting in lower rankings in search results.
- Lower Rankings: Duplicate content can cause search engines to devalue your website’s overall authority, leading to lower rankings for relevant search queries.
- Reduced Organic Traffic: Lower rankings directly translate to less organic traffic. This reduces visibility to potential customers and consequently impacts business growth.
- Negative User Experience: Duplicate content might lead to a confusing user experience, as users might encounter the same information on different pages, which can negatively impact their perception of your website.
- Potential Penalties: Search engines might impose penalties on websites with substantial duplicate content, impacting search engine visibility and rankings.
How Canonicalization Addresses Duplicate Content
Canonicalization is a crucial technique for managing duplicate content. It helps search engines understand which version of a page is the primary one, thereby avoiding the issues associated with duplicate content. It essentially tells search engines which URL represents the definitive source of information.
Duplicate Content Scenarios and Canonicalization Solutions
This table demonstrates how canonicalization can address various duplicate content scenarios, mitigating potential damage.
| Scenario | Impact on | Canonical Tag Solution | Explanation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Identical Product Pages (Different Variations) | Lower rankings, diluted authority | Use canonical tags on variation pages pointing to the main product page. | This ensures search engines treat the main product page as the authoritative version, preventing penalties for duplicated content. |
| Dynamically Generated Content (Filter Results) | Duplicate content for various filter combinations. | Use canonical tags on filter results pages pointing to the original product listing page. | This approach helps search engines recognize the main page as the source of information, preventing confusion. |
| Content Syndication (Without Proper Attribution) | Reduced authority, possible penalty | Implement canonical tags on the syndicated content pointing to the original source. | This allows search engines to distinguish the original source, ensuring the original website retains its authority. |
| Multiple URLs for the Same Content | Confused search engines, potential lower ranking | Identify the canonical URL and use canonical tags on all other URLs to point to the canonical URL. | This ensures search engines only index the primary version, preventing confusion and maintaining the correct representation of the content. |
Implementing Canonical Tags: What Is Canonicalization How To Use Canonical Tags
Implementing canonical tags is crucial for search engine optimization (). It helps search engines understand which version of a webpage is the primary one, preventing duplicate content issues and improving overall website ranking. This, in turn, saves crawl budget and avoids confusing search engines.Canonical tags are essentially instructions for search engines. They point search engines to the preferred version of a page when multiple versions of the same content exist.
This ensures that search engines index only the intended page, preventing issues with duplicate content penalties.
Correct Syntax and Structure
The canonical tag is an HTML element that tells search engines which URL is the preferred version of a page. It’s placed within the `
` section of the HTML document.The correct syntax for a canonical tag is `` where `canonical_url` is the URL of the preferred page.
Canonical Tag Implementations for Various Website Structures
Various website structures can benefit from canonical tags. Here are some examples:
- Pagination: When you have multiple pages of content, such as blog posts, product listings, or search results, the canonical tag helps search engines understand the relationship between these pages. The canonical tag on each page should point to the main page, ensuring that all pages are indexed correctly.
- Different Product Variations: E-commerce sites often have multiple product variations (e.g., different colors, sizes, or models). Canonical tags ensure that search engines index only one version, preventing duplicate content issues. Each variation page should link to the main product page as the canonical URL.
- Different URL Variations: Websites may have different URL structures (e.g., with or without www, with or without trailing slashes). Canonical tags can be used to specify a single preferred URL, directing search engine crawlers to the correct version.
- Dynamic URLs: For websites with dynamic content, like those using parameters or query strings, canonical tags help avoid duplicate content issues by directing search engines to the correct, preferred URL.
Examples of Canonical Tag Implementation
The table below illustrates various URL structures, their canonical versions, and corresponding HTML code examples.
| Original URL | Canonical URL | HTML Code Example | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| https://www.example.com/product/red-shirt | https://www.example.com/product | Canonical tag for a product variation page linking to the main product page. | |
| https://www.example.com/page/2 | https://www.example.com/ | Canonical tag for a pagination page linking to the main page. | |
| https://www.example.com/products?color=red | https://www.example.com/products | Canonical tag for a dynamic URL with parameters linking to the main products page. | |
| http://example.com/page1 | http://example.com/ | Canonical tag for a page pointing to the homepage. |
Advanced Canonicalization Strategies
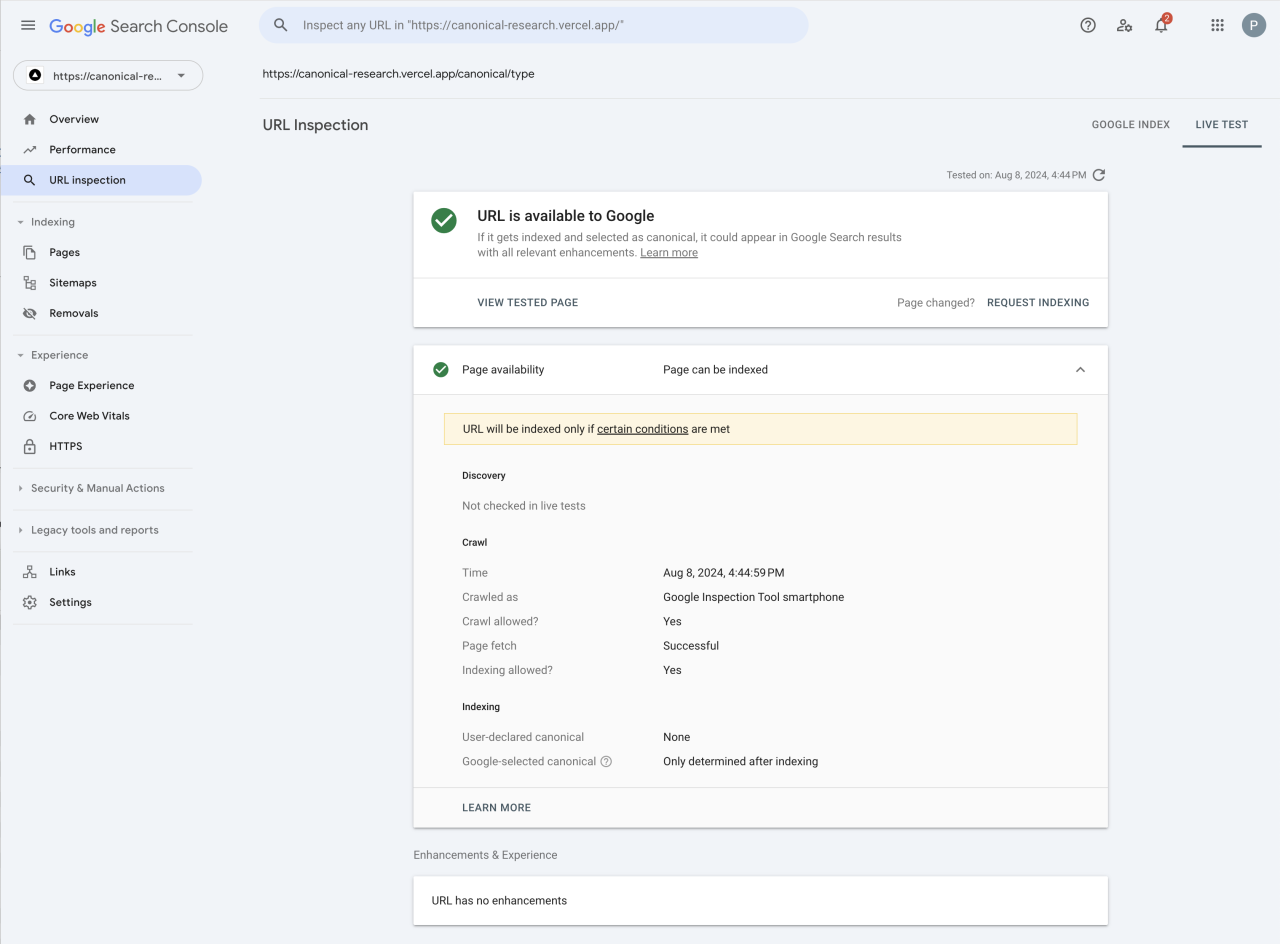
Canonicalization, while fundamental for , becomes more intricate when dealing with complex website structures. This section delves into advanced strategies for handling canonicalization across multiple domains, subdomains, and diverse website configurations. Understanding these nuanced techniques ensures optimal search engine indexing and avoids duplicate content penalties.
Handling Canonicalization Across Multiple Domains or Subdomains, What is canonicalization how to use canonical tags
Different domains or subdomains often host similar content. Proper canonicalization directs search engines to the preferred version, preventing issues with duplicate content. A crucial aspect is choosing the correct canonical URL. If a subdomain (e.g., blog.example.com) mirrors content on the main domain (example.com), the main domain should be the canonical source. Similarly, if content exists on multiple domains, the primary domain, usually the one with the most authority, should be designated as the canonical.
Usage of Canonical Tags with Parameters or Query Strings
Query strings, like “?page=2” or “?sort=price,” often append to URLs, creating multiple variations of the same page. Canonical tags effectively address this. For example, if you have product listings with various sorting options, the canonical tag should point to the base URL without the query string parameters. This prevents search engines from indexing each variation as a unique page.
Understanding canonicalization and using canonical tags correctly is crucial for SEO. It helps search engines understand which version of a page is the primary one, preventing duplicate content issues. This directly impacts your site’s overall performance, and using the right tools like best pagespeed tools is essential to optimize for speed. Ultimately, proper canonicalization ensures search engines are pointing to the correct, high-performing version of your page.
Using the canonical tag to the base URL without parameters helps avoid duplicate content issues stemming from different query string variations.
Impact of Canonicalization on Mobile-Friendly Versions of Websites
Mobile-friendly versions of websites are crucial for user experience. Canonicalization plays a vital role in ensuring that search engines correctly index the mobile version. The mobile version, being the user-friendly version, should be designated as the canonical for better user experience and indexing. This practice also prevents confusion for search engines and ensures the mobile site receives the proper search ranking.
Understanding canonicalization and how to use canonical tags is crucial for SEO. Essentially, it’s about telling search engines which version of a page is the primary one. This is especially important when you have duplicate content, like different URLs for the same article. A good way to manage this is to use a content brief; a content brief helps you plan and organize your content effectively, leading to a streamlined process when implementing canonical tags.
For a deeper dive into this topic, check out our guide on content brief strategies. Ultimately, using canonical tags correctly helps search engines understand your website’s structure and improves your ranking.
Impact of Canonicalization on Internationalization and Localization
Internationalization and localization are essential for global reach. Different language versions of the same content require careful canonicalization. The canonical URL should point to the preferred version, ensuring search engines index the appropriate localized content. The choice of the canonical URL depends on factors like target audience and the desired focus for specific regions. For example, a German version of a website could be the canonical for the German market.
Table Illustrating Scenarios
| Scenario | Query Strings | Mobile Version | Internationalization |
|---|---|---|---|
| Multiple Domains (example.com, blog.example.com) | Use canonical tag to main domain (example.com) | Use canonical tag to the mobile version | Use canonical tag to the preferred language version |
| Subdomain (blog.example.com) | Use canonical tag to the base URL without query strings | Use canonical tag to the mobile-friendly version | Use canonical tag to the correct localized version |
| Different Language Versions | Use canonical tag to the URL without query strings | Use canonical tag to the mobile version | Use canonical tag to the preferred language version |
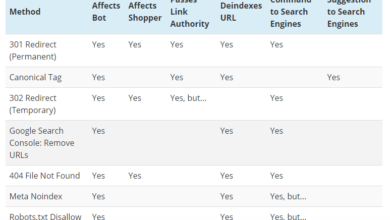
Troubleshooting Canonicalization Issues
Canonicalization, while a crucial tactic, can sometimes trip up even seasoned webmasters. Incorrect implementation or unforeseen circumstances can lead to duplicate content penalties from search engines, hindering your site’s visibility. This section delves into common pitfalls, explains why canonical tags might not be functioning as intended, and provides practical solutions to resolve these issues.Understanding the underlying reasons behind canonicalization problems is key to effective troubleshooting.
Search engines analyze numerous factors beyond just the canonical tag itself. Website architecture, server configurations, and even user behavior can all impact how canonical tags are interpreted. This comprehensive guide offers practical steps to identify and fix problems, maximizing your site’s search engine optimization.
Common Mistakes in Implementing Canonical Tags
Incorrect implementation is a frequent source of canonicalization problems. Ensure the canonical tag is placed correctly within the `
` section of the HTML document. It’s crucial that the tag points to the correct, preferred version of the page. Misplaced or incorrectly formatted tags can lead to confusion for search engines. Incorrect attributes or incorrect values in the tag attribute also can cause issues.Reasons Why Canonical Tags Might Not Be Working
Several factors can contribute to canonical tags not working as expected. Network issues, server errors, or problems with the site’s configuration can prevent the tags from reaching search engine crawlers. A canonical URL that is incorrect or unavailable also can be a problem. The source of the issue might be a problem on the server itself. Search engines might not have crawled the canonical URL, so the link isn’t in their index.
Examples of Common Errors and Their Solutions
One common error is using the wrong URL in the canonical tag. If the tag points to a page that doesn’t exist, or to a page on a different site, search engines will struggle to understand the intended relationship. This is easily solved by carefully double-checking the URL in the canonical tag to match the correct, preferred version of the page.Another mistake involves the tag not being included in the HTML response.
For example, if the tag is present on the source code but missing from the rendered page, search engines might not be able to recognize it. This usually stems from a server-side error. To resolve this, verify the canonical tag appears in the page’s source code, and the server is delivering the tag in the response.
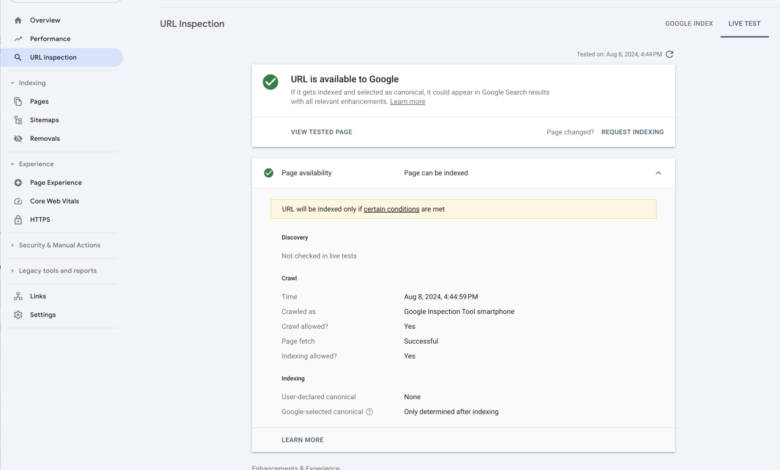
Diagnosing and Resolving Canonicalization Issues
Diagnosing canonicalization issues requires a methodical approach. First, examine the website’s source code to confirm the canonical tag’s presence and correctness. Use your browser’s developer tools to inspect the page’s HTML response and ensure the canonical tag is present in the headers. Check the server logs for errors related to the canonical URL, and confirm that the canonical URL actually exists.
Utilize web analytics tools and search console reports to identify any unusual patterns or issues with indexing. These tools can help pinpoint whether search engines are following the canonical tags correctly.
Typical Canonicalization Issues
| Issue | Cause | Diagnostic Method | Solution |
|---|---|---|---|
| Canonical tag not found | The canonical tag is missing from the HTML source code. | Inspect the page’s source code using developer tools. | Add the canonical tag to the `` section of the HTML. |
| Incorrect canonical URL | The canonical URL in the tag is incorrect or points to a non-existent page. | Verify the canonical URL in the tag matches the intended page. | Correct the URL in the canonical tag. |
| Canonical tag not reflected in the HTML response | Server-side issue preventing the tag from being included in the final HTML page. | Inspect the server logs for errors. Verify the canonical tag is present in the response headers. | Resolve server-side issues and ensure the canonical tag is included in the HTTP response. |
| Search engine not crawling the canonical URL | Search engines haven’t indexed the canonical URL yet, or the canonical URL has issues with crawlability. | Check the Google Search Console for crawl errors and indexing status. | Improve website structure and technical to ensure proper crawling and indexing. |
Tools and Resources
Navigating the complexities of canonicalization can be simplified with the right tools. This section details essential tools and resources for checking, verifying, managing, and monitoring your canonicalization strategies, ensuring optimal performance. Effective implementation hinges on accurate identification of issues and consistent monitoring of results.Tools for verification and implementation are crucial for accurate and efficient canonicalization. By leveraging these tools, you can streamline your processes and ensure your website is properly indexed by search engines.
Effective monitoring of your strategies is essential for making necessary adjustments to optimize results.
Tools for Checking Canonicalization Implementations
Various tools aid in identifying and rectifying canonicalization issues. These tools provide detailed reports on your site’s structure, allowing you to pinpoint areas needing attention. These insights are invaluable for ensuring that your canonicalization efforts align with search engine best practices.
- Google Search Console: A free tool offered by Google, Search Console provides insights into how Googlebot sees your website. It can detect issues with canonicalization, such as incorrect implementation or missing tags. It also helps identify crawl errors that may impact the effectiveness of canonicalization.
- Screaming Frog Spider: This crawler tool is widely used for website auditing. It can analyze your website’s structure and identify canonical tags, providing a comprehensive report of potential canonicalization problems. This includes checking for duplicate content and improperly set canonical tags, which can lead to reduced search engine visibility.
- Moz Tools: Moz offers a suite of tools, including a site crawler that can identify canonicalization issues. It provides reports on crawl errors, duplicate content, and other factors that affect canonicalization effectiveness. These tools help you to understand how search engines are indexing your website and identify potential issues.
Canonicalization Management Platforms
Several platforms streamline canonicalization management, making the process more efficient and user-friendly. These platforms often offer features to manage multiple websites, identify and resolve duplicate content issues, and monitor the effectiveness of your strategies.
- Yoast : A popular WordPress plugin, Yoast offers features to manage canonical tags and identify potential duplicate content issues. It provides tools for setting canonical URLs and monitoring the impact on search rankings. The plugin offers an easy-to-use interface for handling canonicalization tasks, crucial for maintaining website health.
- Rank Math : Another WordPress plugin, Rank Math provides tools to manage canonical tags and implement best practices for duplicate content issues. It offers features for handling canonical URLs, ensuring proper implementation of canonicalization strategies for better results. This helps to avoid negative consequences from duplicate content.
Monitoring Canonicalization Effectiveness
Monitoring the impact of canonicalization is vital for ensuring its effectiveness. Tools provide insights into changes in rankings, traffic, and crawl rates, allowing you to assess the impact of your strategies. Tracking these metrics provides crucial data for adjusting strategies as needed.
- Google Analytics: Track changes in organic traffic, rankings, and bounce rates. Changes in these metrics can indicate the effectiveness of your canonicalization efforts. Analyzing these metrics can pinpoint areas where your canonicalization strategy is successful and where adjustments might be needed.
- Search Console (again): Review changes in crawl rates and index coverage. Any discrepancies can point to issues that may affect canonicalization success. Regular monitoring allows for proactive identification of problems and their timely resolution.
Resources for Learning More About Canonicalization Best Practices
Staying informed about best practices is essential for optimal results. These resources provide detailed information and examples to enhance your understanding of canonicalization strategies. This helps in implementing these practices effectively.
- Moz Blog: Offers in-depth articles and guides on topics, including canonicalization. This helps to understand the best practices and strategies in more detail. The detailed information and case studies provide valuable insights for implementing these practices.
- Search Engine Journal: A leading source for news and updates. It provides comprehensive coverage of canonicalization best practices, including strategies for implementation and troubleshooting. The website covers the latest developments and insights in the field.
- Google Webmaster Central Blog: Official blog from Google. Provides insights on best practices and guidelines, including those related to canonicalization. This resource helps in understanding the latest best practices from the source itself, ensuring your implementation is in line with Google’s recommendations.
Closing Summary
In conclusion, mastering canonicalization is key to achieving optimal performance. By understanding how canonical tags work, you can avoid duplicate content issues, ensure consistent indexing, and ultimately improve your website’s visibility in search engine results. Remember, proper canonicalization isn’t just about avoiding problems; it’s about proactively shaping your site’s online presence. So, put these techniques to use and see your website soar!