The Ultimate List of 301 Redirect Examples for SEO
The ultimate list of 301 redirect examples for seo – The ultimate list of 301 redirect examples for is your comprehensive guide to mastering these crucial search engine optimization techniques. We’ll delve into everything from the basics of 301 redirects and their purpose in to practical examples, technical considerations, and troubleshooting. Learn how to effectively handle website restructuring, broken links, and outdated pages, ensuring your remains strong and your website visitors smoothly navigate your content.
This guide provides a practical, step-by-step approach to implementing 301 redirects across various scenarios. From simple redirects to complex redirect chains, you’ll gain actionable insights and concrete examples to boost your strategy. We’ll cover the ‘why,’ ‘how,’ and ‘what’ of 301 redirects in detail, equipping you with the knowledge to maintain a seamless and effective website experience.
Introduction to 301 Redirects for
redirects are crucial tools in search engine optimization (). They essentially tell search engines and users that a specific webpage has permanently moved to a new location. This seamless transition is vital for maintaining a positive user experience and preserving valuable search engine rankings. Properly implemented, 301 redirects help prevent broken links and ensure that users and search engines are directed to the correct, updated content.Understanding how 301 redirects work from both a user and search engine perspective is key to successful implementation.
Users are automatically taken to the new location without any noticeable disruption, while search engines are informed about the change in the page’s URL. This transfer of authority and relevance is crucial for maintaining the website’s overall health.
Importance of Proper Implementation
Proper implementation of 301 redirects is essential for maintaining a positive user experience and preserving valuable search engine rankings. Incorrect implementation can lead to broken links, lost traffic, and negatively impact search engine rankings. The proper redirection helps search engines understand the site’s structure and how to appropriately index its content.
Scenarios Where 301 Redirects Are Necessary or Beneficial
redirects are necessary in numerous situations, from simple website restructuring to content updates. A common scenario is when a website undergoes a significant redesign, requiring a change in the URL structure. Another crucial use is when a website changes domains or when content is moved to a new location.
- Website Redesign: When a website is redesigned, old URLs might no longer be valid or point to the new content. 301 redirects ensure that search engines and users are directed to the updated content, preventing lost traffic and maintaining rankings.
- Content Updates: If content is moved or updated, a 301 redirect helps ensure that search engines and users find the updated information without being confused by outdated links.
- Domain Changes: When a website changes domains, 301 redirects are vital to maintain rankings and traffic. They inform search engines about the new domain and direct users and search engines to the appropriate content.
- Mergers and Acquisitions: If a company merges with another or is acquired, 301 redirects can be used to consolidate the website content into the new structure and seamlessly integrate the sites into one.
- Eliminating Duplicate Content: If a website has duplicate content, 301 redirects can be used to consolidate the content to a single URL, helping to improve and avoid search engine penalties.
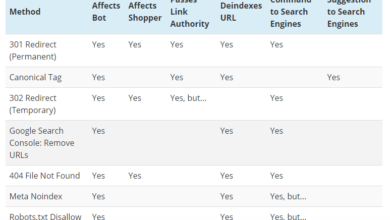
Status Codes and Their Meanings
Understanding the different status codes associated with redirects is crucial for proper implementation. The status code indicates the type of redirect and the level of permanence.
| Status Code | Meaning | Implications |
|---|---|---|
| 301 Moved Permanently | Indicates a permanent change in the URL. | Search engines understand this as a permanent move, transferring authority and ranking from the old to the new URL. |
| 302 Found (Temporary Redirect) | Indicates a temporary change in the URL. | Search engines might not fully recognize the redirect as a permanent move, potentially leading to issues with indexing and ranking. |
| 307 Temporary Redirect | Indicates a temporary change in the URL, similar to 302 but often better handled in certain situations. | Similar to 302, might not transfer ranking as effectively. |
Common Use Cases for 301 Redirects
redirects are essential tools in a website owner’s toolkit. They allow you to seamlessly transfer the authority and value of one page to another, preventing loss of search engine ranking and user traffic. Proper implementation of 301 redirects is crucial for maintaining a healthy and functioning website. These redirects are particularly vital during website restructuring, when dealing with broken links, and when moving content to new URLs.Understanding the various scenarios where 301 redirects are necessary is paramount for a successful strategy.
Using these redirects effectively can safeguard the website’s search engine ranking and maintain a positive user experience.
Website Restructuring
Website restructuring is a common practice to enhance user experience, improve site architecture, and adapt to evolving business needs. A well-planned restructuring often involves changing the website’s internal structure, including the organization of pages and navigation. This transition can significantly impact search engine rankings if not managed properly. 301 redirects play a crucial role in mitigating these potential negative impacts.
By redirecting old URLs to their corresponding new URLs, website owners ensure that search engines and users can find the desired content. This preserves the value associated with the old URLs.
Broken Links and Outdated Pages
Broken links and outdated pages can harm user experience and negatively affect search engine rankings. These issues lead to frustrating user experiences and lost potential visitors. 301 redirects provide a solution to address these problems. By redirecting broken links to their functional counterparts, website owners maintain the value of the original content and avoid lost traffic.
Redirecting outdated pages to updated versions ensures users find relevant information.
Redirecting Specific URLs or File Extensions
When dealing with specific URLs or file extensions, proper redirection is critical for maintaining value. For instance, redirects can handle various URL formats, ensuring smooth transitions during website upgrades or when adjusting the website’s structure. This seamless transition guarantees that search engines and users can access the correct content, avoiding any potential issues.
Best Practices for Redirection
Redirecting pages with specific URLs or file extensions requires careful planning and implementation. The choice of the correct redirect method is crucial, ensuring that the value is maintained and transferred effectively. Using the appropriate 301 redirect method preserves the value of the old page and ensures a smooth transition for search engines and users.
Illustrative Table of Redirection Scenarios
| Scenario | Old URL | New URL | Reason |
|---|---|---|---|
| Moving a product page | /products/old-product.html | /products/new-product.html | Product was renamed or moved to a new category. |
| Fixing a broken link | /broken-page.html | /new-page.html | The original page no longer exists. |
| Updating a page | /old-blog-post.html | /new-blog-post.html | Content was updated and the old version is no longer relevant. |
| Changing domain name | http://oldwebsite.com/page.html | http://newwebsite.com/page.html | Domain name change. |
Examples of 301 Redirect Implementations
Putting a 301 redirect in place is a crucial part of . It’s often necessary when a website undergoes a change, like a redesign, a name change, or when content is moved to a new location. Properly implemented redirects maintain value and user experience by seamlessly guiding users and search engines to the new location. Without a proper redirect, users might land on a 404 error page, and search engines could lose track of the page’s content, impacting rankings.This section delves into practical examples of 301 redirects, covering various scenarios and emphasizing best practices for preserving the value of the original content and metadata.
Specific Redirect Examples
These examples demonstrate how to redirect specific URLs to their new counterparts, preserving important information.
-
Example 1: Redirecting a product page. Original URL:
https://www.example.com/products/old-product-name. New URL:https://www.example.com/new-product-line/new-product-name. This redirect ensures that search engines and users are directed to the updated product page. -
Example 2: Redirecting a category page. Original URL:
https://www.example.com/category/electronics. New URL:https://www.example.com/products/electronics. This redirect ensures that search engines and users are directed to the updated category page, maintaining the value of the previous category page. -
Example 3: Redirecting a blog post. Original URL:
https://www.example.com/blog/2023/old-blog-post. New URL:https://www.example.com/blog/new-blog-post-category/new-blog-post. Redirecting blog posts maintains their value and directs users and search engines to the new, updated post. -
Example 4: Redirecting a page with a specific query string. Original URL:
https://www.example.com/search?q=old-. New URL:https://www.example.com/search?q=new-. This example shows how to redirect a page with a query string, ensuring users with the old search term are sent to the new one. -
Example 5: Redirecting a page with multiple query parameters. Original URL:
https://www.example.com/product?category=electronics&color=red. New URL:https://www.example.com/new-product-page?category=electronics&color=crimson. Redirecting pages with multiple parameters ensures users are sent to the updated product page with the corresponding parameters.
Table of Redirect Examples
This table demonstrates how to redirect various types of pages to new locations.
| Original URL | New URL | Page Type |
|---|---|---|
https://www.example.com/old-page.html |
https://www.example.com/new-page.html |
General Page |
https://www.example.com/products/old-shirt.html |
https://www.example.com/new-products/new-shirt.html |
Product Page |
https://www.example.com/category/electronics.html |
https://www.example.com/shop/electronics.html |
Category Page |
https://www.example.com/blog/2022/old-post.html |
https://www.example.com/blog/new-category/new-post.html |
Blog Post |
Preserving Content and Metadata
Maintaining original page content and metadata is crucial for . Search engines use this information to understand the page’s context. A 301 redirect should preserve the original page’s content and metadata, as much as possible, to ensure a seamless transition for users and search engines. This includes elements like title tags, meta descriptions, and canonical tags.
Redirecting Pages with Query Strings
Redirecting pages with query strings requires careful consideration. The redirect should maintain the original query string parameters as closely as possible.
| Original URL | New URL | Method 1: Preserve Parameters | Method 2: Redirect to a new page with query string parameters |
|---|---|---|---|
https://www.example.com/search?q=old- |
https://www.example.com/search?q=new- |
Preserve parameters | Redirect to a new search page |
https://www.example.com/product?id=123&color=red |
https://www.example.com/new-product?id=123&color=red |
Preserve parameters | Redirect to a new product page |
Technical Considerations for 301 Redirects
Properly implementing 301 redirects is crucial for maintaining value and ensuring a smooth user experience. A poorly configured redirect can lead to lost traffic, broken links, and a negative impact on search engine rankings. Careful consideration of the technical aspects is paramount.Implementing 301 redirects involves more than just specifying the destination URL. Understanding the underlying mechanisms and utilizing the appropriate tools and methods is essential for a successful transition and to prevent unexpected consequences.
This section dives into the technical aspects, from choosing the right tools to configuring web server configurations.
Choosing the Right Redirect Tool or Method
Selecting the right method for handling 301 redirects depends on several factors, including the size and complexity of your website, your technical expertise, and the desired level of control. Using a dedicated redirect management tool, if your website has a high volume of redirects, can streamline the process and offer more advanced features. A dedicated tool often provides reporting, debugging, and bulk management capabilities.
Manual implementation through server configurations is suitable for smaller websites or situations requiring granular control.
Implementing 301 Redirects Through Web Server Configuration
Configuring 301 redirects through your web server (Apache or Nginx) allows for precise control over the redirect process. This method is often preferred for its flexibility and control over specific URL patterns.
Apache Configuration
- Understanding the Apache .htaccess file: The .htaccess file is a configuration file that allows you to customize the behavior of your Apache web server. It’s often used for tasks like URL rewriting and redirects.
- Using the Redirect directive: The `Redirect` directive is a simple way to create a 301 redirect. However, it’s less flexible than the `RewriteRule` directive.
Example:
Redirect 301 /old-page.html /new-page.html - Using the RewriteRule directive: The `RewriteRule` directive provides more control and allows for complex URL patterns and conditions. It’s typically the preferred method for more intricate redirects.
Example:
RewriteRule ^old-page(/.*)?$ /new-page/$1 [R=301,L] - Testing the redirect: After configuring the redirect, it’s crucial to thoroughly test it to ensure it functions as intended. Use tools like a browser’s developer tools or a dedicated redirect testing tool.
Nginx Configuration
- Understanding Nginx server blocks: Nginx uses server blocks to define configuration settings for different parts of your website. Redirects are often configured within these blocks.
- Using the `rewrite` directive: The `rewrite` directive is used to perform URL rewriting and redirects.
Example:
rewrite ^/old-page(/.*)?$ /new-page/$1 permanent;This ultimate list of 301 redirect examples for SEO is crucial for maintaining a healthy website. Understanding why SEO is important is key to grasping the significance of redirects. Properly implemented redirects are vital for maintaining a seamless user experience and ensuring your site is easily discoverable by search engines. Learning more about the ‘why’ behind SEO can be found at why is seo important.
Ultimately, a well-structured 301 redirect strategy can significantly improve your website’s SEO performance.
- Ensuring proper syntax: Careful attention to the syntax and formatting of the configuration files is essential. Errors can prevent redirects from working as expected.
- Testing the redirect: Similar to Apache, testing is vital to confirm the redirect’s functionality and identify any potential issues.
Comparing Different Methods for Creating and Managing 301 Redirects
Various tools and methods exist for implementing 301 redirects. The choice depends on factors like website size, desired control, and technical expertise.
| Method | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|
| Web Server Configuration (Apache/Nginx) | Granular control, flexibility, often faster performance | Requires technical expertise, potential for errors if not properly configured |
| Redirect Management Tools | Ease of use, bulk management, reporting capabilities | Might have limitations on complex redirects, potentially higher cost |
Troubleshooting 301 Redirect Issues

redirects are crucial for , but issues can arise during implementation. Understanding common problems and their solutions is vital for maintaining website health and search engine rankings. This section delves into troubleshooting techniques, helping you identify and resolve problems effectively.Identifying and fixing 301 redirect problems is essential for maintaining a healthy website. Correctly implemented redirects ensure a smooth transition for users and search engines, avoiding lost traffic and damaged .
Common Errors in Implementing 301 Redirects
Incorrectly configured 301 redirects can lead to significant issues. Errors range from simple typos to more complex configurations, causing redirects to fail or point to the wrong destination. Understanding these common errors is the first step to effective troubleshooting.
Navigating 301 redirect examples for SEO can be tricky, but having a comprehensive list is key. While popups can sometimes boost conversions, it’s important to consider if they’re the right fit for your site. For a deeper dive into the pros and cons of website popups, check out this insightful article: should i use website popups.
Ultimately, mastering 301 redirects is crucial for a smooth user experience and search engine optimization, so having the right examples readily available is invaluable.
Five Common Redirect Issues and Solutions
- Incorrect Target URL: A common mistake is entering the wrong URL as the destination for the redirect. Double-check the target URL for accuracy, ensuring correct spelling, structure, and path. Using a website debugger or inspecting the source code can help pinpoint errors.
- Missing or Incorrect HTTP Status Code: A 301 redirect must include the correct HTTP status code (301). Incorrect or missing status codes can hinder the redirect process. Tools like web developer tools in your browser can help check the response code.
- Broken Redirect Chain: Sometimes, redirects are configured in a chain. If one redirect in the chain is broken, the final destination might not be reached. Inspecting the redirect chain through the browser’s developer tools or a website analysis tool can identify the source of the problem.
- Server Configuration Issues: Problems with the web server can prevent the redirect from working correctly. Verify that the server configuration is properly set up to handle the redirect request. Server logs are valuable in finding the source of server-side issues.
- Caching Issues: Browser or server caching can sometimes prevent the redirect from being applied immediately. Clearing browser cache or using the appropriate cache-control headers can solve this problem. Testing the redirect in different browsers and devices is also crucial.
Identifying Broken Redirects or Issues in the Redirect Chain
Diagnosing broken redirects or redirect chain issues requires careful inspection. Tools like web developer tools in browsers, dedicated redirect checkers, and website analysis tools are essential. Use the browser’s developer tools to examine the HTTP response headers for the redirect.
Verifying 301 Redirects Using Tools and Methods, The ultimate list of 301 redirect examples for seo
Several tools and methods can be used to verify the functionality of 301 redirects. Using a browser’s developer tools or dedicated redirect checking tools is often sufficient. Website analysis tools can also provide comprehensive information on redirects and their status. Regular checks with these tools are crucial for identifying and fixing issues promptly.
Troubleshooting Steps and Potential Solutions
| Issue | Troubleshooting Steps | Potential Solutions |
|---|---|---|
| Incorrect Target URL | Verify the target URL in the redirect rule. Check for typos and ensure the path is correct. | Correct the target URL in the redirect configuration. |
| Missing or Incorrect HTTP Status Code | Inspect the HTTP response headers using browser developer tools. | Ensure the correct HTTP status code (301) is present in the redirect response. |
| Broken Redirect Chain | Trace the redirect chain using browser developer tools or a redirect checker. | Identify and fix the broken link in the redirect chain. |
| Server Configuration Issues | Review the server logs for errors related to the redirect. Check server configuration settings. | Resolve any server-side errors preventing the redirect from working. |
| Caching Issues | Clear browser cache and cookies. Check server cache settings. | Configure cache control headers appropriately to ensure redirects are applied immediately. |
Best Practices for Implementing 301 Redirects: The Ultimate List Of 301 Redirect Examples For Seo
Choosing the right 301 redirect method is crucial for maintaining value and ensuring a seamless user experience. A poorly implemented redirect can lead to lost traffic and diminished search engine rankings. Understanding best practices is key to achieving optimal results.Effective 301 redirect implementation hinges on meticulous planning and execution. A well-structured approach ensures that users and search engines are effectively guided to the updated destination.
This involves careful consideration of various factors, from the specific redirect method to comprehensive testing and ongoing monitoring.
Selecting the Most Effective Redirect Method
Different methods exist for implementing 301 redirects, each with its own advantages and disadvantages. The optimal method depends on the specific circumstances. Consider factors like the server environment, existing infrastructure, and the scale of the redirection project. Using a dedicated redirect management tool, if available, can automate and streamline the process, reducing the chance of errors.
Maintaining a Clear and Concise Redirect Structure
A well-organized redirect structure is essential for efficient management and future modifications. A clear hierarchy allows for easy identification and maintenance of redirects. Employing a structured approach, such as a spreadsheet or a dedicated redirect management tool, can help maintain clarity and track changes.
So, you’re tackling the ultimate list of 301 redirect examples for SEO? Understanding how these redirects impact your site’s structure is crucial. This is all directly related to effective email automation marketing, which, as explained in more detail here email automation marketing explained , can be a powerful tool for boosting engagement and conversions. Ultimately, mastering 301 redirects is vital for a seamless user experience and strong SEO performance.
Best Practices for 301 Redirects
A well-defined set of best practices can greatly improve the effectiveness and maintainability of 301 redirects. These best practices ensure smooth transitions, preserve value, and enhance user experience.
- Thorough Planning: Before implementing any redirects, create a comprehensive plan outlining the old URLs, new URLs, and the redirect method. This ensures a structured approach to the process and minimizes errors.
- Prioritize User Experience: Maintain a smooth user experience during the redirect process. Avoid confusing redirects that send users to unexpected destinations.
- Test Thoroughly: Thoroughly test redirects before making them live to catch any potential issues or errors. Simulate various scenarios to ensure proper functioning.
- Choose Appropriate Method: Select the most appropriate redirect method based on the specific circumstances and server environment. Consider server limitations and potential impact on performance.
- Implement with Precision: Implement redirects with precision, paying close attention to details like the target URL, status codes, and redirect types. Carefully review and verify all implemented redirects.
Testing Redirects Before Implementation
Testing redirects before going live is critical to identifying and resolving any potential issues. Testing ensures that the redirect works correctly across different browsers and devices, and helps prevent unexpected errors or problems for users. Simulate user scenarios and use testing tools to verify the redirect chain.
Monitoring Redirect Effectiveness
Ongoing monitoring is essential for ensuring that redirects continue to function correctly. Regularly monitor the effectiveness of redirects to detect any issues or changes that might impact performance. Tools and techniques are available to track redirect performance and user experience.
Illustrative Examples of Redirect Scenarios
Understanding how 301 redirects work is crucial for maintaining value when updating your website. This section provides practical examples of common redirect scenarios, demonstrating how to effectively manage URL changes while preserving search engine rankings. These examples will guide you through the process of migrating content, handling product updates, and addressing removals, ensuring a seamless user experience and optimal performance.
Domain Name Change
A common website update involves changing the domain name. Redirecting users from the old domain to the new one is essential to maintain existing search engine rankings and user traffic. The old domain is effectively a historical record of the website’s presence, and a 301 redirect preserves this history, passing the authority and ranking to the new domain.
A 301 redirect permanently moves users and search engine crawlers from one URL to another. It’s the best choice when a page has been permanently moved.
For instance, if your old website was located at `oldwebsite.com`, and you’re moving to `newwebsite.com`, you would implement a 301 redirect from `oldwebsite.com` to `newwebsite.com`. This ensures that users who arrive at `oldwebsite.com` are automatically taken to the corresponding page on `newwebsite.com`.
Product Page Relocation
Sometimes, a product page needs to be moved to a new URL. This could be due to a change in the website’s structure, an update to the product catalog, or a reorganization of the product categories. A 301 redirect is crucial in this scenario to preserve the value of the old URL.
By implementing a 301 redirect from the old product page URL to the new one, you ensure that search engines and users are directed to the correct location.
Suppose you have a product page at `oldproductpage.com/product-a` and you’ve moved it to `newproductpage.com/new-product-a`. A 301 redirect from `oldproductpage.com/product-a` to `newproductpage.com/new-product-a` is essential to preserve the value of the original page and maintain a seamless user experience.
Page Removal
When a page is removed from a website, it’s vital to redirect users and search engines to an appropriate alternative page. A 301 redirect is the preferred method for this scenario.
Redirecting to a relevant alternative ensures that users are not met with a “404 Not Found” error and that search engines understand the content has been permanently removed.
If a blog post, `oldblogpost.com/article-x`, is removed, a 301 redirect to a similar blog post, or potentially a homepage, is appropriate. This prevents broken links and maintains a positive user experience.
Redirect Chain
A redirect chain involves multiple redirects from one URL to another, and then to another. While technically possible, redirect chains are often problematic.
Excessive redirects can negatively impact and user experience.
For example, a redirect chain from `oldpage.com` to `intermediatepage.com` and then to `newpage.com` can cause slow loading times and potentially confuse search engines. It’s best to avoid such chains if possible and instead use a direct 301 redirect from the source page to the final destination.
Last Recap

In conclusion, mastering 301 redirects is vital for any website aiming to maintain a strong presence. This guide has provided a detailed roadmap for implementing and troubleshooting 301 redirects across diverse scenarios. By understanding the nuances and practical examples presented, you’ll be well-equipped to optimize your website’s structure, maintain user experience, and enhance your search engine ranking.