Setting Up Destination URL Goals in Google Analytics
Setting up a destination URL goal in Google Analytics is crucial for understanding user journeys and conversions on your website. This guide will walk you through the process, from defining your target URLs to implementing and troubleshooting your goals, ensuring you get the most accurate and valuable insights from your data.
We’ll explore various URL matching techniques, like exact matches and regular expressions, and delve into the different goal types suitable for destination URL tracking. You’ll learn the steps involved in creating and configuring destination URL goals in Google Analytics, including the required fields and their purposes. The guide will also cover troubleshooting common issues, advanced tracking methods, and the importance of accurate URL tracking for data analysis.
Defining Destination URLs
Destination URLs are crucial for setting up effective goal tracking in Google Analytics. They define the specific pages or actions that signify a user completing a desired goal, such as making a purchase, filling out a form, or downloading a file. Properly identifying and configuring destination URLs ensures accurate measurement of your marketing campaigns’ effectiveness.Correctly identifying destination URLs is paramount for accurate goal tracking.
Without precise targeting, your data will be skewed, and you won’t have a clear understanding of which marketing efforts are driving conversions. A well-defined destination URL ensures you’re only counting relevant actions, preventing inaccurate reporting.
Destination URL Types
Understanding the various types of destination URLs allows you to tailor your tracking to specific user interactions. Different types of goals require different destination URLs, so matching the correct one is vital for accurate data collection. This includes specific pages, events triggered by user actions, and form submissions.
- Specific pages, like thank-you pages or product detail pages, represent straightforward destination URLs.
- Events, triggered by user interactions like clicking a button or submitting a form, can also be destination URLs.
- Forms, whether for contact inquiries or lead generation, provide another type of destination URL to track form completions.
Regular Expressions for Multiple Destination URLs
Regular expressions (regex) are powerful tools for matching multiple destination URLs that share a common pattern. This is particularly useful for tracking variations or slight differences in URLs that represent the same goal completion.
Regex allows you to define a pattern that matches multiple URLs.
For example, if you want to track multiple “thank-you” pages, each with a unique order number appended, you could use a regex.
- Example: `/thank-you-[0-9]+.html` This regex matches any URL starting with `/thank-you/`, followed by one or more digits, and ending with `.html`.
- Another example: `/thank-you-(.+).html` This regex will capture a group of characters after the `-` and before the `.html`.
This enables a single goal to track multiple variations of the same conversion event.
URL Matching Techniques Comparison
The following table compares different URL matching techniques for destination URLs in Google Analytics:
| Technique | Description | Example | Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|
| Exact Match | Matches the exact URL. | /thank-you.html | Simple tracking, where only one specific URL represents a goal. |
| Regular Expression | Matches URLs based on patterns. | /thank-you-(.+).html | Tracking multiple variations of a goal, like order numbers or custom parameters. |
Setting Up Goals in Google Analytics
Getting insights from your website traffic is crucial for optimizing your online presence. Google Analytics provides powerful tools to track specific actions, like purchases or form submissions. Setting up goals is key to understanding which parts of your website are most effective. This guide will walk you through the process of setting up a destination URL goal in Google Analytics, enabling you to monitor key user interactions.Understanding how to properly set up goals in Google Analytics empowers you to gain actionable insights about your website’s performance.
Setting up a destination URL goal in Google Analytics is crucial for tracking website success. It’s a straightforward process, but you need to be careful not to fall prey to unethical SEO tactics like those detailed in the 29 black hat SEO list. Ultimately, focusing on legitimate strategies and proper goal setup will yield more reliable and meaningful results for your website analysis.
A well-defined goal, like tracking website purchases, can reveal the effectiveness of your marketing campaigns and inform crucial business decisions. This comprehensive guide will help you set up a destination URL goal to monitor user progress towards specific objectives.
Destination URL Goal Types
Destination goals are designed to track when a user reaches a specific page on your website, signifying a desired outcome. This is highly useful for tracking conversions like completed purchases, form submissions, or downloads. The effectiveness of your website’s content and marketing strategies can be accurately measured by these goals.
Steps to Set Up a Destination URL Goal
This step-by-step process guides you through creating a destination URL goal in Google Analytics:
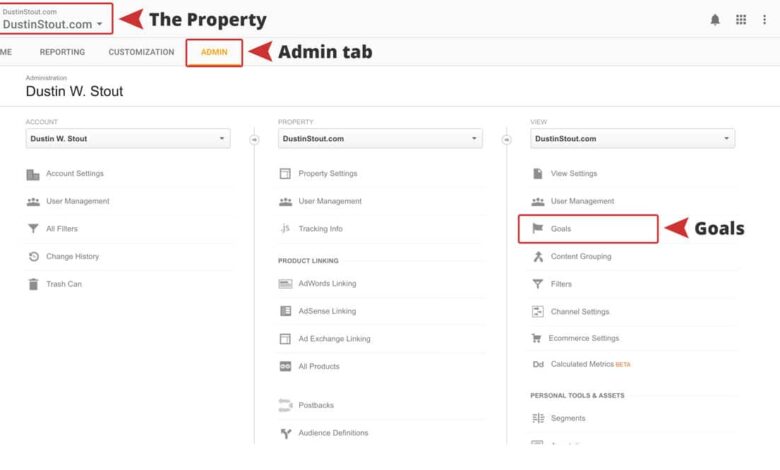
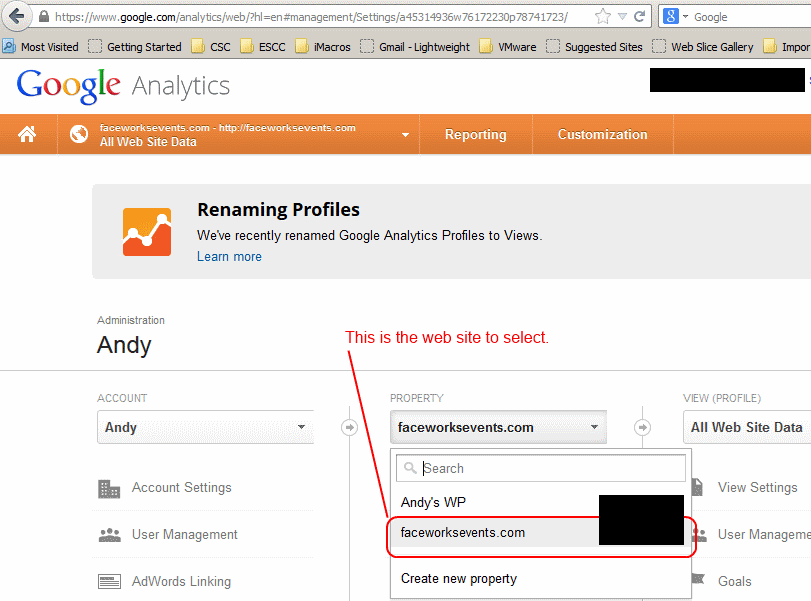
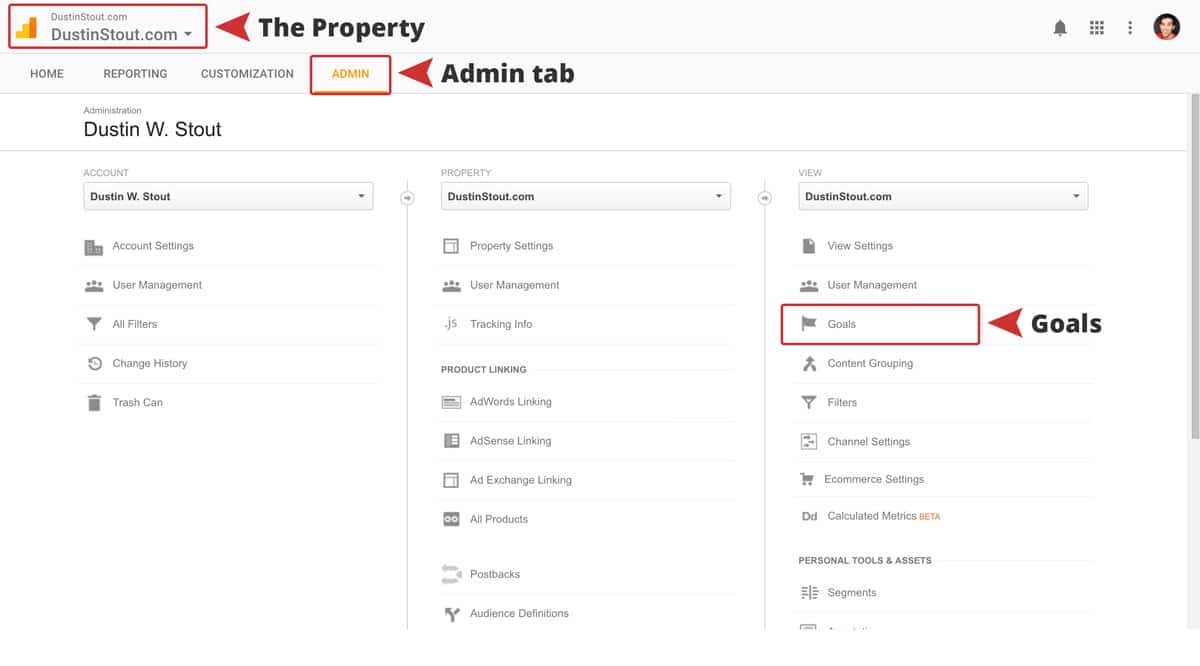
- Log in to your Google Analytics account.
- Navigate to the “Admin” section.
- Select the property where you want to set up the goal.
- In the “Property” column, click “Goals.”
- Click “Create Goal.”
- Choose “Destination” as the goal type.
- Give your goal a descriptive name, such as “Complete Purchase.”
- Enter a detailed description, like “Tracking purchase completion.”
- Enter the destination URL that represents the goal completion. For example, if a user completes a purchase, the destination URL might be `/thank-you`.
- Configure any advanced settings as needed.
- Review the goal settings and click “Save.”
Required Fields for a Destination URL Goal
Setting up a destination URL goal in Google Analytics requires several key fields:
| Field | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Goal Name | Descriptive name for the goal. | Complete Purchase |
| Goal Description | More detailed description. | Tracking purchase completion. |
| Goal Type | Type of goal (destination, duration, etc.) | Destination |
| Destination URL | The specific URL that signifies goal completion. | /thank-you |
| Custom Dimensions (Optional) | Allows you to further categorize and analyze your data. | Sales Region |
| Custom Metrics (Optional) | Enables adding relevant data to your goal. | Order Value |
A well-defined goal, like “Complete Purchase,” can provide crucial insights into the effectiveness of marketing campaigns.
Goal Setting Procedure
This structured procedure provides a clear pathway to setting up a destination URL goal:
1. Account Selection
Access your Google Analytics account and navigate to the desired property.
2. Goal Creation
Within the property settings, locate the “Goals” section and click “Create Goal.”
3. Goal Type Selection
Choose “Destination” from the available goal types.
4. Goal Naming
Provide a descriptive name (e.g., “Complete Purchase”).
5. Goal Description
Include a detailed description (e.g., “Tracking purchase completion”).
6. Destination URL Configuration
Enter the precise destination URL (e.g., “/thank-you”) that signifies the goal’s completion.
7. Advanced Settings (Optional)
Configure any optional settings like custom dimensions or metrics.
8. Goal Validation
Review all settings carefully and click “Save” to finalize the goal setup.
Implementing Destination URL Goals
Destination URL goals in Google Analytics are a powerful tool for measuring the effectiveness of website traffic. By defining specific URLs as targets, you can gain valuable insights into how users interact with your site and ultimately achieve desired actions. This method goes beyond simple page views, enabling you to track conversions and user journeys. Knowing which pages users land on and how they interact with them is critical for understanding the overall performance of your website and optimizing it for better results.Implementing destination URL goals involves a few key steps and considerations.
Setting up a destination URL goal in Google Analytics is crucial for tracking the effectiveness of your online campaigns. This helps you understand which channels drive conversions, like email marketing campaigns. Knowing which specific landing pages users are visiting after clicking on your emails is key to optimizing your email marketing management strategies. For a deeper dive into the best practices for email marketing management, check out this helpful resource: email marketing management.
Ultimately, a well-defined destination URL goal in Google Analytics gives you the data needed to refine your overall marketing strategy.
Understanding the different methods and applying them to various website functionalities is essential for effectively utilizing this feature. Furthermore, tracking specific parameters in the destination URLs is critical for getting precise insights into user behavior and campaign effectiveness.
Methods for Implementing Destination URL Goals
Defining and implementing destination URL goals in Google Analytics is straightforward. The core process involves setting up a goal in your Google Analytics account, defining the specific URL(s) as the destination, and choosing the appropriate conversion settings. Different methods cater to diverse needs and website functionalities.
- Direct Destination URL Implementation: This method is the most common approach, where you directly specify a URL as the goal destination. For example, if a user completes a purchase, the “thank you” page URL could be set as the destination URL. This straightforward method is suitable for simple conversion tracking.
- Destination URLs with Parameters: Many websites use parameters within their URLs to track specific information, like campaign sources or product IDs. In this case, you can use these parameters to further refine your goal tracking. For instance, if you have a product page with a specific ID, you can use the product ID as a parameter within the destination URL. This lets you measure conversions based on specific products or campaigns.
Examples of Destination URL Goal Implementation
Various website functionalities can benefit from destination URL goals. Let’s examine a few scenarios.
- E-commerce: For online stores, the “thank you” page after a purchase, or the confirmation page for an order, can be set as the destination URL. This helps track the conversion rate and revenue generated from different marketing channels. Detailed analysis of parameter tracking can pinpoint successful product promotions.
- Lead Generation: If a user fills out a contact form, the confirmation page URL can be used as the destination. Tracking which landing pages generate the most leads can help you optimize your lead generation campaigns.
- Content Downloads: When users download a white paper or other documents, the thank you page after the download can be the destination. This will let you see how many people are engaging with your valuable content and how well different download links are performing.
Tracking Specific Parameters in Destination URLs
Parameters in URLs can provide granular insights into user behavior. They allow you to filter and segment your data based on specific criteria, enhancing the analysis of your website’s performance.
- Campaign Tracking Parameters: Parameters like ‘utm_source,’ ‘utm_medium,’ and ‘utm_campaign’ allow you to trace the origin of traffic to your site. By tracking these parameters in the destination URLs, you can determine which marketing campaigns are most effective in driving conversions. This allows you to refine your marketing strategies.
- Product Tracking Parameters: If a user is directed to a product page, including the product ID as a parameter allows you to track sales and conversions for each product individually. This data is crucial for understanding product popularity and optimizing inventory management.
Importance of Accurate URL Tracking
Accurate URL tracking is crucial for data analysis. Inaccurate tracking can lead to skewed results, affecting your understanding of website performance.
Accurate URL tracking is essential for reliable data analysis, impacting decisions and optimizations.
Inaccurate tracking can lead to inaccurate conclusions about user behavior and conversion rates, ultimately affecting the effectiveness of marketing strategies and website optimization efforts.
Tracking User Flows and Conversions
Destination URL goals provide a clear view of user flows and conversions. By monitoring which URLs users visit before reaching the destination, you can gain a better understanding of the user journey.This helps you optimize your website to guide users through the conversion funnel more efficiently. Understanding the steps users take from initial engagement to the final destination URL is crucial for improving the user experience and increasing conversions.
Troubleshooting Destination URL Goals: Setting Up A Destination Url Goal In Google Analytics
Setting up destination URL goals in Google Analytics is crucial for measuring website success. However, errors can sometimes arise during the setup process, impacting the accuracy of your data. This section dives into common issues and provides actionable solutions for effectively troubleshooting your destination URL goals.Troubleshooting destination URL goals involves identifying and resolving errors to ensure accurate data collection.
Careful analysis of the goal setup and the destination URLs themselves is key to pinpointing problems. This section focuses on common pitfalls and provides detailed strategies for fixing them.
Common Issues in Destination URL Goal Setup
Incorrectly configured destination URLs are a frequent source of errors. Missing or extra parameters, typos, or even slight variations in the URL structure can lead to inaccurate tracking. It is essential to meticulously check the setup to ensure accurate data collection. This can often be as simple as a misplaced character or a missing parameter. The key is careful verification and attention to detail.
Setting up a destination URL goal in Google Analytics is crucial for tracking website traffic. It helps you understand where your visitors are coming from and ultimately, which campaigns are working. This is especially important when you’re focusing on social media marketing, like using twitter marketing to drive traffic to specific pages. By defining a specific landing page as a goal, you can measure the success of your Twitter campaigns and refine your strategy accordingly.
This detailed tracking lets you see how effective your efforts on platforms like Twitter are, making sure you’re getting the most out of your analytics data.
Identifying and Resolving Errors
Thorough verification of your goal setup is the first step. Ensure that the destination URLs are precisely matched to the actual URLs users navigate to after completing the desired action. Checking the destination URL in your goal setup against the actual URL visited is crucial. Also, examine the URL structure to identify discrepancies, and validate the parameters.
Tracking Issues with URLs Containing Parameters or Query Strings
Parameters and query strings in URLs can sometimes cause tracking issues. These elements are vital components of many URLs, particularly in e-commerce and marketing campaigns. These elements can be problematic in goal setups if not correctly configured. Ensure that any parameters or query strings included in your destination URL match those in your website’s actual URL structure.
This can often be resolved by including the entire query string in your goal destination URL, including any specific parameter values, to guarantee accurate matching.
Debugging Issues with Custom Parameters
Custom parameters are often used to track specific user actions or product details. If your goal setup involves custom parameters, ensure these are correctly defined in both your goal setup and the actual URLs. Custom parameters, if not accurately configured, can also cause issues in tracking, so accurate implementation is critical. A crucial step involves comparing the parameters in the goal setup to the actual URLs to ensure they match precisely.
Validating Destination URLs and Goal Setups
Validation is essential to ensure accurate data collection. A practical approach involves using a combination of techniques to ensure accuracy. First, check the destination URLs in your goal setup against the actual URLs on your website. If discrepancies exist, resolve them to ensure accurate tracking. Another crucial step involves testing the setup by simulating user actions.
This allows you to verify that the goal is triggered correctly for various scenarios. By simulating various user interactions and examining the resulting data, you can identify and resolve potential problems early in the process.
Advanced Destination URL Tracking
Diving deeper into Google Analytics destination URL tracking reveals more sophisticated methods for measuring user engagement and achieving specific business objectives. Beyond simply tracking when a user reaches a designated page, advanced techniques allow for a granular understanding of the user journey, including multiple destinations, sub-page interactions, and the path leading up to a desired outcome. This empowers businesses to optimize their websites and marketing strategies by pinpointing areas for improvement and identifying high-value user flows.Tracking users’ interactions with multiple potential destinations requires a strategic approach.
A single goal can be configured to monitor the success of different paths to conversion. This flexibility enables businesses to monitor and compare the effectiveness of different marketing channels, content strategies, or website designs.
Multiple Destination URLs for a Single Goal
This approach allows for a single goal to monitor different conversion paths. Instead of creating separate goals for each potential destination URL, you can define a single goal with multiple destination URLs. This simplifies goal management and provides a unified view of overall conversion performance across different paths. For example, a website selling a product might have multiple paths to purchase, such as direct product pages, category pages, or external referrals.
Using a single goal with multiple destination URLs allows for consolidated reporting on the effectiveness of these different paths.
Tracking Users Reaching Multiple Destination URLs
Using multiple destination URLs in a single goal allows for reporting on the success of reaching any of those URLs. Google Analytics automatically counts a conversion whenever a user lands on any of the defined destination URLs. This consolidated view simplifies analysis by avoiding the need to separately track each destination. It provides an overall picture of conversion rates from different entry points, allowing businesses to focus on optimizing the entire conversion funnel rather than individual steps.
Tracking Specific Subpages or Events Within a Destination URL
To gain deeper insights into user behavior within a specific destination, you can use the “URL parameters” to identify sub-pages or events. For instance, a specific product page might have multiple sections (e.g., details, reviews, FAQs). By tagging these sections with unique parameters, you can track which parts of the page are most engaging and identify bottlenecks in the user journey.
This level of granularity allows businesses to pinpoint areas for improvement and optimize the user experience within the conversion process. For example, if the user journey through specific sub-pages is showing a high drop-off rate, then that specific section can be optimized for better engagement.
Tracking Users’ Journey Through Multiple Pages Before Reaching the Destination
The comprehensive approach to destination tracking allows for tracing the steps taken by users before reaching the desired destination. This is crucial for understanding the user journey and identifying points where users are dropping off or becoming disengaged. This analysis is often achieved using the “Campaign URL Builder” in Google Analytics or by implementing custom parameters. By incorporating these parameters in the website’s URLs, you can track specific events or actions that occur before a user reaches the final destination, providing detailed insight into user behavior.
For example, a user might browse multiple product categories before purchasing a specific product. By tracking the journey, you can understand the reasons behind the purchase decision, leading to better targeting and product placement.
User Journey Flowchart to a Destination URL, Setting up a destination url goal in google analytics
(Placeholder for a flowchart, showing the various paths a user might take to reach a destination URL. The flowchart would show different entry points, sub-pages visited, and events triggered. The flowchart would also include a representation of the different paths that might lead to the same destination, for instance, if a user clicks on an advertisement, or navigates from a specific page. It should also include various paths of users dropping off in the journey.)
Final Conclusion
In conclusion, setting up destination URL goals in Google Analytics empowers you to track user interactions effectively, monitor conversions accurately, and ultimately optimize your website’s performance. By understanding the various techniques, from basic matching to advanced tracking, you can gain actionable insights from your data. Remember, accurate URL tracking is paramount for robust data analysis, enabling you to make informed decisions for improving user experience and achieving your business objectives.