Ultimate Guide to Search Engine Friendly Pagination
Ultimate guide to search engine friendly pagination lays out a comprehensive strategy for optimizing your website’s pagination for search engines. This detailed guide delves into crucial aspects of pagination, from understanding its fundamental role in to implementing best practices for crawlability, URL structure, content optimization, user experience, mobile-friendliness, performance, and rigorous testing.
We’ll explore the nuances of crafting a seamless and search-engine-friendly pagination system, ensuring your website ranks higher and provides a superior user experience across all devices. This guide will equip you with the knowledge and actionable steps to create a robust and effective pagination system for your WordPress site.
Introduction to Pagination
Pagination, in the context of search engines, is the process of breaking down a large set of results into smaller, manageable pages. This crucial element significantly impacts how search engines index and rank websites, and it’s a vital part of user experience. Properly implemented pagination can lead to better search engine visibility and a more positive user journey.
Without effective pagination, users might be overwhelmed by an overwhelming amount of information, and search engines might struggle to crawl and index the entire site.Search engine-friendly pagination is essential for website optimization because it allows search engines to easily crawl and index all pages of a website. This is crucial for ranking well in search results. Poorly implemented pagination can result in duplicate content penalties or even exclusion from search engine indexes, significantly hindering a website’s visibility and organic traffic.
It’s also crucial for delivering a seamless user experience.
Pagination Methods
Different methods exist for paginating content. Understanding these methods is vital for creating a search engine-friendly website. These methods vary in their effectiveness for search engine crawlers and user experience.
- Server-Side Pagination: This method generates each page of results dynamically on the server. Each page request triggers a new server-side process to fetch and display the appropriate data, ensuring that each page is unique. This is generally the best option for search engines, as it produces distinct content for each page.
- Client-Side Pagination: This method loads a portion of results initially and uses JavaScript to load more pages as the user scrolls or clicks. While it can be faster for the user, it can also be problematic for search engines, as they might not see all the content initially.
- Database Pagination: This method utilizes database queries to retrieve a specific set of results for each page. This method can be efficient, especially for very large datasets. This method is well-suited for complex applications requiring dynamic content retrieval.
Impact on User Experience
Effective pagination enhances user experience. It prevents overwhelming users with an overwhelming amount of content, making navigation more manageable. This leads to improved user satisfaction and engagement, as users can easily find what they are looking for without being overwhelmed. Intuitive and well-designed pagination improves site usability and ensures a positive user journey.
Want to boost your website’s search engine rankings? A crucial aspect is search engine friendly pagination. Understanding how to structure your site’s pages for optimal SEO is key. For instance, a great example of a marketer focusing on this is Amber Theinert, marketing manager at Ted’s Cafe, amber theinert marketing manager teds cafe. Her insights and experience highlight the importance of well-structured pagination.
Ultimately, a strong understanding of search engine friendly pagination will significantly improve your site’s visibility and user experience.
HTML Table Structure for Basic Pagination
The following HTML table structure provides a basic framework for a pagination system. This example demonstrates a basic implementation.
| Page Number | Link to Page |
|---|---|
| 1 | 1 |
| 2 | 2 |
| 3 | 3 |
This simple table provides a structure for presenting page links. A more sophisticated implementation would use JavaScript to dynamically update the table based on the total number of pages and the current page.
Search Engine Crawlability and Pagination
Search engines like Google rely on crawlers to discover and index web pages. Understanding how these crawlers navigate paginated content is crucial for ensuring your website’s visibility and discoverability. Poorly structured pagination can lead to missed pages and incomplete indexing, impacting your search rankings. This section delves into the specifics of how search engine crawlers interact with paginated sites, common crawl issues, and actionable strategies to optimize crawlability.Crawlers typically follow links on a page to discover new content.
However, the way paginated sites are designed can sometimes confuse these automated explorers. This can result in missed pages, leading to incomplete indexing of your site’s content. A robust strategy for pagination, therefore, is essential for maximizing your website’s exposure in search results.
Crawler Navigation Through Paginated Content
Crawlers follow links to discover new pages. In paginated websites, the crawler encounters links to subsequent pages, often using parameters like page numbers (e.g., ?page=2). The crawler follows these links, typically navigating through multiple pages to understand the complete content. This process is essential for comprehensive indexing.
Common Crawl Issues with Pagination
Several issues can arise when crawlers encounter paginated content. Duplicate content is a common problem, as each page may contain largely similar information. This redundancy can confuse the crawler and result in only one page being indexed, which can lead to missed opportunities. A poorly structured pagination system may also cause the crawler to stop crawling before reaching all relevant pages.
This can be due to infinite scroll implementations or pagination systems that do not provide clear signals to the crawler about the presence of more pages.
Strategies to Improve Crawlability for Paginated Websites
Several strategies can enhance crawlability and ensure proper indexing of all pages. Implementing clear and consistent pagination is essential. This involves using proper HTML attributes and well-defined links. Employing a predictable pagination structure helps crawlers understand the site’s organization and navigate through the pages. Furthermore, robots.txt directives can be used to guide crawlers away from pages that are not yet ready for indexing or are low in value.
Also, utilizing canonical tags to point to the main page can help in handling duplicate content issues effectively.
Techniques to Ensure All Pages Are Indexed Properly
Various techniques can help ensure all pages are indexed correctly. Using proper pagination structures is critical. Using numerical or descriptive pagination links, rather than obscure parameters, helps crawlers understand the structure of the site and find subsequent pages. For instance, use “page 2” instead of a cryptic parameter. This is essential for efficient crawling.
Implementing pagination schemes that don’t require complex or unpredictable patterns is key. Ensure each page has unique content and value.
Best Practices for Search Engine-Friendly Pagination
| Crawler Perspective | Best Practice |
|---|---|
| Understanding Pagination Structure | Use predictable, numerical pagination links (e.g., page 1, page 2, etc.). |
| Handling Duplicate Content | Implement canonical tags to indicate the main page for similar content. |
| Crawling Depth | Ensure crawlers can easily identify the total number of pages. |
| Crawling Frequency | Employ robots.txt to control crawling frequency and prevent crawling irrelevant pages. |
| Link Structure | Avoid using complex or cryptic pagination parameters. |
URL Structure and Pagination
Crafting user-friendly and search engine-friendly URLs for paginated content is crucial for optimal visibility. A well-structured URL hierarchy reflects the site’s content organization, aiding search engines in understanding the relationship between pages and improving the user experience. This section delves into the importance of URL structure for search engine visibility, focusing on descriptive anchor text, canonical tags, and semantically relevant URL construction.A well-structured URL provides crucial information about the content, allowing search engines to quickly grasp the topic and context of a page.
This in turn helps in ranking the page appropriately in search results.
Impact of URL Structure on Search Engine Visibility
The structure of your pagination URLs directly influences how search engines index and rank your paginated content. Clear, concise, and descriptive URLs help search engines understand the context of each page. Poorly structured URLs can lead to duplicate content issues, confusing search engine crawlers, and ultimately hindering visibility. Search engines need to easily understand the relationship between different pages of a site, and pagination URLs contribute significantly to this understanding.
So, you’re diving deep into the ultimate guide to search engine friendly pagination? Knowing how to optimize your site for search engines is crucial. Think about how video marketing can boost your SEO efforts. A strong video marketing guide will help you craft engaging videos that attract viewers and improve your search ranking. Ultimately, mastering pagination will be a game-changer for your site’s visibility and user experience.
Descriptive Anchor Text in Pagination Links
Using descriptive anchor text in pagination links is vital for guiding both users and search engines. Instead of generic terms like “Next Page” or “Previous Page,” utilize s relevant to the content on the subsequent page. For instance, if you’re paginating a blog post about “best coffee beans,” instead of “Next Page,” use “Read More Coffee Beans”. This provides context to search engines and improves user experience.
Descriptive anchor text enhances user navigation and allows search engines to better understand the content of each page within the pagination sequence.
Role of Canonical Tags in Managing Duplicate Content Issues
Canonical tags are essential for managing duplicate content issues often arising with pagination. By specifying a canonical URL, you tell search engines which version of a page is the definitive one. This is particularly crucial for pagination, where multiple pages may contain similar content. Using a canonical tag for the main page of a series of paginated results prevents search engines from treating the paginated pages as separate, duplicate entries.
This is important because it prevents the issue of search engines treating pages as separate and duplicate entries. It ensures search engines understand that all the pages are part of a single entity, boosting your overall visibility.
Constructing Semantically Relevant URLs for Pagination
Creating semantically relevant URLs for paginated content involves using s and contextually relevant terms to describe the page content. This is important for both users and search engines. A URL structure that incorporates page numbers clearly and logically can enhance both user experience and search engine crawlability. For example, instead of `example.com/page2`, a semantically relevant URL might be `example.com/best-coffee-beans/page/2`.
This structure clearly indicates the content of the page and the page number.
Comparison of URL Structures for Paginated Results
| URL Structure | Impact on |
|---|---|
| `example.com/page1` | Less descriptive, potentially confusing for search engines. May lead to indexing issues. |
| `example.com/category/product-name/page-2` | More descriptive, providing context to search engines. Improved visibility and better understanding for search engines. |
| `example.com/best-coffee-beans/page/2` | Highly descriptive and semantically relevant. Stronger signal to search engines about page content. Improves user experience. |
Content Optimization for Each Page
Crafting unique and engaging content for each page of a paginated series is crucial for search engine visibility and user experience. Search engines prioritize pages with valuable, distinct information, and users appreciate a seamless journey through the content. This optimization extends beyond just listing information; it’s about providing relevant, in-depth data for each segment of your content.Creating a comprehensive strategy for content optimization on each page ensures that each piece of the larger content set is discoverable and valuable to the user.
It involves more than just copying and pasting; it’s about tailoring the content to the specific information needs of the user, making each page a standalone entity within the larger series.
Importance of Unique and Relevant Content
Each page in a paginated series should offer unique and relevant content that answers a specific need or question related to the overall topic. Duplicating content across pages dilutes the value of each individual page and sends mixed signals to search engines. Search engines are designed to identify and rank content that is both informative and unique. This approach improves the overall user experience and demonstrates a commitment to providing high-quality content.
Creating Unique Content Aligned with Search Intent
To create unique content for each page, identify the specific search intent behind each page’s position in the series. Consider the questions users are likely to ask at that point. If the series covers different aspects of a product, the initial page may cover the product overview, while later pages might delve into specific features, pricing, or customer reviews.
The content should reflect this progression and provide increasingly detailed information as the user navigates the pagination. The ultimate goal is to address different facets of the topic, rather than just repeating the same information.
Internal Linking for Enhanced Navigation
Internal linking is essential for connecting related pages within the site. Linking from one page to another within the paginated series strengthens the site’s architecture and helps search engines understand the relationship between different topics. This method guides users smoothly through the content, improves user experience, and signals to search engines that related topics exist within the website.
- Linking from a page discussing a product feature to a page outlining its benefits strengthens the user’s understanding and provides additional context.
- Linking from a page explaining a complex concept to a page with illustrative examples helps users grasp the concept effectively.
Crafting Effective Meta Descriptions
Meta descriptions are concise summaries of each page’s content that appear in search engine results pages (SERPs). Crafting compelling and unique meta descriptions for each page in a paginated series can significantly improve click-through rates. These descriptions should clearly communicate the page’s specific content and encourage users to click through.
- A good meta description is specific to the page’s content and avoids generic phrases.
- A well-written meta description can significantly impact a page’s visibility in search results.
Content Requirements for Various Pagination Types
The following table Artikels the content requirements for different pagination types:
| Pagination Type | Content Requirements |
|---|---|
| Numeric Pagination (e.g., 1, 2, 3…) | Each page should cover a distinct section of the topic. The content should gradually build on the previous pages, adding more depth and detail. |
| Infinite Scroll | Content should be easily digestible and concise. Content should be focused and provide clear value for each chunk of content. |
| Sliding Pagination | Content should be well-organized and clearly presented, allowing users to easily navigate through the different sections. Each page should contain a clear and concise summary of the topic and offer valuable information that aligns with the user’s search intent. |
User Experience and Pagination
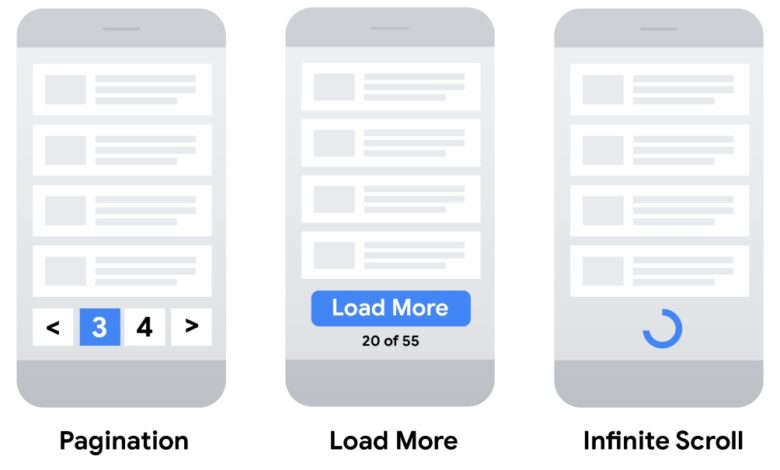
A crucial aspect of any website, especially those with extensive content, is how users navigate through the information. Pagination, the process of dividing content into pages, directly impacts the user experience. A well-designed pagination system can significantly improve site usability and engagement, while a poorly implemented one can frustrate users and lead to higher bounce rates.Effective pagination is not just about displaying numbers; it’s about creating a seamless transition between pages that feels intuitive and natural to the user.
This means considering the user’s journey and providing clear, consistent, and helpful cues throughout the process. By prioritizing the user experience, website owners can create a positive and engaging online environment.
Importance of Intuitive Navigation
Intuitive navigation is paramount in pagination. Users should effortlessly move between pages, understanding the context and their location within the overall content. A confusing or poorly designed pagination system can quickly disorient users, leading to frustration and a diminished user experience.
Strategies for Seamless User Experience
A seamless user experience hinges on several key strategies. These include providing clear visual cues, using appropriate terminology, and maintaining a consistent design language throughout the site.
- Clear Visual Cues: Use visually distinct elements to highlight the pagination links. This could include a different color, font style, or visual emphasis, such as bolding. For example, the active page could be highlighted with a different color, or pagination links could be arranged in a clean, visually separated section.
- Appropriate Terminology: Use clear and concise language. Instead of “Page 1 of 10,” consider “Next 10 Results” or “1-10 of 100 Results.” Avoid overly technical or ambiguous language that may confuse the user. This helps to create a more welcoming and approachable interface for users.
- Consistent Design Language: Ensure the pagination elements maintain a consistent visual style across the entire website. A consistent design language ensures that the pagination elements don’t clash with other elements of the website. This helps create a unified and user-friendly experience.
Impact of Pagination on Website Navigation
Pagination directly influences how users navigate a website. A well-structured pagination system can streamline the user’s journey, allowing them to quickly access the desired information. Conversely, poor pagination can impede navigation, leading to a frustrating experience. The ability to easily move between pages is crucial for a positive user experience.
Ensuring Easy and Intuitive Navigation for Users
Ensuring intuitive navigation involves more than just displaying numbers. Users need to understand the scale of the content they’re navigating and their position within it. This is critical for maintaining engagement and encouraging users to explore the entire site.
- Providing Contextual Information: Displaying the total number of results and the current page number provides a clear understanding of the user’s position. For instance, “Results 1-10 of 100” clearly communicates the user’s place in the overall content.
- Implementing Jump Functions: Allow users to quickly jump to specific pages or sections of the content. This is particularly helpful when dealing with extensive results or when users need to access a specific page without navigating through numerous pages.
- Using Responsive Design: Ensuring that pagination elements adapt to different screen sizes and devices is essential for a positive user experience. A well-designed responsive pagination system ensures that users on all devices have a seamless and intuitive experience.
Creating Clear and Informative Pagination Elements
Clear and informative pagination elements are essential for a positive user experience. These elements should clearly communicate the user’s position within the content and provide easy access to the next or previous pages.
My ultimate guide to search engine-friendly pagination is crucial for a website’s visibility, but it’s also worth noting that a shift towards a web without third-party cookies like web without third party cookies is impacting how we think about SEO. This change necessitates a reevaluation of strategies to maintain optimal search rankings, which is why a strong understanding of pagination is more important than ever for navigating this new landscape.
Ultimately, search engine-friendly pagination remains vital for effective website organization and user experience.
- Using Descriptive Labels: Instead of just using numbers, use descriptive labels for pagination elements. For instance, “Previous 10 Results” or “Next 10 Results” provide context and make the navigation more user-friendly.
- Implementing Load Indicators: If loading takes time, indicate this process to the user, e.g., a loading spinner. This prevents the user from becoming frustrated by long loading times.
- Considering User Expectations: Consider the user’s expectations regarding pagination. Familiar patterns and designs often provide the best user experience.
Mobile-Friendliness and Pagination
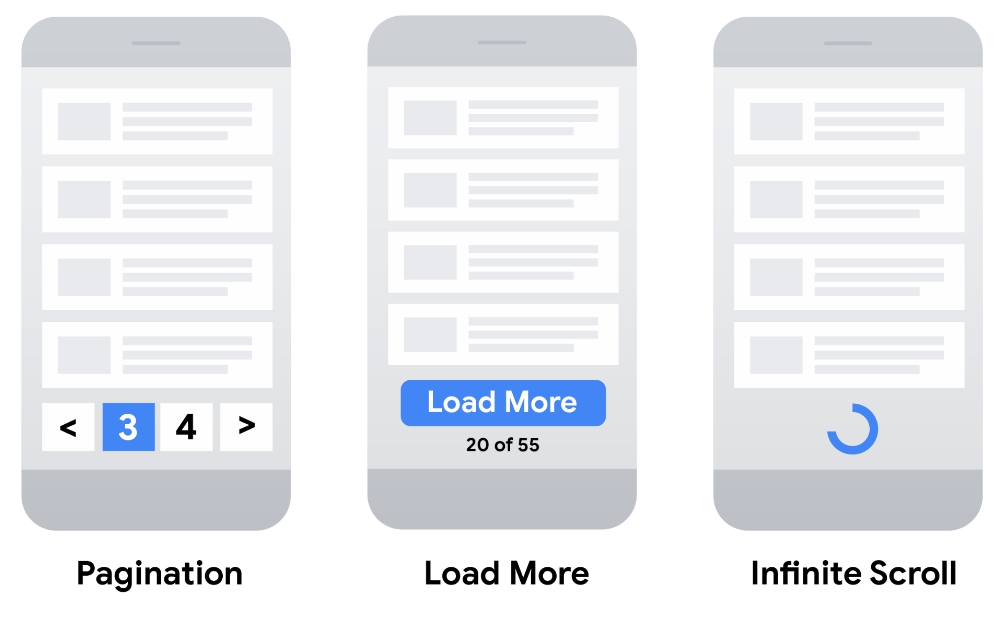
Mobile-friendly pagination is crucial for a positive user experience and improved search engine rankings. Users increasingly access websites via smartphones and tablets, making it essential for your site to adapt seamlessly to various screen sizes. A well-designed mobile pagination system ensures smooth navigation, preventing frustrating scrolling or cumbersome clicks.Responsive pagination design is not just about fitting content on a smaller screen; it’s about optimizing the entire user journey.
A user on a mobile device shouldn’t have to contend with a clunky or confusing pagination system that hinders their ability to quickly access the information they need.
Importance of Responsive Design
Responsive pagination design adapts to the screen size of the device a user is using. This adaptability is vital for a positive user experience. Users browsing on smartphones or tablets shouldn’t encounter difficulties navigating through pages. A responsive design automatically adjusts the layout, ensuring readability and ease of use, regardless of screen size.
Examples of Responsive Pagination Designs
Several techniques exist for creating responsive pagination designs. One common method involves using CSS media queries to tailor the display of pagination elements based on screen width. For example, a horizontal pagination bar might transition to a vertical list on smaller screens. Another approach utilizes JavaScript to dynamically adjust the pagination elements, ensuring that the user interface remains intuitive and user-friendly across different devices.
Ensuring a Seamless Experience Across Devices
To ensure a seamless experience, implement a consistent design language across all devices. This includes using appropriate font sizes, button sizes, and spacing. Use clear visual cues to indicate the current page and the available options. Also, ensure that interactive elements (like buttons and links) are easily accessible and intuitive to use. This consistency builds user trust and confidence in the website’s navigation.
Common Mobile Issues with Pagination
Common mobile issues include:
- Cluttered Interface: A visually cluttered interface can make it difficult for users to locate and interact with pagination controls, especially on smaller screens.
- Hidden or Inaccessible Controls: Pagination controls that are hidden or difficult to access on mobile devices lead to frustration and abandonment.
- Poorly Designed Button Layout: Buttons that are too small, spaced inappropriately, or lacking clear visual feedback create a negative user experience.
- Slow Loading Times: Pagination that results in slow loading times leads to a poor user experience, particularly on mobile devices with limited bandwidth.
These issues directly impact user satisfaction and potentially your search engine ranking.
Mobile-Friendly Pagination Techniques
| Technique | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Responsive CSS | Uses CSS media queries to adapt the pagination layout based on screen size. | Employing different CSS styles for small screens and larger screens to maintain a consistent experience. |
| Touch-Friendly Controls | Designs pagination controls with larger touch targets and appropriate spacing to ensure easy interaction on touch screens. | Buttons with ample spacing and larger sizes are more easily tapped on mobile devices. |
| JavaScript-Driven Pagination | Utilizes JavaScript to dynamically adjust the pagination elements as the user interacts with the content. | Dynamically updating the pagination controls as the user scrolls or changes pages. |
| Progressive Enhancement | Creates a basic, functional pagination experience that progressively enhances for mobile devices. | Ensure core functionality works across devices, with enhanced features available on higher-resolution displays. |
These techniques can significantly improve the user experience and accessibility of your website’s pagination system.
Performance Optimization and Pagination: Ultimate Guide To Search Engine Friendly Pagination
Pagination, while crucial for user experience on large websites, can significantly impact website loading speed if not implemented efficiently. Poorly optimized pagination can lead to slow page load times, negatively affecting user engagement and search engine rankings. Understanding the performance implications and employing effective optimization strategies are vital for maintaining a positive user experience and a high-ranking website.
Impact of Pagination on Website Loading Speed
Pagination increases the number of server requests. Each page request necessitates fetching and processing data, potentially impacting the overall loading time. A large number of pages can significantly slow down a website, causing users to abandon the site. This delay negatively affects user experience and potentially impacts search engine rankings. Furthermore, excessive server requests put a strain on server resources, potentially leading to server overload.
Strategies for Optimizing Pagination for Performance
Several strategies can be employed to optimize pagination for performance. These strategies aim to reduce the number of server requests, minimize the amount of data transferred, and enhance the server’s processing capabilities.
- Caching: Implementing caching mechanisms can significantly reduce server load by storing frequently accessed data. This strategy reduces the need for repeated database queries, thus improving page load times.
- Asynchronous Loading: Employing asynchronous loading techniques allows for the simultaneous loading of data and elements on the page. This method can reduce perceived loading time and improve the overall user experience.
- Efficient Database Queries: Optimizing database queries for pagination is critical. Using appropriate SQL statements to retrieve only the necessary data for each page reduces the amount of data transferred, enhancing performance.
- Content Delivery Networks (CDNs): Leveraging content delivery networks (CDNs) allows for distributing content across various servers geographically closer to users. This strategy reduces latency, resulting in faster page load times.
Minimizing Server Load
Minimizing server load is crucial for maintaining website performance. Several strategies can be employed to achieve this goal.
- Database Optimization: Efficient database design and optimization directly correlate with the performance of paginated websites. Indexing relevant columns and using appropriate database structures are vital for reducing the time needed to retrieve data.
- Server-Side Rendering: Rendering pages on the server side can reduce the amount of client-side processing. This technique allows for delivering fully rendered pages to users, potentially enhancing performance and .
- Appropriate Resource Management: Effective resource management, such as optimizing image sizes and compressing CSS and JavaScript files, contributes significantly to reducing server load.
How Pagination Impacts Website Speed
Pagination directly impacts website speed by increasing the number of requests to the server. Each page in a pagination scheme requires a separate server request, potentially resulting in delays. Consequently, a larger number of pages leads to a longer loading time. Poorly implemented pagination can degrade the overall user experience and potentially negatively affect search engine rankings.
Performance Optimization Techniques for Paginated Sites
| Technique | Description | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Caching | Storing frequently accessed data to reduce server requests. | Reduced server load, faster page load times. |
| Asynchronous Loading | Simultaneously loading data and elements to reduce perceived load time. | Improved user experience, reduced loading times. |
| Efficient Database Queries | Optimizing SQL statements to retrieve only necessary data. | Reduced data transfer, enhanced performance. |
| Content Delivery Networks (CDNs) | Distributing content across servers closer to users. | Reduced latency, faster page load times. |
| Database Optimization | Efficient database design and indexing to reduce data retrieval time. | Enhanced database performance, faster data retrieval. |
| Server-Side Rendering | Rendering pages on the server to reduce client-side processing. | Potentially improved performance and . |
| Resource Management | Optimizing image sizes and compressing CSS/JavaScript files. | Reduced server load, faster page load times. |
Testing and Monitoring Pagination
Ensuring your paginated content is easily discoverable and user-friendly requires rigorous testing and continuous monitoring. A well-implemented pagination strategy significantly impacts both search engine crawlability and user experience, making proactive testing and monitoring crucial. This section will delve into practical methods for evaluating pagination effectiveness, monitoring search engine rankings, and identifying and resolving potential issues.Effective pagination requires careful consideration of user behavior and search engine algorithms.
Comprehensive testing and continuous monitoring are essential to ensure the optimal performance and accessibility of your paginated content.
Testing Pagination Strategies, Ultimate guide to search engine friendly pagination
Thorough testing of different pagination styles is essential to identify the most effective approach for your specific website. This involves analyzing various pagination types to determine their impact on search engine crawlability, user experience, and overall performance.
- Different Pagination Styles: Evaluate the performance of different pagination styles, such as numbered pages, next/previous buttons, or infinite scroll. Analyze the impact of each on search engine crawlability, ensuring all pages are indexed. Consider using a tool to simulate user behavior on different pagination types to see which style yields the best results.
- Crawlability Simulation: Employ tools that simulate how search engine crawlers navigate your paginated content. Assess whether the crawlers can access and index all pages within the pagination scheme. This is crucial for ensuring comprehensive indexing.
- User Experience Testing: Conduct user testing to gauge how easily users navigate the paginated content. Observe how users interact with different pagination styles, focusing on factors like speed, clarity, and overall satisfaction. Gather user feedback and use it to identify areas for improvement.
Monitoring Search Engine Rankings
Regular monitoring of search engine rankings for paginated content is vital to assess the effectiveness of your pagination strategy. This allows you to identify potential issues and make necessary adjustments.
- Ranking Tracking Tools: Utilize tools specifically designed to track rankings and overall search visibility. Monitor the ranking positions of your paginated content for targeted s. Analyze changes over time to identify trends and correlations with pagination changes.
- Trend Analysis: Track fluctuations in search engine rankings. Identify any patterns or correlations between ranking changes and specific pagination elements or updates. This helps you understand how search engines respond to your pagination approach.
- Performance: Analyze the performance of s across different pages within the pagination structure. This analysis can reveal which pages are performing well and which require optimization.
Identifying and Resolving Pagination Issues
Addressing potential issues with pagination is crucial for maintaining search engine visibility and a positive user experience. Prompt identification and resolution of these problems are essential to avoid negative consequences.
- 404 Errors: Proactively check for 404 errors, which can occur if pages within the pagination are not properly linked or if content is missing. Implementing robust error handling is critical to preventing these issues.
- Canonicalization: Ensure proper canonicalization for all pages in your pagination. Using canonical tags prevents duplicate content issues, which are detrimental to search engine rankings.
- Indexing Problems: Check if search engines are successfully indexing all pages within the pagination structure. Identify and resolve any indexing problems by checking for issues like incorrect robots.txt directives or other technical errors.
Tracking User Engagement
Analyzing user engagement with paginated content provides valuable insights into the effectiveness of your pagination strategy. This information can help identify improvements and enhancements.
- Click-Through Rates (CTRs): Monitor click-through rates to understand user engagement with pagination links. Higher CTRs indicate that users find the pagination system clear and intuitive. Analyze click patterns to understand which pagination elements are most appealing.
- Bounce Rates: Analyze bounce rates for different pages within the pagination. High bounce rates may indicate that the pagination is confusing or does not meet user expectations. This information can help you refine the design and layout.
- Time on Page: Monitor the average time users spend on each page within the pagination. Lower time-on-page metrics may suggest that the content is not engaging or the pagination is hindering user experience.
Testing Process Documentation
This table Artikels a structured approach to document the testing process for different pagination types.
| Pagination Type | Testing Criteria | Expected Outcome | Result | Action Required |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Numbered Pages | Crawlability, User Experience, 404 Errors | All pages indexed, intuitive navigation, no 404s | ||
| Next/Previous Buttons | Crawlability, User Experience, Site Speed | All pages indexed, seamless navigation, optimal load time | ||
| Infinite Scroll | Crawlability, User Experience, Site Speed | All pages indexed, seamless loading, smooth scrolling |
Concluding Remarks
In conclusion, this ultimate guide to search engine friendly pagination offers a complete roadmap for optimizing your paginated content for search engines. By addressing crucial aspects like crawlability, URL structure, content optimization, user experience, and mobile-friendliness, you can significantly enhance your website’s visibility and user satisfaction. Remember, consistent testing and monitoring are essential for identifying and resolving any issues, ultimately ensuring your paginated content achieves its full potential.