Google Shopping Ads A Comprehensive Guide
Google Shopping Ads are a powerful tool for businesses to reach potential customers actively searching for products online. This guide dives deep into the intricacies of Google Shopping Ads, covering everything from setup and optimization to performance tracking and budget management. We’ll explore the various types of products you can advertise, the best targeting strategies, and how to maximize your return on investment.
Understanding these ads is key to succeeding in today’s digital marketplace.
From crafting compelling product listings to setting up effective campaigns, we’ll provide actionable steps and valuable insights. Learn how to leverage bidding strategies, optimize product feeds, and use ad extensions to boost visibility and conversions. We’ll also discuss the crucial metrics to track, how to analyze campaign performance, and implement A/B testing for continuous improvement.
Introduction to Google Shopping Ads
Google Shopping Ads are a powerful tool for businesses to showcase their products directly within Google’s search results and shopping experiences. They connect consumers actively searching for specific products with merchants offering those products. Instead of just displaying text ads, Shopping Ads prominently feature product images, prices, and details, significantly increasing click-through rates and driving sales.The fundamental mechanics involve Google’s sophisticated algorithms analyzing product listings submitted by merchants.
These algorithms then match these listings with user searches. When a user searches for a product, relevant Shopping Ads appear alongside organic search results, making it easier for potential customers to find and compare products. This streamlined process allows for a highly targeted approach to advertising, ensuring your products are seen by the most receptive audience.
Types of Products Advertised
A wide array of products can be advertised through Google Shopping Ads. This includes physical goods like clothing, electronics, home appliances, and even services like travel packages or concert tickets. The key is that the products must be available for purchase and clearly defined within the merchant’s listing.
Target Audience for Google Shopping Ads
The target audience for Google Shopping Ads campaigns is comprised of individuals actively searching for products. This implies a high level of intent to purchase. Users typically have specific needs and are prepared to make a purchase, making them a highly valuable audience segment for businesses.
Google Shopping Ads: Ad Type Breakdown
| Ad Type | Features | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|---|
| Standard Shopping Ads | These ads feature product images, titles, prices, and star ratings, alongside the merchant’s business name. | Highly visual and attractive, easily stand out in search results. Provides crucial information at a glance, making them highly effective in driving conversions. | Requires meticulous product data management, including high-quality images and accurate pricing. Maintaining consistency across all listings is crucial. |
| Comparison Shopping Ads | These ads enable users to compare multiple products side-by-side, showcasing prices and features from various merchants. | Provides a highly competitive advantage by allowing consumers to directly compare products. Encourages more informed purchasing decisions. | Competition for placement can be intense, and visibility may vary depending on the market and competition level. |
| Local Shopping Ads | These ads highlight products from nearby retailers, focusing on location-based search queries. | Excellent for local businesses targeting customers in specific geographic areas. Encourages local purchases. | May be less effective for national or international campaigns. Requires accurate location information for the business. |
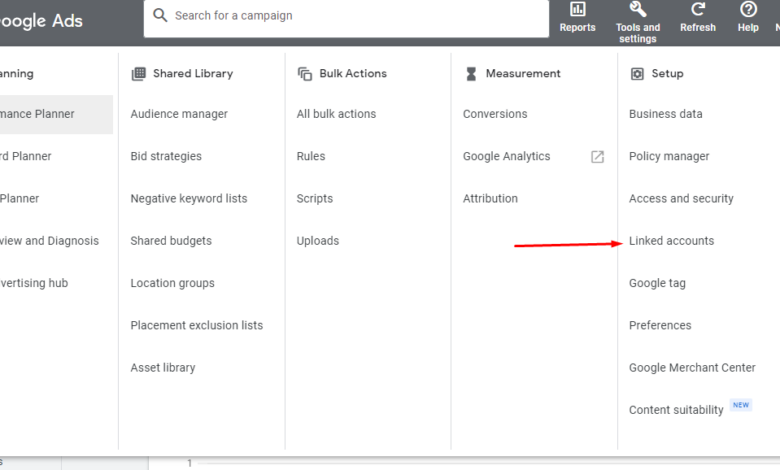
Campaign Setup and Management
Setting up and managing a successful Google Shopping Ads campaign requires a strategic approach that balances meticulous planning with ongoing optimization. This involves understanding the nuances of bidding strategies, campaign structure, and crucial performance metrics. Effective management leads to higher visibility, increased conversions, and a stronger return on investment (ROI).Careful consideration of these factors will translate into a more efficient and effective online advertising campaign, leading to a higher volume of qualified leads and ultimately, more sales.
Understanding the interplay between these elements is key to maximizing the potential of your Google Shopping Ads.
Essential Steps in Setting Up a Google Shopping Campaign
To effectively launch a Google Shopping campaign, several critical steps must be followed. These steps are vital for establishing a solid foundation for future success.
- Product Feed Creation: A high-quality product feed is paramount. It’s the cornerstone of your campaign, providing Google with accurate and comprehensive information about your products. This includes details like product titles, descriptions, images, prices, and availability. Ensure your feed is meticulously structured and adheres to Google’s specifications to avoid errors and ensure smooth campaign operation.
- Account Setup: Establish a Google Ads account and link it to your merchant center. This integration is critical for providing Google with access to your product data.
- Campaign Structure: Organize your campaign into logical ad groups and targeting categories to improve performance and efficiency. This segmentation allows you to refine your approach based on various factors such as product type, price range, or target audience.
- Bidding Strategy Selection: Choose the bidding strategy that aligns with your business goals. Each strategy has different implications for budget management and performance. A clear understanding of these strategies is critical for optimal results.
- Target Audience Definition: Identify your target audience by considering factors such as demographics, interests, and behaviors. Precise targeting maximizes the impact of your campaign by ensuring your ads reach the most relevant potential customers.
Bidding Strategies for Google Shopping Ads
Selecting the right bidding strategy is critical for optimizing your campaign’s performance and ensuring a healthy return on investment.
- Max CPC (Cost Per Click): This strategy sets a maximum bid amount per click. It provides control over your budget but might not yield the best possible results if not optimized properly. It’s best suited for businesses with a strong understanding of their target audience and campaign performance.
- Target CPA (Cost Per Acquisition): This strategy aims to achieve a specific cost per conversion. It focuses on achieving a target return on ad spend (ROAS) by setting a desired cost per conversion. It’s ideal for businesses prioritizing conversions over clicks.
- Target ROAS (Return on Ad Spend): This strategy aims to achieve a specific return on ad spend. It focuses on achieving a target return on ad spend by setting a desired ROAS. It’s often the most comprehensive approach for businesses prioritizing sales and profitability.
- Enhanced CPC: This strategy automatically adjusts your bids based on real-time data and performance. It dynamically optimizes your bids to achieve the best possible balance between cost and performance.
Campaign Structure for Optimal Performance
A well-structured campaign is key to maximizing the potential of your Google Shopping Ads. Logical organization allows for better management and optimization of resources.
- Ad Groups: Group products based on similarities, such as product category, features, or target audience. This enables more focused ad targeting.
- Targeting: Refine targeting to reach specific demographics, interests, or locations to maximize relevance and efficiency. Consider using negative s to exclude irrelevant searches.
- Bidding: Select the most appropriate bidding strategy based on your goals and budget. Regular monitoring and adjustments are essential.
Step-by-Step Shopping Campaign Setup
This structured approach provides a clear roadmap for establishing your campaign.
- Account Setup: Create a Google Ads account and link it to your merchant center.
- Product Feed Creation: Prepare a high-quality product feed that meets Google’s specifications.
- Campaign Creation: Create a new campaign and select the “Shopping” campaign type.
- Ad Group Creation: Organize products into relevant ad groups based on product categories.
- Bidding Strategy Selection: Choose the most appropriate bidding strategy (e.g., Target CPA, Target ROAS).
- Targeting: Set up your targeting parameters based on your ideal customer profile.
- Campaign Launch: Review and launch your campaign.
Critical Performance Metrics to Track
Tracking key performance indicators (KPIs) provides insights into campaign effectiveness.
| Metric | Description | Target |
|---|---|---|
| Clicks | Number of times users clicked on your ads. | High, but relative to other metrics. |
| Conversions | Number of desired actions taken by users (e.g., purchases). | High and increasing. |
| Conversion Rate | Percentage of clicks that result in conversions. | High and increasing. |
| Cost Per Conversion | Cost of each conversion. | Low and decreasing. |
| Return on Ad Spend (ROAS) | Revenue generated per dollar spent on advertising. | High and increasing. |
Targeting Strategies
Google Shopping Ads offer a wide array of targeting options to help you reach the right customers. Mastering these strategies is crucial for maximizing your ad spend and driving conversions. From broad targeting to highly specific audience segments, understanding the available tools empowers you to create campaigns that resonate with your ideal customer.
Targeting Options
Google Shopping Ads provide various targeting options to precisely reach your desired audience. This allows you to tailor your campaigns to specific customer groups, locations, and interests. By refining your targeting, you can ensure your ads are seen by individuals most likely to convert.
- Targeting: This fundamental targeting approach focuses on s related to your products. When users search for these terms on Google, your Shopping Ads can appear in search results. This is often a foundational element of a successful campaign, as it leverages the search intent of potential customers. For instance, if you sell running shoes, s like “men’s running shoes,” “women’s running shoes,” or “best running shoes for marathon training” would be relevant.
- Audience Targeting: This sophisticated approach allows you to reach specific demographics, interests, and behaviors. By understanding your ideal customer profile, you can target customers with similar traits, increasing the chances of conversion. Examples include targeting users who have previously shown interest in similar products or those who frequently visit sports websites. Google provides detailed audience segmentation, allowing you to filter by age, gender, location, and more.
- Location Targeting: This targeting strategy allows you to show your Shopping Ads to users within specific geographical areas. It is particularly useful for businesses with a physical storefront or those targeting customers in specific regions. You can target customers within a defined radius of your store or across different countries or cities. For example, a local bakery can target customers within a 10-mile radius of their shop.
Google Shopping Ads are a fantastic way to boost online visibility, but sometimes the content marketing supporting those ads can fall flat. A recent article, exploring the pitfalls of content marketing when the writer isn’t quite up to snuff, content marketing less stellar writer , highlights how poor quality content can hinder your ad campaigns. Ultimately, effective Google Shopping Ads rely on a strong foundation of compelling and well-researched product information, so quality content is crucial for success.
- Product Targeting: This approach allows you to target your ads to specific products related to your offerings. You can either choose from products already present in your Google Merchant Center account or use Google’s product database to target products that complement your own. This method is particularly effective for cross-selling or upselling.
Effectiveness of Targeting Methods
The effectiveness of a targeting method depends heavily on the specific campaign goals and the target audience. targeting, for example, is powerful for reaching users actively searching for specific products. Audience targeting, on the other hand, is more effective for reaching users who may not be actively searching but have demonstrated an interest in similar products. Location targeting works best for local businesses, driving foot traffic to brick-and-mortar stores.
Audience Targeting in Shopping Campaigns
Effective audience targeting in Shopping campaigns hinges on a clear understanding of your target customer. Use Google’s audience insights to identify key demographics, interests, and behaviors. For instance, if your product targets environmentally conscious consumers, target audiences based on their expressed interests in sustainability or eco-friendly products. The more specific your targeting, the higher the chances of attracting the right customers.
Location Targeting for Shopping Campaigns
Location targeting is essential for campaigns focusing on local customers. By defining precise geographical areas, you can ensure your Shopping Ads are displayed to users in proximity to your store. Use geographic targeting to drive foot traffic to your retail stores, for instance, or to target customers in specific areas with high purchasing power. For example, if you have a clothing store in a major city, targeting users in the surrounding suburbs or neighborhoods is likely to be more effective than targeting users across the entire country.
Cost Considerations of Targeting Options
The cost associated with different targeting options varies based on competition, ad quality, and the specificity of the target audience. Broader targeting options, such as s or general audience segments, may be more affordable but might not reach the most relevant customers. Targeted campaigns with highly specific audience segments often come with higher costs.
| Targeting Type | Description | Cost Considerations |
|---|---|---|
| Targeting | Targeting users actively searching for specific s. | Generally more affordable for broad s; cost increases with competition. |
| Audience Targeting | Targeting users based on demographics, interests, and behaviors. | Cost depends on the specificity of the audience segment; more specific = higher cost. |
| Location Targeting | Targeting users within a specific geographical area. | Cost varies based on the location and competition; targeting specific, smaller locations can be more expensive. |
| Product Targeting | Targeting users based on products similar to yours. | Cost is influenced by competition for the targeted products. |
Performance Measurement and Analysis
Mastering Google Shopping Ads hinges on understanding and effectively using performance data. This crucial aspect allows you to optimize campaigns, identify areas for improvement, and ultimately maximize returns on your investment. Knowing how to interpret key metrics is paramount to success in this dynamic advertising environment.
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) for Google Shopping Ads
Performance monitoring in Google Shopping Ads relies on a suite of key performance indicators (KPIs). These metrics provide insights into the effectiveness of your campaigns and reveal opportunities for improvement. Tracking these indicators is essential for gauging the impact of your strategies.
- Conversion Rate: This KPI measures the percentage of users who complete a desired action, such as making a purchase, after clicking on your ads. A high conversion rate indicates that your ads are effectively attracting qualified leads and driving conversions. A conversion rate of 2.5% is generally considered good, but optimal values depend on industry benchmarks and individual campaign specifics.
- Cost Per Acquisition (CPA): CPA reflects the average cost incurred to acquire a customer through your Google Shopping Ads. Lower CPA values are desirable as they indicate a more cost-effective acquisition strategy. Monitoring CPA allows you to optimize bids and targeting to reduce the cost per conversion.
- Click-Through Rate (CTR): CTR represents the percentage of users who click on your ads after viewing them. A high CTR signifies that your ad copy, s, and product images are compelling and relevant to users. A CTR of 2-4% is a good starting point, but it can vary depending on the product and target audience.
- Return on Ad Spend (ROAS): ROAS calculates the revenue generated for every dollar spent on advertising. A higher ROAS indicates that your advertising campaigns are highly profitable. For example, a ROAS of 3.00 means for every $1 spent on advertising, $3.00 in revenue is generated.
Importance of Tracking and Analyzing Campaign Performance
Regularly monitoring and analyzing your Google Shopping Ads campaign performance is crucial. It enables you to identify trends, pinpoint areas needing improvement, and refine your strategies for optimal results. This iterative process allows you to react to changing market conditions and customer behavior, ensuring your campaigns remain effective and efficient.
Google Shopping Ads are a fantastic way to drive traffic to your online store, but understanding your audience is key. To really optimize your campaigns, you need to delve into social media analytics. This crucial data, found in detailed reports like those provided by platforms like Facebook and Instagram, is vital to refining your strategies. Learning how to interpret this information is covered in depth in this excellent guide on social media analytics marketing explained.
Ultimately, a good understanding of social media analytics allows you to target your Google Shopping Ads with laser precision, maximizing your return on investment.
Methods for Identifying Areas for Improvement
Various methods can be employed to pinpoint areas requiring improvement in Google Shopping Ads campaigns. Careful examination of data and consistent analysis are key to refining your strategies.
- A/B Testing: Experimenting with different ad copy, product images, and targeting parameters to determine which variations yield the best results is crucial. By testing different approaches, you can refine your campaigns to achieve higher conversion rates.
- Competitor Analysis: Examining the strategies of your competitors can reveal insights into successful approaches and potential areas for improvement in your campaigns. This allows you to adapt and refine your campaigns.
- Performance Reports: Evaluating performance data helps to identify underperforming or irrelevant s. Adjusting your strategy accordingly can lead to more effective targeting and higher conversion rates.
Using Data to Refine Targeting and Bidding Strategies
Campaign data provides valuable insights into how to refine your targeting and bidding strategies. The goal is to focus on the most promising opportunities while minimizing wasted ad spend.
- Refined Targeting: By analyzing user behavior and conversion data, you can refine your targeting criteria to focus on the most promising customer segments. This includes adjusting your demographics, interests, and locations to match your ideal customer profile more accurately.
- Optimized Bidding Strategies: Using data insights to optimize bidding strategies is vital for cost-effective campaigns. This involves adjusting bids based on conversion rates, ROAS, and other key metrics to achieve the best possible return on investment.
KPI Examples
| KPI | Typical Value | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| Conversion Rate | 2-5% | Percentage of users who complete a desired action after clicking on an ad. |
| Cost Per Acquisition (CPA) | $50-$150 | Average cost to acquire a customer through the campaign. |
| Click-Through Rate (CTR) | 2-4% | Percentage of users who click on the ad after viewing it. |
| Return on Ad Spend (ROAS) | 2-5x | Revenue generated for every $1 spent on advertising. |
Ad Extensions and Enhancements: Google Shopping Ads
Google Shopping Ads offer a powerful toolkit for enhancing ad visibility and performance. Beyond the basic product information, extensions provide valuable extra details that can significantly impact your click-through rates and conversions. Understanding how to leverage these extensions is crucial for maximizing the ROI of your Shopping campaigns.Ad extensions are like adding extra features to your shopping ad, making it more compelling and informative for potential customers.
They provide extra space to showcase more details about your products and business, which can help you stand out from the competition.
Available Ad Extensions for Shopping Campaigns
Various ad extensions are available for use in Google Shopping campaigns. They are designed to provide additional information and context to your product listings, making them more attractive to potential customers. Each extension serves a specific purpose, enhancing your ad’s visibility and engagement.
Sitelink Extensions
Sitelink extensions are crucial for directing users to specific pages within your website. They provide direct links to relevant product pages, landing pages, or other valuable content, guiding users seamlessly through the customer journey.Implementing sitelink extensions in Shopping campaigns is straightforward. You need to provide clear and concise links to pages that match the user’s search intent and product offering.
For instance, if someone searches for “red running shoes,” you can include sitelinks that lead to pages about men’s running shoes, women’s running shoes, or a specific red running shoe model.
Examples of Ad Extensions in Shopping Campaigns, Google shopping ads
Several ad extensions are beneficial for Shopping campaigns, boosting visibility and user engagement. Callout extensions, for example, can highlight key features, benefits, or promotions. Location extensions can specify the physical store’s location, if applicable.Other useful extensions include structured snippets, which showcase specific product details like color or size options, and price match extensions, which indicate price comparison with competitor offers.
Table of Ad Extensions and Benefits
| Extension Type | Description | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Sitelink Extensions | Provides additional links to specific pages on your website. | Drives users directly to relevant product pages, improving conversion rates and user experience. |
| Callout Extensions | Highlights key product features or benefits. | Adds compelling information about the product, improving ad relevance and click-through rates. |
| Location Extensions | Specifies the physical location of your business (if applicable). | Helps users find your physical store, increasing foot traffic and local sales. |
| Structured Snippets | Showcase product details like color or size options. | Provides clear and concise product information, increasing ad visibility and relevance. |
| Price Match Extensions | Indicates price comparison with competitor offers. | Enhances trust and credibility by highlighting competitive pricing, potentially boosting click-through rates. |
Budget Management and Cost Optimization
Controlling your Google Shopping Ads budget is crucial for maximizing return on investment (ROI). A well-managed budget allows you to stay within your financial limits while achieving your marketing goals. Understanding how to allocate resources effectively and identify areas for cost reduction is key to a successful campaign.
Setting a Budget for Google Shopping Ads
Establishing a realistic budget is the first step in effective campaign management. Consider factors like your overall marketing goals, product pricing, target audience, and expected sales volume. Don’t just guess; analyze historical data and projected sales figures to determine a budget that aligns with your objectives. A conservative initial budget is often preferable to avoid overspending, and it allows for adjustments based on performance.
Google Shopping Ads are a powerful tool, but understanding how Google’s search algorithms work is key. Knowing how Google indexes apps and delivers “on-tap” information, as explained in this helpful guide everything you need to know about googles new app indexing and on tap information , can significantly improve your Shopping Ads performance. Ultimately, staying updated on Google’s evolving strategies is crucial for success with your Google Shopping Ads campaigns.
Strategies for Effective Budget Management
Effective budget management involves more than just setting a figure. Strategies include:
- Phased Budget Allocation: Begin with a smaller budget and gradually increase it as the campaign performs and demonstrates profitability. This approach allows for monitoring and adjustments based on performance, preventing unnecessary overspending.
- Budget Allocation by Product Category: Allocate budget based on the profitability of different product categories. High-profit items might warrant a larger budget allocation, while lower-profit items may require a more cautious approach. This targeted allocation improves ROI.
- Daily Budget Optimization: Adjust daily budgets based on the campaign’s performance. High-performing days might warrant a slight increase, while underperforming days might need a decrease. This adaptive approach ensures the budget is utilized effectively, and resources are not wasted.
Methods to Reduce Costs While Maintaining Performance
Cost reduction doesn’t have to mean sacrificing performance. Strategies include:
- Optimization: Focusing on highly relevant s and refining your search term strategy can lead to improved quality scores and lower costs per click. This means focusing on the precise words and phrases your target audience uses when searching.
- Bidding Strategies: Utilizing advanced bidding strategies, like target CPA or target ROAS, allows you to set a maximum cost-per-action or return-on-ad-spend goal. This can significantly reduce costs while maintaining the desired performance metrics.
- Negative s: Identifying and adding negative s prevents your ads from showing for irrelevant searches. This reduces wasted spending on searches that don’t result in conversions. This is a crucial aspect of cost optimization.
- Campaign Structure Optimization: Organizing campaigns by product categories, ad groups, and s improves targeting and performance. A well-structured campaign helps allocate resources effectively, resulting in lower costs and better ROI.
Tools for Optimizing Google Shopping Ads Budget
Various tools can help manage and optimize your Google Shopping Ads budget:
- Google Ads interface: The Google Ads platform itself provides various tools for budget monitoring, bidding strategy adjustments, and performance tracking.
- Third-party analytics tools: Tools like SEMrush or similar provide comprehensive campaign performance insights, allowing for detailed budget analysis and identification of areas for improvement.
- Budget allocation spreadsheets: Manually tracking budget allocations and performance metrics across different campaigns and product categories can be achieved using spreadsheets. This is a useful tool for visualizing spending patterns and identifying areas for optimization.
Budget Allocation Strategies Comparison
| Strategy | Description | Effectiveness |
|---|---|---|
| Fixed Daily Budget | Maintaining a consistent daily budget throughout the campaign. | Simple to implement but may not optimize for performance. |
| Dynamic Daily Budget | Adjusting the daily budget based on campaign performance. | More effective as it allocates resources dynamically. |
| Target CPA/ROAS | Setting a target cost-per-acquisition or return-on-ad-spend. | Highly effective in optimizing for specific conversion goals. |
A/B Testing and Campaign Optimization
A/B testing is crucial for optimizing Google Shopping Ads campaigns. By systematically comparing different variations of your ads, you can identify what resonates best with your target audience, leading to increased conversions and a better return on investment (ROI). This iterative process allows for continuous improvement and ensures your campaigns are performing at peak efficiency.Understanding the nuances of your audience and refining your approach based on data is paramount to success in the dynamic world of online advertising.
Experimentation is key to achieving the desired results, and A/B testing provides a structured method for doing so.
Importance of A/B Testing in Google Shopping Ads
A/B testing allows advertisers to identify the most effective elements of their campaigns. This iterative process, by testing different variations of ad copy, product images, and targeting strategies, helps uncover what truly resonates with customers. The result is more impactful ads that generate higher click-through rates (CTR) and conversion rates, thereby maximizing ROI.
Creating Effective A/B Test Scenarios
Effective A/B test scenarios are designed to isolate specific variables for comparison. Focus on a single element for testing at a time, such as headline variations, image alternatives, or different product descriptions. For instance, one variation might feature a bold headline, while the other uses a more descriptive approach. This structured approach helps pinpoint what elements generate more engagement.
Methods for Analyzing A/B Test Results
Analyzing A/B test results requires a keen eye for detail. Focus on key metrics like click-through rate (CTR), conversion rate, and cost-per-acquisition (CPA). Statistical significance is vital; look for results that demonstrate a statistically significant difference between variations. Don’t just look at raw numbers; consider the context of your campaign and target audience when interpreting the results.
For example, a slight improvement in CTR might be significant if the cost-per-acquisition also improves.
Using Test Results to Improve Campaign Performance
Implementing test results is crucial for continuous optimization. Identify the winning variations and incorporate them into your main campaign. Analyze the reasons for the variations’ success or failure. Understanding the underlying cause of higher conversion rates in one variation, for example, could involve identifying a particular phrase or image that resonated strongly with the target audience. By continually testing and refining your campaigns, you maintain a competitive edge in the dynamic online advertising landscape.
Template for Structuring A/B Testing in a Google Shopping Ads Campaign
A structured template is beneficial for tracking A/B test progress. This template should include details like the test objective, variations being tested, the duration of the test, the key metrics to track, and the anticipated outcomes.
| Test Objective | Variations | Duration | Key Metrics | Anticipated Outcomes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Increase CTR by 10% | Headline A (bold) vs. Headline B (descriptive) | 14 days | CTR, Conversion Rate, CPA | Improved CTR and conversion rate, reduced CPA |
A well-structured A/B testing template ensures consistent analysis and helps identify patterns that contribute to successful campaigns.
Last Word
In conclusion, Google Shopping Ads offer a dynamic and results-driven approach to online product promotion. By mastering the strategies Artikeld in this guide, businesses can effectively reach their target audience, optimize their campaigns, and achieve impressive returns. Remember, consistent monitoring, analysis, and adaptation are key to long-term success. This guide provides a solid foundation for navigating the world of Google Shopping Ads, equipping you with the knowledge to maximize your online presence and drive sales.