Email vs Push Notifications A Deep Dive
Email vs push notifications: which is the better way to reach your audience? This in-depth comparison explores the strengths and weaknesses of each method, from technical details to user experience and future trends. We’ll delve into everything from delivery speed to scalability and security.
Emails remain a crucial channel for many businesses, offering a robust and reliable way to deliver information. Push notifications, on the other hand, provide a more immediate and direct connection with users, but with different strengths and weaknesses. This comparison will explore how each communication channel best fits different needs.
Defining Email and Push Notifications
Email and push notifications are two prevalent methods for delivering information and updates to users. Understanding their characteristics, delivery mechanisms, and technical differences is crucial for effective communication strategies. This exploration delves into the specifics of each method, providing a comprehensive comparison.Email communication has been a cornerstone of digital communication for decades. Push notifications, on the other hand, have emerged as a powerful tool for real-time engagement, particularly in mobile applications.
This comparison highlights the strengths and weaknesses of each approach.
Email Communication Definition
Email communication involves the transmission of messages through electronic means. It typically involves a sender, a recipient, and a server acting as a mediator. Messages are composed using text, attachments, and multimedia elements. Emails are often stored in designated inboxes for later review. The message content can be complex and encompass a wide range of information.
Choosing between email and push notifications can be tricky. While emails are great for detailed announcements, push notifications are perfect for immediate updates. To maximize your Instagram reach, though, understanding Instagram hashtag analytics is crucial. instagram hashtag analytics maximize your reach by showing you which hashtags are most effective. Ultimately, the best approach depends on your specific goals, and a balanced strategy incorporating both email and push notifications might be the most successful for keeping your audience engaged.
Push Notification Characteristics, Email vs push notifications
Push notifications are real-time alerts delivered directly to a user’s device, usually a mobile phone or tablet. These notifications are triggered by specific events or actions, often without the user actively checking for updates. They are designed for immediate attention and engagement. Push notifications can be delivered in various formats, including text messages, icons, and sounds.
Delivery Mechanisms Comparison
Email relies on an established infrastructure of servers and protocols, enabling asynchronous communication. Users can access and read emails at their convenience. Push notifications, in contrast, utilize a direct connection between the application and the device. This allows for immediate delivery of alerts, regardless of user activity.
Technical Differences in Sending and Receiving
Email transmission involves sending messages through an email client to an email server, which then routes the message to the recipient’s email server. Receiving emails typically involves checking an inbox. Push notifications, on the other hand, involve a continuous connection between the application and the device. The application sends the notification directly to the device’s operating system, which then displays the notification to the user.
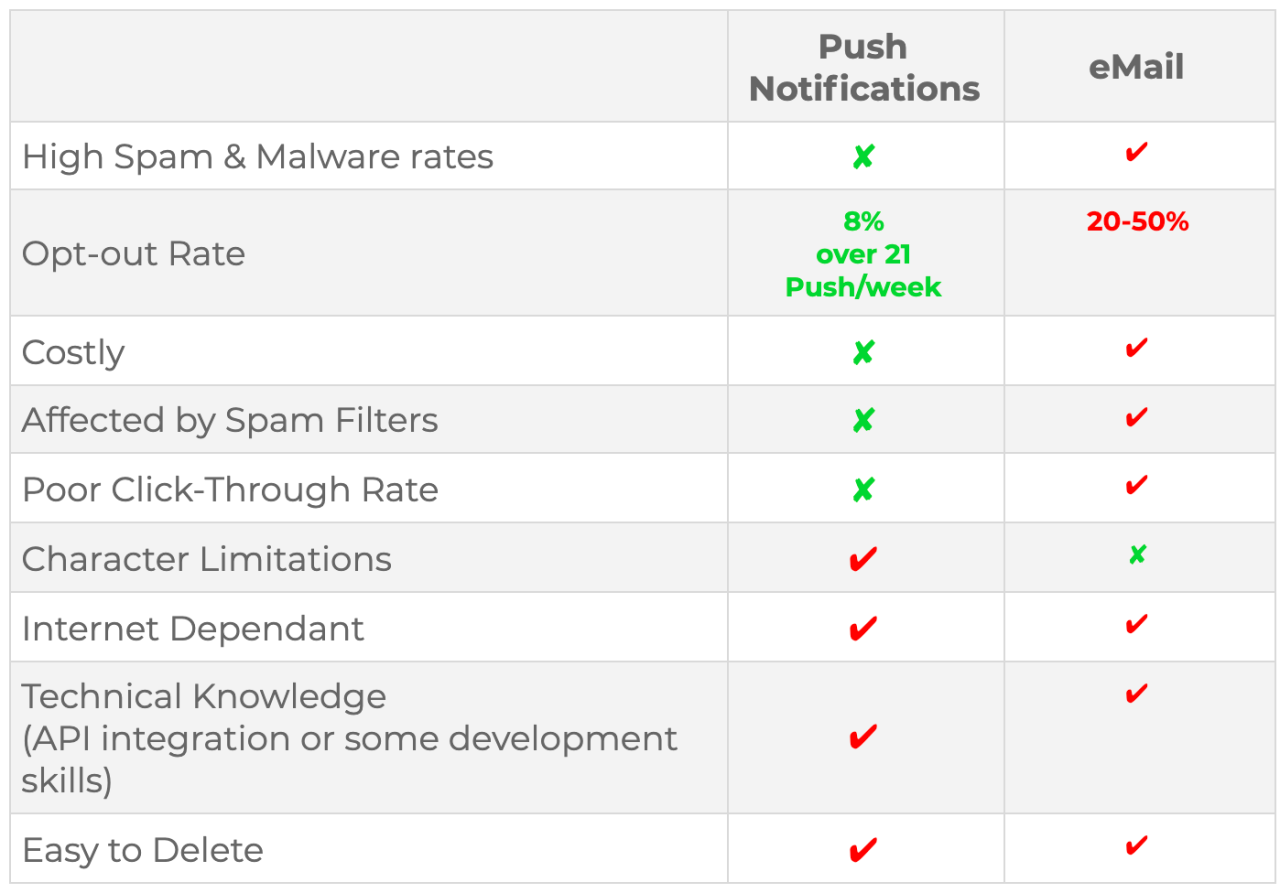
Comparison Table
| Feature | Push Notifications | |
|---|---|---|
| Delivery Speed | Slower; dependent on network conditions and server load. | Faster; delivered immediately upon triggering the event. |
| Reliability | Generally reliable, but potential delays or issues with server availability. | Highly dependent on network connectivity and application functionality. |
| Cost | Generally lower cost, especially for bulk emailing using a service like Mailchimp or similar tools. | Lower cost in many cases, as it avoids the complexity and infrastructure costs associated with email servers. |
Use Cases and Examples
Choosing between email and push notifications depends heavily on the specific communication goal. Understanding the nuances of each method allows for effective delivery of information and improved user experience. Emails are a powerful tool for detailed information, while push notifications are ideal for urgent or timely updates.This section explores typical use cases for both email and push notifications, illustrating when each method is the preferred choice.
Examples and a comparison table will highlight the differences and demonstrate how the best communication method can significantly impact user engagement and satisfaction.
Typical Email Use Cases
Email excels in situations requiring in-depth information, detailed instructions, or complex updates. These messages can be thoroughly crafted, allowing for a more comprehensive and engaging experience for the recipient. Consider this when deciding between email and push notifications.
- Transactional Emails: These emails are triggered by specific actions, such as order confirmations, password resets, or shipping updates. The detailed nature of this information necessitates the comprehensive approach of email. For example, a shipping update requires specifics about the carrier, tracking number, and estimated delivery date. This level of detail is better conveyed through an email than a push notification.
- Marketing Campaigns: Email campaigns are ideal for disseminating detailed information about promotions, product announcements, or company news. The ability to include rich media, detailed descriptions, and calls to action makes email a superior tool for engaging with customers and driving conversions. For example, an email announcing a new product line can feature high-quality images, detailed specifications, and a clear call to action to purchase.
- Complex Updates: Emails are well-suited for situations demanding thorough explanation and background context. These could include important policy changes, system updates, or detailed reports. For instance, an email outlining a new company policy can include explanations of the rationale, FAQs, and contact information for further inquiries. This comprehensive approach ensures clarity and reduces ambiguity.
Typical Push Notification Use Cases
Push notifications are the best choice for immediate and timely updates, especially when speed and urgency are crucial. These notifications provide immediate alerts, keeping users informed about important events as they happen. The limited space of push notifications makes them ideal for concise and urgent messages.
- Urgent Updates: Push notifications are perfect for critical alerts, such as security breaches, system failures, or account activity changes. These messages are vital to the user’s ongoing engagement and operational activities. For example, a security breach notification is vital to ensure that users can take immediate action to protect their accounts. The immediacy of a push notification is essential in this scenario.
- Real-time Events: Push notifications can alert users to real-time events, such as live updates, breaking news, or critical information changes. The immediacy of these notifications is critical for timely responses. For example, real-time updates on sports scores, concert announcements, or flight delays can be instantly shared through push notifications.
- Interactive Updates: Notifications can be used to provide timely updates or reminders for appointments, tasks, or important deadlines. This is an efficient way to keep users informed about upcoming events without disrupting their current tasks. For example, a reminder for a doctor’s appointment or a notification about an important task can help keep users on track.
Comparison Table
| Communication Type | Push Notifications | |
|---|---|---|
| Transactional Emails | Order confirmations, shipping updates, password resets. Detailed information is crucial. | Order confirmations (brief summary only). Urgent alerts related to the order. |
| Marketing Campaigns | Product announcements, promotions, newsletters. Comprehensive information, calls to action. | Promotional offers, limited-time deals. Incentives to drive immediate engagement. |
| Urgent Updates | System updates, policy changes, security breaches. Detailed explanations and context. | Security breaches, system failures, account activity changes. Immediate alerts. |
Examples Demonstrating Differences
Different scenarios illustrate the best approach. Emails provide in-depth information, while push notifications focus on timely alerts.
- A user placing an order online needs a detailed confirmation email with tracking information and potential delivery dates. A push notification might briefly confirm the order but not provide full details.
- A user subscribing to a newsletter receives an email detailing new articles and promotions. A push notification might alert the user to a new article or a special promotion, but not provide the complete article details.
- A user’s bank account is compromised. A push notification immediately alerts the user to the potential breach. A follow-up email provides detailed information about the breach and steps to take.
Pros and Cons of Each Method
Both email and push notifications have advantages and disadvantages depending on the situation.
- Email Pros: Comprehensive information, detailed explanations, rich media, and archiving capabilities. Cons: Can be less engaging, potentially missed in a cluttered inbox, and not ideal for real-time updates.
- Push Notification Pros: Immediate alerts, real-time updates, and high engagement potential. Cons: Limited space, potentially disruptive, and may not be appropriate for sensitive information.
User Experience and Engagement
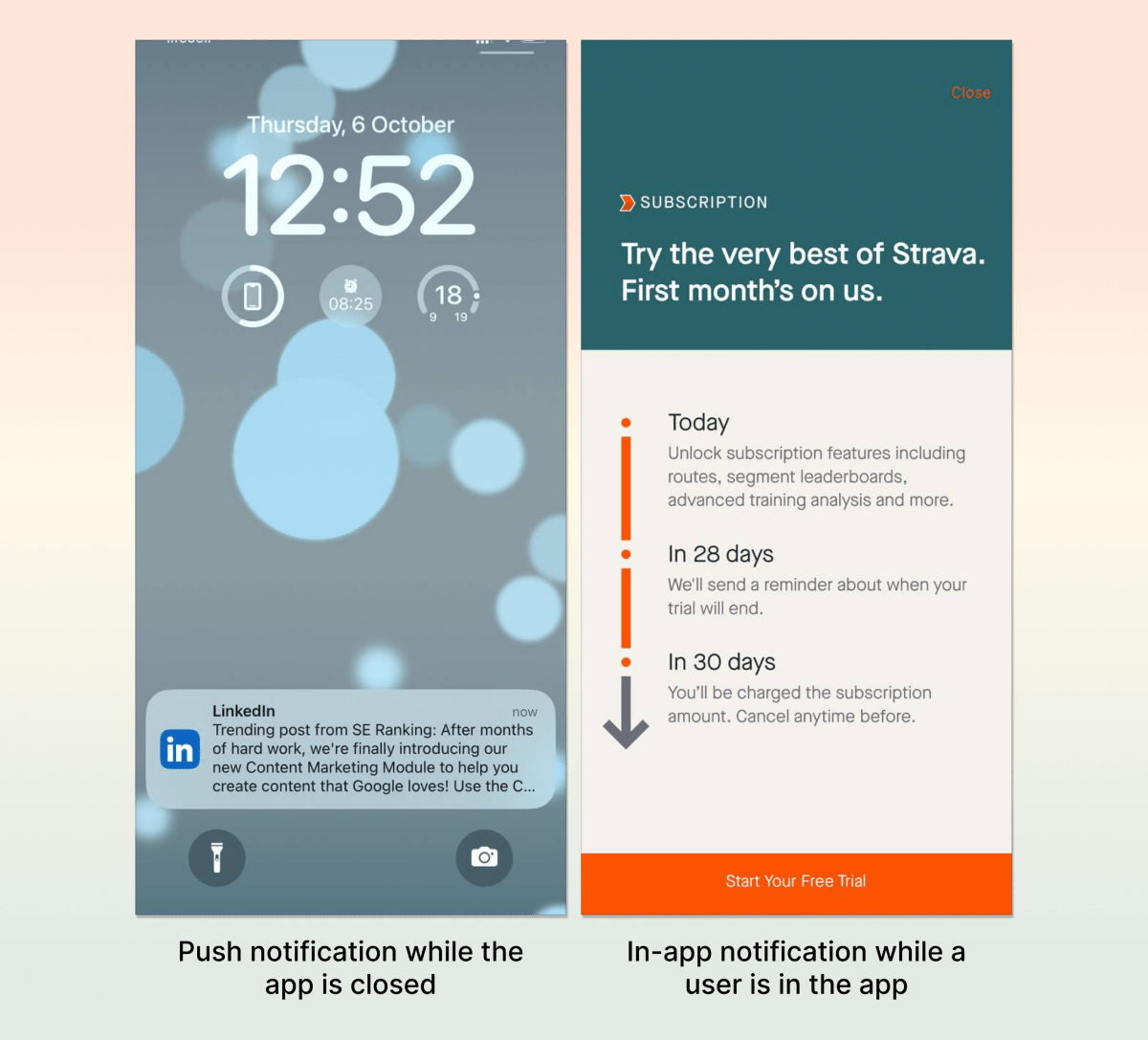
Email and push notifications are powerful tools for communication, but their effectiveness hinges on a positive user experience. Understanding how users interact with these channels is crucial for maximizing engagement and driving desired outcomes. A seamless and relevant experience fosters loyalty and encourages continued interaction with the platform.Effective communication channels prioritize the user experience, recognizing that a smooth and personalized interaction directly impacts user satisfaction and engagement.
A well-designed user experience minimizes friction and encourages users to actively engage with the content.
Impact of Email on User Engagement and Satisfaction
Email, a cornerstone of digital communication, plays a vital role in user engagement. Well-crafted emails, tailored to individual user needs and preferences, can nurture relationships, foster loyalty, and ultimately increase user satisfaction. Personalized subject lines, relevant content, and clear calls to action are key components in creating engaging email experiences. The ability to easily unsubscribe or manage preferences contributes to a positive user experience, showing respect for the user’s time and choices.
User Experience Aspects of Push Notifications
Push notifications, with their ability to deliver timely alerts and updates, can enhance user engagement. However, their impact is heavily influenced by the user’s perception of their intrusiveness. Users must find the notifications valuable and relevant to their needs. Overuse or irrelevant notifications can quickly lead to frustration and a negative user experience. Balancing the need for timely communication with respecting the user’s desire for control is paramount.
Choosing between email and push notifications can be tricky. Emails offer a more comprehensive way to communicate, but push notifications are great for immediate updates. However, consider your target audience’s behavior and engagement habits, as well as the nature of your content. A deeper dive into the SEO implications of different domain name extensions, like exploring the nuances of a .tech vs a .shop extension, can significantly impact how your message reaches your audience.
Check out this helpful guide to domain name extensions SEO guide to domain name extensions seo for more insights. Ultimately, the best strategy depends on your specific goals and your audience, making email vs. push notifications a constant balancing act.
Factors Affecting User Engagement with Email and Push Notifications
Several factors significantly influence user engagement with both email and push notifications. The relevance of the content, the frequency of communication, and the overall design of the communication channels are crucial. The ability to customize preferences, manage subscriptions, and provide clear unsubscribe options contribute positively to the user experience. Additionally, the perceived value of the information delivered plays a key role in user engagement, as users are more likely to engage with content they find useful or interesting.
Evaluating Effectiveness of Communication Channels
Evaluating the effectiveness of email and push notifications in relation to user engagement requires a multifaceted approach. Tracking key metrics such as open rates, click-through rates, and conversion rates for email campaigns provides valuable insights. For push notifications, measuring engagement through metrics like notification click-through rates and in-app activity following notification delivery offers a clear picture of their impact.
Choosing between email and push notifications for marketing can be tricky. While emails offer a more comprehensive approach, push notifications can be a great way to deliver timely updates, especially for a new app like new app peach what is the marketing potential for peach. Ultimately, the best strategy likely involves a combination of both, leveraging the strengths of each to maximize engagement.
A/B testing different approaches to communication can further refine strategies to optimize user engagement.
User Experience Comparison Table
| Feature | Email UX | Push Notification UX |
|---|---|---|
| Readability | Emails are generally designed for focused reading, allowing for detailed information and longer messages. Clear formatting and font choices enhance readability. | Push notifications are typically concise and prioritized for quick information intake. Short, impactful messages are crucial for effective communication. |
| Personalization | Emails offer significant opportunities for personalization, tailoring content based on user preferences, purchase history, and other relevant data. | Personalization in push notifications is often limited to specific user segments or targeted events, making it more difficult to offer truly personalized content. |
| Engagement | Engagement with emails is often measured by open rates, click-through rates, and conversions. Users have more control over their engagement with emails, making it a more deliberate interaction. | Engagement with push notifications is often measured by click-through rates and in-app activity. Push notifications are more intrusive, and engagement hinges on their perceived value and relevance to the user. |
Technical Aspects and Implementation: Email Vs Push Notifications
Diving into the nuts and bolts of email and push notification delivery reveals a fascinating interplay of design, infrastructure, and security. Understanding the technical underpinnings is crucial for crafting effective communication strategies that meet the specific needs of your application or service.The choice between email and push notifications isn’t merely a stylistic one; it’s a strategic decision based on factors like user engagement, device compatibility, and the nature of the information being communicated.
This section delves into the technical aspects, from constructing a basic email framework to establishing a robust push notification system.
Email Sending Framework
Email delivery relies on a robust framework that manages the entire process, from composing the message to ensuring its arrival in the recipient’s inbox. A basic framework would typically involve these stages:
- Message Composition: This involves crafting the email content, including subject line, body, attachments (if any), and metadata like sender and recipient information.
- Email Client Integration: A crucial step involves integrating with an email client library or API. This allows your application to compose and send emails, often using SMTP (Simple Mail Transfer Protocol).
- Email Server Interaction: Your application interacts with an email server, which is responsible for routing the email to the recipient’s mail server. This server handles tasks like authentication, message queuing, and delivery.
- Delivery Confirmation: A significant aspect is tracking email delivery. Mechanisms are in place to verify that the email has reached the recipient’s server successfully. Often, this involves receiving delivery receipts or using email server logs.
Push Notification System Setup
Setting up a push notification system involves integrating with a push notification service provider (like Firebase Cloud Messaging or Apple Push Notification service). This service handles the communication between your application and the user’s device.
- Registration and Authentication: Users must register their devices with the push notification service, enabling the service to send notifications to the specific device.
- Notification Creation: The application creates and sends notifications using the push notification service’s API. These notifications can vary in format, content, and urgency.
- Device Compatibility: Push notifications are tailored to specific operating systems (like iOS and Android). This often involves different APIs and protocols for different platforms.
- Error Handling: Robust error handling is crucial. The system needs to identify and address issues like failed deliveries or connection problems.
Technical Infrastructure
The infrastructure required for both methods varies significantly.
- Email: Requires an email server, possibly a dedicated SMTP server, and potentially an email marketing service for large-scale campaigns.
- Push Notifications: Relies on a push notification service provider’s infrastructure, which handles message delivery and device registration.
Security Considerations
Security is paramount in both email and push notification systems. Compromised systems can lead to significant risks.
- Email Security: Measures include email encryption (like PGP), sender authentication (SPF, DKIM, DMARC), and spam filtering to prevent unauthorized access and malicious content.
- Push Notification Security: Securing push notifications involves using secure communication channels, authenticating devices, and verifying sender identities to prevent unauthorized access and message interception.
Email Security Measures: Authentication protocols (SPF, DKIM, DMARC) to verify sender identity, encryption methods (PGP), and spam filters to block malicious content.Push Notification Security Measures: Secure communication channels (TLS/SSL), device authentication, and verification of sender identities to prevent unauthorized access and message interception.
Performance and Scalability
Email and push notifications, while seemingly simple, require careful consideration of performance and scalability, especially as user bases grow. Understanding the strengths and weaknesses of each method in handling increasing volumes of communication is crucial for building robust systems. Choosing the right channel for a specific task, like a one-time announcement vs. a continuous update stream, is key to optimizing the user experience and maintaining system health.The performance and scalability of communication channels directly affect the user experience.
A slow or unreliable system can lead to frustration and lost engagement. Conversely, a system that can handle high volumes of requests without degradation provides a seamless experience. This section will delve into the specifics of performance and scalability, comparing email and push notifications in detail.
Email Delivery Performance Across Platforms and Devices
Email delivery performance varies significantly depending on the recipient’s email provider, the email client used, and the user’s internet connection. Factors like server load, spam filters, and network congestion can all impact delivery time. Some email providers have better infrastructure and handle high volumes more effectively than others. A critical aspect is the complexity of the email itself; large attachments and intricate HTML formats can slow delivery and increase processing time.
Measuring Scalability of Email and Push Notifications
Scalability is assessed by monitoring key metrics such as delivery rate, open rate, click-through rate, and error rates. For email, these metrics can be tracked using email marketing platforms. For push notifications, tracking app usage and notification delivery through analytics tools provides comparable data. The ability to handle a growing number of users and messages without performance degradation is a primary indicator of scalability.
Testing with simulated user loads is a valuable tool to gauge system responsiveness under pressure.
Email Scalability Limitations
Email scalability has inherent limitations. Firstly, delivery times can be unpredictable and depend heavily on third-party factors. Secondly, high email volume can lead to issues with inbox management, potentially burying important messages under a deluge of others. Finally, emails require more processing power on the recipient’s end. This means that large-scale deployments could overwhelm mail servers and clients, leading to slower performance and user frustration.
The recipient’s email client configuration and internet connection also play a crucial role in determining the overall performance.
Push Notification Scalability Limitations
Push notifications, while often considered highly scalable, have limitations. Firstly, the number of concurrent notifications a device can handle is limited. Secondly, the user’s device, its battery life, and network connection impact the delivery and processing of notifications. Thirdly, some users might opt-out of push notifications for specific apps, reducing the effectiveness of the notification system. Lastly, high volumes of notifications might lead to a notification fatigue problem, where users ignore notifications because they are overwhelmed.
Scalability Considerations for Email and Push Notifications
A key scalability consideration is server infrastructure. Choosing the right email service provider (ESP) with appropriate server capacity is crucial for email. For push notifications, efficient backend systems that can handle high message volumes and manage user subscriptions are necessary. Efficient load balancing and redundancy are essential for both to ensure reliability during peak usage periods.
Methods to Improve Performance
To enhance email performance, use a reputable ESP with reliable infrastructure and optimized delivery protocols. Implementing strategies like message segmentation and targeted campaigns can enhance engagement. For push notifications, utilizing efficient message delivery mechanisms and optimizing app performance contribute to improved scalability. Regular monitoring of system performance indicators, such as message delivery times and error rates, is essential to identify and address potential bottlenecks.
Future Trends and Innovations
The digital landscape is constantly evolving, and email and push notifications are no exception. Emerging technologies are reshaping how we communicate, personalize experiences, and interact with digital services. This section explores the future of these two crucial communication channels, examining potential innovations and their impact.
AI-Powered Personalization
AI is revolutionizing how businesses tailor email campaigns and push notifications to individual user preferences. Sophisticated algorithms analyze user behavior, purchase history, and interactions to deliver highly relevant content. This personalized approach enhances user engagement and increases conversion rates. For example, an e-commerce platform might send targeted product recommendations via email based on browsing history, or a streaming service could use push notifications to alert users about new content tailored to their viewing habits.
Interactive Emails
The future of email communication is interactive. Emails are moving beyond static text and images to incorporate elements like quizzes, surveys, and clickable elements that engage users in a more dynamic way. Interactive emails can gather valuable feedback, improve customer understanding, and boost user engagement. For example, an airline might use an interactive email to allow passengers to select their preferred seating and meal options directly within the email itself.
Push Notification Segmentation
Push notifications are evolving beyond generic alerts to become more targeted and contextually relevant. Segmentation based on user behavior, device type, and location allows businesses to deliver notifications that are more likely to be seen and acted upon. For example, a restaurant might send a push notification about a special offer to users in the immediate vicinity, while a news publication might target specific user segments with relevant breaking news alerts.
Enhanced Security and Privacy
The increasing awareness of data privacy is driving innovations in email and push notification security. Advanced encryption techniques and secure communication protocols are becoming standard to protect user data from unauthorized access. This focus on security and privacy is crucial for building trust and maintaining user confidence in digital communication channels.
Table of Emerging Trends and Technologies
| Technology | Push Notifications | |
|---|---|---|
| AI-Powered Personalization | Dynamic content recommendations, personalized subject lines, tailored email segments | Personalized alerts based on user behavior, location, and device type |
| Interactive Emails | Interactive quizzes, clickable elements, surveys embedded in emails | Interactive push notifications with links to specific app features or content |
| Enhanced Security and Privacy | Advanced encryption protocols, secure email delivery systems | Secure push notification channels, enhanced data privacy settings |
Epilogue
Ultimately, the choice between email and push notifications depends on the specific needs of your application or website. Emails excel in providing detailed information and fostering long-term engagement, while push notifications are ideal for immediate updates and maintaining user interaction. This comprehensive analysis highlights the nuances of both methods, empowering you to make informed decisions about your communication strategy.