First Party Data Your Users, Your Insights
First party data is the goldmine of insights buried within your website traffic. It’s the direct feedback loop from your users, revealing their preferences, behaviors, and needs. Understanding this data isn’t just about marketing; it’s about creating a richer, more meaningful experience for your audience, and ultimately, driving sustainable growth. From simple website forms to complex survey data, this treasure trove of information offers unprecedented opportunities for personalization and deeper engagement.
This deep dive explores everything from defining and collecting first party data, to its practical applications in personalization, marketing, and product development. We’ll also touch upon the crucial aspects of data security and privacy, highlighting the importance of ethical considerations throughout the entire process. Get ready to unlock the power of your own user data and transform your business for the better!
Defining First-Party Data
First-party data is information directly collected by a company from its own customers. Unlike data gathered from third-party sources or purchased datasets, this data is rooted in direct interactions with the target audience. This gives businesses a unique opportunity to understand their customers’ needs and preferences, leading to more effective marketing strategies and improved customer relationships.This direct connection allows for a deeper understanding of customer behavior and preferences.
First party data is crucial for any marketer looking to understand their audience better. Recently, I was reading about the Ignite Marketer of the Week, Lara Hood Balazs, CMO & GM at Intuit, ignite marketer of the week lara hood balazs cmo gm at intuit , and her insights into leveraging first party data were particularly compelling.
Her experience highlights how crucial this data is for targeted campaigns and personalized customer journeys.
Companies can tailor their offerings and messaging to resonate more effectively with their specific customer base. This leads to a more personalized experience for customers and can ultimately drive higher conversion rates and customer loyalty.
First-party data is crucial for understanding your customers, right? It’s all about the insights you gather directly from them, like purchase history and website interactions. A great example of someone leveraging this data effectively is Darin Dugan, CMO of Jimmy Johns ( darin dugan cmo jimmy johns ). He’s clearly using first-party data to tailor marketing strategies and drive sales.
Ultimately, mastering first-party data is key to building strong customer relationships and a successful business.
Key Characteristics of First-Party Data
First-party data is distinguished from other data types by its origin and control. It’s collected directly by the company from its own customers, ensuring that the company owns the data and holds complete control over its use. This direct collection also allows for detailed tracking and understanding of customer behavior, enabling businesses to develop more accurate profiles and targeted campaigns.
Sources of First-Party Data
A wide range of sources contribute to a company’s first-party data. These sources are often integrated and combined to provide a complete picture of the customer.
- Website interactions: Website browsing history, page views, time spent on specific pages, and product searches are valuable sources of first-party data. This allows companies to understand what customers are interested in and how they navigate their website. For example, a clothing retailer can track which styles of clothing a customer views and what items are added to their cart, providing valuable insight into their preferences.
- App usage: Similarly, app usage data reveals valuable insights into user behavior and engagement. This includes features used, frequency of app access, and interactions within the app. A banking app can track the frequency of transactions, the types of financial products used, and the preferred communication methods.
- Customer surveys and feedback: Surveys and feedback forms directly solicit customer opinions and preferences. This allows companies to understand what aspects of their products or services resonate with customers and where improvements can be made. For example, a hotel chain could ask guests for feedback on their stay to identify areas for improvement in their services and amenities.
- Customer service interactions: Interactions with customer service representatives, such as calls, emails, and live chats, provide valuable insights into customer needs and problems. These interactions can reveal issues with a product or service that might not be apparent from other sources of data. For instance, a tech support team might learn about a specific software bug or recurring issue through customer service interactions.
Types of First-Party Data
The following table Artikels different types of first-party data, their sources, and their potential use cases.
| Data Type | Source | Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| Website browsing history | Website interactions | Understanding customer interests, identifying product preferences, optimizing website navigation |
| Purchase history | Online and in-store transactions | Personalized recommendations, targeted promotions, identifying customer segments |
| Customer demographics | Registration forms, surveys | Segmenting customers, tailoring marketing campaigns, understanding customer needs |
| Customer service interactions | Phone calls, emails, live chat | Identifying product issues, resolving customer complaints, understanding customer pain points |
| App usage data | App interactions | Identifying user needs, improving app features, personalizing user experience |
Collecting First-Party Data
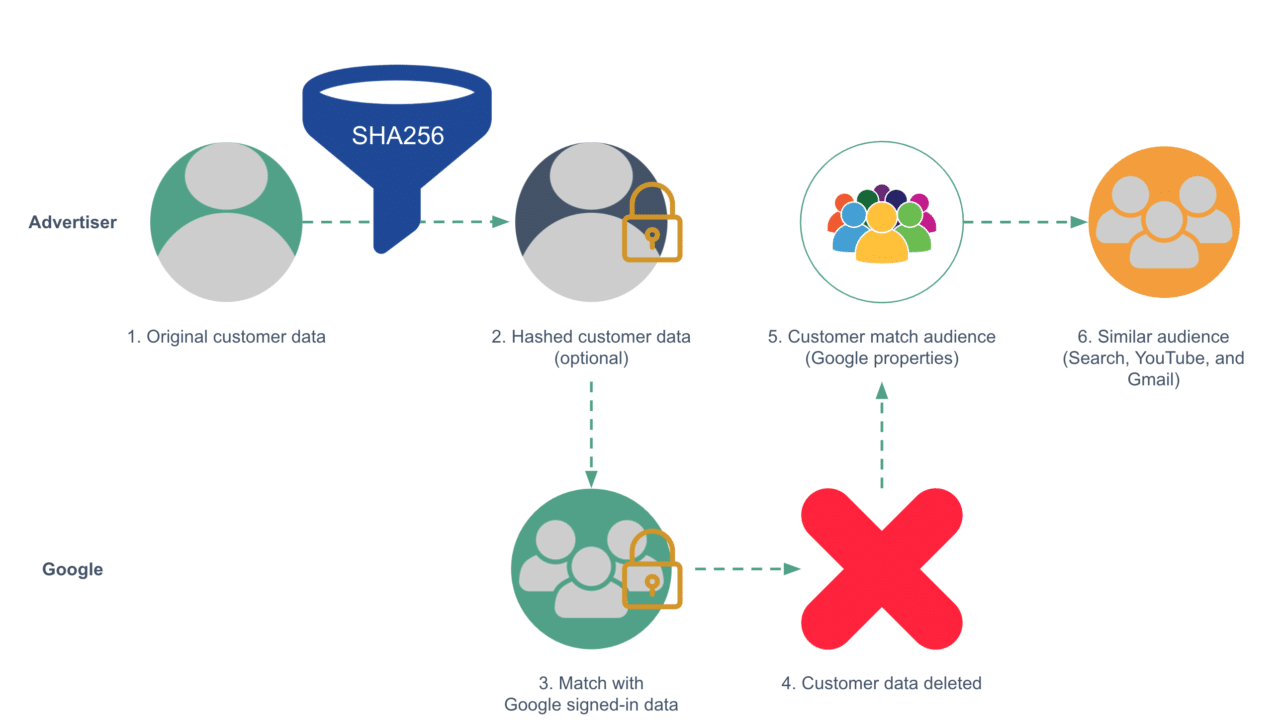
Gathering first-party data is a crucial aspect of building strong customer relationships and understanding user needs. It’s about directly collecting information from your audience, rather than relying on third-party sources. This direct interaction allows for a deeper, more personalized understanding of your customers, fostering loyalty and driving impactful business decisions.Effective first-party data collection is not just about gathering information; it’s about building trust and demonstrating respect for user privacy.
Ethical considerations, user consent, and clear data usage policies are paramount. This proactive approach not only strengthens customer relationships but also safeguards your brand reputation and complies with evolving data privacy regulations.
Best Practices for Ethical Data Collection
Ethical data collection prioritizes user consent and data privacy. Transparency is key. Users should be clearly informed about what data is being collected, how it will be used, and their rights regarding their data. This includes providing clear opt-in and opt-out options, ensuring data security, and respecting user preferences.
Importance of User Consent and Data Privacy
User consent is fundamental to ethical data collection. Users must explicitly agree to the collection and use of their data. This consent must be freely given, specific, informed, and unambiguous. Moreover, data privacy policies must be comprehensive and easily accessible, outlining how collected data will be protected and used. Clear and concise language is essential to ensure understanding.
Different Methods for Collecting First-Party Data
Various methods exist for collecting first-party data, each with its own strengths and weaknesses. The choice of method should align with your business goals and the type of information you need. A multi-faceted approach, employing several methods, often yields the most comprehensive insights.
- Forms: Well-designed forms can efficiently gather structured data, such as contact information, preferences, and demographics. Form fields should be concise and relevant, minimizing user frustration and maximizing data quality. Clear labels and instructions improve the user experience and data accuracy.
- Surveys: Surveys provide valuable insights into user opinions, feedback, and motivations. Questions should be carefully crafted to avoid bias and encourage honest responses. Incentivizing participation can increase response rates, though transparency about how the incentives are used is essential.
- Website Tracking: Website tracking methods, like cookies and analytics platforms, can track user behavior on your site. This data reveals patterns in user interaction, allowing for improvements in site design and user experience. Careful consideration of privacy implications is critical. Clear opt-out options are essential to respect user choices. Using only necessary data points is also important to reduce the data collected.
Legal and Ethical Considerations in Data Collection
Adhering to relevant data protection regulations, like GDPR and CCPA, is crucial. These regulations establish standards for data collection, storage, and usage. Understanding and complying with these regulations ensures legal compliance and protects user rights. It is essential to consult with legal experts to ensure compliance with all relevant regulations.
Comparison of Data Collection Methods
| Method | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|
| Forms | Efficient for structured data; direct control over questions; customizable; low cost. | Can be time-consuming for users; limited to structured information; potential for low response rates if not user-friendly. |
| Surveys | Gather insights into user opinions and feedback; uncover deeper understanding of motivations; good for feedback collection. | Can be complex to design and analyze; may take longer to complete; potential for bias in questions. |
| Website Tracking | Provides insights into user behavior; allows for personalized experiences; helps in improving site performance. | Privacy concerns are significant; user consent is crucial; may violate privacy regulations if not implemented correctly. |
Utilizing First-Party Data

First-party data, meticulously collected directly from your customers, holds immense potential for businesses seeking to foster stronger relationships, enhance customer experiences, and drive profitable growth. This data, unlike third-party data, provides a deep understanding of your specific customer base, allowing for tailored interactions and targeted strategies. Leveraging this valuable asset is no longer optional; it’s crucial for staying competitive in today’s market.Understanding your customer’s preferences, behaviors, and needs allows for a more personalized and relevant approach to marketing and product development.
This understanding fuels more effective campaigns, higher conversion rates, and ultimately, increased profitability.
Personalization and Targeted Marketing
First-party data enables highly targeted marketing campaigns. By understanding individual customer preferences, companies can tailor messages and offers to resonate with specific needs. For instance, a clothing retailer might send a personalized email recommending products based on past purchases and browsing history. This targeted approach increases the likelihood of conversions and fosters a sense of connection. The key is recognizing that customers appreciate relevant interactions rather than generic advertisements.
Improving Customer Experiences, First party data
First-party data provides invaluable insights into customer pain points and preferences. Analyzing this data can identify areas where customer journeys can be optimized. For example, a travel agency could use data on customer booking habits to streamline the booking process, offering seamless navigation and personalized recommendations. Such proactive improvements create a more positive and efficient customer experience, increasing customer satisfaction and loyalty.
Building Customer Relationships
By understanding customer preferences and behaviors, companies can build stronger relationships. This data enables businesses to anticipate customer needs and provide proactive support. For instance, a software company might use data on usage patterns to proactively offer assistance and address potential issues before the customer encounters them. Proactive support cultivates trust and fosters loyalty, turning customers into brand advocates.
Product Development and Improvement
First-party data is invaluable for product development and improvement. Analyzing purchase patterns, usage trends, and feedback reveals insights into customer needs and desires. A coffee shop, for example, might use data on customer orders to identify popular combinations and develop new specialty drinks. This data-driven approach can help create products that directly address customer needs, resulting in higher satisfaction and increased sales.
Table of First-Party Data Uses
| Use | Target Audience | Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Personalized Recommendations | Existing Customers | Increased sales, higher customer satisfaction, stronger customer relationships |
| Targeted Marketing Campaigns | Potential Customers | Higher conversion rates, improved ROI on marketing campaigns, increased brand awareness |
| Improved Customer Onboarding | New Customers | Faster adoption of products/services, reduced customer support requests, higher customer retention |
| Proactive Customer Support | Existing Customers | Enhanced customer experience, increased customer loyalty, reduced customer churn |
| Product Development Insights | All Customers | Improved product features, development of new products that cater to customer needs, higher customer satisfaction |
Security and Privacy of First-Party Data
Protecting first-party data is paramount for building trust with customers and maintaining a strong business reputation. Data breaches can have severe financial and reputational consequences, leading to customer churn, legal repercussions, and a loss of market share. Robust security measures are not just a best practice; they are a necessity in today’s digital landscape.Data security measures are crucial for safeguarding first-party data, preventing unauthorized access, and maintaining data integrity.
Effective security protocols mitigate the risk of breaches and safeguard sensitive information, protecting both the business and its customers. Implementing these measures is not just about compliance; it’s about demonstrating a commitment to responsible data handling.
Importance of Data Security Measures
Data security measures are essential for safeguarding first-party data, protecting customer privacy, and maintaining the integrity of the data. Strong security measures create a reliable environment for data collection and use, minimizing the risk of unauthorized access and breaches. Robust protocols are vital for maintaining trust with customers and ensuring compliance with regulations.
First party data is gold, right? Knowing your audience intimately is key to crafting effective campaigns. This translates directly into better SMS marketing strategies. For example, using data to personalize text messages can boost open and click-through rates. You can use this valuable information to segment your audience for tailored campaigns within your sms marketing efforts.
Ultimately, understanding your customers through first party data is the best way to make your marketing truly resonate.
Methods for Ensuring Data Integrity and Confidentiality
Several methods contribute to data integrity and confidentiality. Data encryption, access controls, and secure storage are critical components. Implementing strong passwords, multi-factor authentication, and regular security audits are crucial steps in safeguarding data.
Role of Data Encryption and Access Controls
Data encryption is a fundamental method for protecting data confidentiality. It transforms readable data into an unreadable format, making it inaccessible to unauthorized individuals. Access controls restrict data access to authorized personnel, limiting the potential damage from a security breach. This approach ensures only authorized users can access and manipulate the data.
Examples of Data Breaches and Their Impact on Businesses
Numerous data breaches have demonstrated the devastating impact on businesses. For instance, the 2017 Equifax breach exposed sensitive information of millions of consumers, leading to significant financial and reputational damage. This example underscores the importance of proactively addressing data security risks. Another example is the recent Target data breach, which highlighted the vulnerability of retail businesses to sophisticated cyberattacks.
The impact of these breaches goes beyond financial losses; it erodes customer trust and can lead to long-term reputational damage.
Data Breach Handling Procedure and User Privacy Protection
A well-defined procedure for handling data breaches is essential. This procedure should include steps for immediate notification of affected individuals, investigation of the breach, and implementation of remedial measures. Protecting user privacy involves ensuring compliance with data protection regulations, such as GDPR, CCPA, and others. This includes obtaining explicit consent for data collection and use, providing clear data privacy policies, and enabling user data access and control.
Security Measures and Effectiveness
Implementing comprehensive security measures requires a structured approach. This table Artikels various security measures, their effectiveness, and implementation considerations.
| Measure | Effectiveness | Implementation |
|---|---|---|
| Strong Passwords | High | Enforce complex password policies, regular password changes, and multi-factor authentication. |
| Multi-Factor Authentication | High | Implement MFA for all user accounts, including administrative accounts. |
| Data Encryption | High | Encrypt sensitive data both in transit and at rest. |
| Regular Security Audits | Medium | Conduct regular security assessments and penetration testing to identify vulnerabilities. |
| Access Controls | High | Implement strict access controls to limit access to sensitive data based on user roles and responsibilities. |
| Secure Network Infrastructure | High | Maintain a secure network infrastructure with firewalls and intrusion detection systems. |
First-Party Data and Emerging Technologies
First-party data, collected directly from customers, is increasingly vital in today’s digital landscape. This direct connection allows businesses to understand customer needs and preferences with unprecedented accuracy. Emerging technologies like AI and machine learning are revolutionizing how companies utilize this valuable data, opening new avenues for innovation and personalized experiences.The power of first-party data is amplified by these advancements.
Companies can now leverage sophisticated algorithms to uncover deeper insights, personalize interactions, and predict future behaviors, ultimately driving better business outcomes. This creates a more robust and meaningful connection between businesses and their customers.
Impact of AI and Machine Learning on First-Party Data
AI and machine learning algorithms are transforming the way businesses analyze and utilize first-party data. These tools can process vast quantities of data at lightning speed, identifying patterns and correlations that would be impossible for humans to discern. This enables businesses to make more informed decisions about product development, marketing strategies, and customer service.
Potential of First-Party Data in Driving Innovation
First-party data holds immense potential for driving innovation across various industries. By understanding customer preferences and behaviors in detail, businesses can develop new products and services tailored to specific needs. This leads to a more customer-centric approach, fostering loyalty and driving revenue growth.
Examples of AI in Analyzing First-Party Data
AI can be used to analyze first-party data in a variety of ways. For instance, businesses can use AI-powered recommendation engines to suggest products or services that customers are likely to purchase based on their past behavior and preferences. This can significantly improve conversion rates and customer satisfaction. Furthermore, sentiment analysis tools can be used to gauge customer satisfaction and identify areas for improvement in products or services.
Personalization of User Experiences with First-Party Data
Personalization is a key benefit of leveraging first-party data. By understanding individual customer preferences, businesses can tailor their digital platforms to provide highly relevant and engaging experiences. This includes personalized recommendations, customized content, and targeted offers, all of which contribute to enhanced customer satisfaction and loyalty.
Comparison of Technologies for Handling First-Party Data
Different technologies offer varying advantages and disadvantages for handling first-party data. Cloud-based solutions, for instance, provide scalability and cost-effectiveness for managing large datasets. However, security concerns and potential data breaches are important considerations. On the other hand, on-premises solutions offer greater control over data security but may be more expensive and require significant infrastructure investment.
Challenges and Considerations: First Party Data
Navigating the world of first-party data presents a unique set of challenges, particularly in the complexities of collection, management, and utilization. Understanding these obstacles is crucial for businesses to effectively leverage first-party data and avoid pitfalls. Successful implementation relies on proactive strategies to address potential issues and optimize the value derived from this valuable asset.
Data Volume, Velocity, and Variety
Managing the sheer volume of first-party data, the rapid pace at which it’s generated (velocity), and the diverse formats in which it exists (variety) presents significant obstacles. Companies must implement robust data infrastructure to store, process, and analyze this data efficiently. Failure to adapt to these evolving characteristics can result in data silos and hindered insights. The sheer amount of data, its rapid influx, and the varied formats often require specialized tools and skilled personnel to effectively manage.
Data Integration Challenges
Integrating first-party data with other data sources, such as CRM data, marketing automation platforms, and third-party data, is another key challenge. Data silos and differing formats often create compatibility issues. A lack of standardized data structures can lead to errors in analysis and hinder the development of a unified view of the customer. Addressing these issues requires a meticulous approach to data mapping and transformation to ensure seamless integration and avoid inconsistencies.
Impact of Data Governance Policies
Data governance policies, encompassing data quality, access controls, and privacy regulations, significantly influence first-party data management. Implementing and adhering to these policies is critical for maintaining data integrity and compliance. Rigorous data governance frameworks, with clearly defined roles and responsibilities, are essential to ensure data quality and security. This also helps prevent data breaches and maintain customer trust.
Successful and Unsuccessful Strategies
Successful strategies for leveraging first-party data often involve a focus on personalization and targeted marketing campaigns. For example, companies that successfully segment their customer base based on first-party data often see a significant increase in conversion rates and customer lifetime value. Conversely, businesses that fail to prioritize data quality or lack a clear strategy for utilizing the data often see limited return on investment.
Poor data quality, incomplete data sets, and a lack of analysis can lead to inaccurate insights and ineffective marketing campaigns.
Challenges in Collecting First-Party Data
Collecting high-quality first-party data can be challenging. Obtaining explicit consent for data collection and ensuring data accuracy are paramount. Ensuring data accuracy and compliance with privacy regulations, like GDPR or CCPA, are critical. The need for explicit consent, compliance with regulations, and addressing potential privacy concerns must be considered.
- Data Collection Methods: Finding the right balance between collecting data from various channels (website, app, email, etc.) and ensuring the data is comprehensive and relevant.
- Data Accuracy: Ensuring the data collected is correct and consistent to avoid misleading insights. Regular data cleansing and validation are essential.
- Data Privacy and Security: Complying with data privacy regulations and ensuring data security to maintain customer trust.
Concluding Remarks
In conclusion, first party data provides a direct line to understanding your users. By ethically collecting, analyzing, and securing this valuable information, businesses can unlock significant advantages in personalization, marketing, and product development. This data, when handled responsibly, can build stronger customer relationships and create truly exceptional experiences. The potential for innovation and growth is immense, making first party data an essential asset in today’s digital landscape.