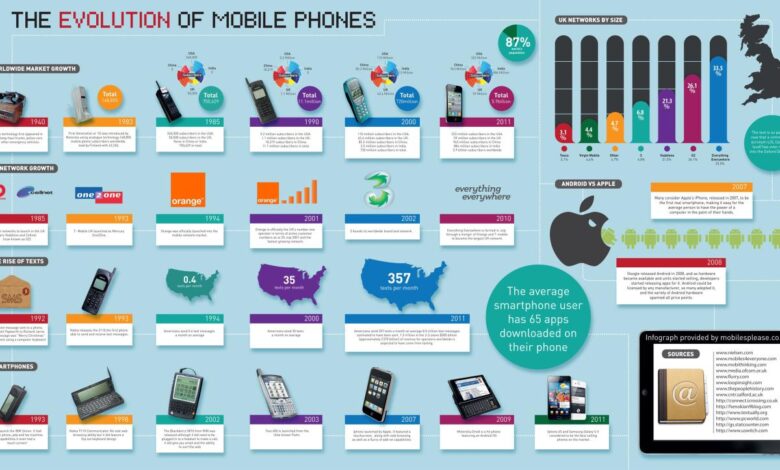
The History of the Smartphone Infographic A Journey Through Time
The history of the smartphone infographic unveils a fascinating journey through the evolution of mobile technology. From the early concepts and precursors to the defining characteristics of the first smartphones, this visual exploration takes us on a ride through key milestones and innovations, examining their cultural and societal impact. We’ll delve into the technological advancements that shaped the modern smartphone, from its humble beginnings to the cutting-edge innovations of today and tomorrow.
Get ready to see how smartphones have transformed our lives, with an infographic that brings it all to life.
This infographic provides a comprehensive overview of the smartphone’s evolution, showcasing its technological progress, cultural influence, and future prospects. It’s a visual feast for anyone interested in the history of technology and its impact on society.
Early Concepts and Precursors
The journey to the modern smartphone wasn’t a sudden leap. It was a gradual evolution, built upon a foundation of innovative ideas and technological advancements across decades. From rudimentary communication devices to the concept of personal computing, the path to handheld computing was paved with intriguing milestones. This section delves into the early phases, highlighting the key concepts and inventions that laid the groundwork for the mobile revolution.The development of the smartphone wasn’t a single event, but a confluence of innovations across various fields.
Early concepts and devices often suffered from limitations in processing power, battery life, and display technology, but they set the stage for future advancements.
Timeline of Key Inventions
Early attempts at mobile communication and computing were often large, bulky, and expensive. These devices, while limited by today’s standards, demonstrate the persistent human desire for portable communication and information access.
- 1940s – 1950s: The concept of mobile communication began to take shape, with the development of early mobile radio technologies. These systems, though primarily used for specialized purposes like emergency services and military communication, were the first steps toward a more pervasive mobile network. The large, bulky equipment required for these early systems highlighted the need for miniaturization and improved power efficiency.
- 1960s: The invention of the transistor revolutionized electronics. Its smaller size and lower power consumption compared to vacuum tubes opened the door for more compact and portable devices. This paved the way for the development of more sophisticated mobile communication systems. Transistors were crucial in the transition from bulky to more manageable equipment.
- 1970s: Integrated circuits (ICs) further miniaturized electronic components. This significant advancement enabled the packing of multiple transistors and other components onto a single chip, significantly reducing the size and cost of electronic devices. This miniaturization was essential for the future creation of portable computers.
- 1973: The first handheld mobile phone call was made. This momentous event marked a critical milestone in the history of personal communication, although the technology remained expensive and limited.
- 1980s: The first generation (1G) of mobile phones emerged. These early cellular networks allowed for basic voice communication, but the technology was still relatively primitive. The limited bandwidth and features meant that these devices were far from the sophisticated smartphones of today.
- 1990s: The second generation (2G) of mobile phones introduced text messaging and improved data transmission. This marked a significant step towards more versatile communication, allowing for data transfer beyond simple voice calls. The introduction of SMS changed the way people communicated, foreshadowing the rise of mobile messaging apps.
Key Technological Advancements
The progress from simple radio communication to sophisticated smartphones was driven by crucial technological breakthroughs. These advancements enabled the integration of computing capabilities into mobile devices.
- Transistors: The invention of the transistor was a pivotal moment, enabling smaller, more efficient, and reliable electronic components. This allowed for more complex circuits to be integrated into smaller packages, which was essential for the development of portable devices. The smaller size and lower power consumption of transistors compared to vacuum tubes were key in making portable electronics possible.
- Integrated Circuits (ICs): Integrated circuits allowed for the integration of multiple transistors and other components onto a single chip. This miniaturization was crucial for the development of more powerful and compact computing devices. The ability to pack significant processing power onto a single chip was essential for creating handheld computers.
- Microprocessors: The development of increasingly powerful microprocessors allowed for the integration of computing capabilities into portable devices. These chips provided the processing power needed to handle complex tasks, from calculations to running applications. The ability to execute complex instructions in a portable format was crucial for creating the computing power found in modern smartphones.
Early Mobile Communication Devices
Early mobile communication devices, while rudimentary compared to modern smartphones, were the building blocks of today’s technology.
- Limitations of Early Devices: Early mobile communication devices often suffered from limitations in battery life, display size, processing power, and storage capacity. These limitations highlighted the challenges of creating truly portable and useful computing devices.
- Examples: Examples include the DynaTAC 8000x, a first generation mobile phone, and various pagers. These devices demonstrated the feasibility of mobile communication but were limited in functionality and usability compared to smartphones.
Evolution of Mobile Phones, The history of the smartphone infographic
The evolution of mobile phones can be categorized into distinct phases, each characterized by advancements in technology and capabilities.
| Phase | Characteristics |
|---|---|
| Early Mobile Phones (1G) | Basic voice communication, limited functionality. |
| Second Generation (2G) | Introduction of text messaging (SMS) and improved data transmission. |
| Third Generation (3G) | Enhanced data speeds, enabling multimedia applications. |
| Fourth Generation (4G) | Faster data speeds, improved connectivity, enabling more demanding applications. |
| Fifth Generation (5G) | Ultra-fast data speeds, enabling a new range of applications and services. |
The Birth of the Smartphone: The History Of The Smartphone Infographic

The dawn of the smartphone wasn’t a single event, but rather a gradual evolution from the basic mobile phones of the past. Early mobile phones, primarily focused on voice communication, lacked the processing power and capabilities to handle the complex functions that define modern smartphones. This shift toward a unified device for communication, computing, and entertainment marked a turning point in personal technology.The key differentiator between early mobile phones and the first smartphones was their expanded functionality.
Smartphones combined mobile phone capabilities with computing power, internet access, and a wide range of applications, making them far more versatile and useful than their predecessors. This transition wasn’t just about adding features; it was about integrating them seamlessly into a single device.
Defining Characteristics of Early Smartphones
Early smartphones distinguished themselves from traditional mobile phones through a combination of factors. They offered more processing power, allowing for complex tasks like email, web browsing, and rudimentary applications. Larger displays enabled a more user-friendly interface and access to more information. The inclusion of a touchscreen interface, often initially resistive, revolutionized how users interacted with the device.
The integration of a robust operating system that managed the different applications was crucial.
Key Companies and Individuals
Several companies and individuals played pivotal roles in the development of early smartphones. Nokia, with its early foray into touchscreen devices, laid some of the groundwork. Research In Motion (RIM) pioneered the use of a unique operating system, Blackberry OS, that initially focused on email communication. Apple, with the introduction of the iPhone, fundamentally reshaped the smartphone market, and brought innovative user experience to the forefront.
Key figures, such as Steve Jobs at Apple, are credited with shaping the vision and design of these early smartphones.
Impact of Internet and Mobile Data Networks
The proliferation of the internet and the development of 2G and 3G mobile data networks were crucial to the smartphone’s rise. The availability of internet connectivity allowed for access to a vast amount of information and applications, significantly increasing the utility of smartphones. Increased mobile data speeds enabled more seamless and responsive browsing, streaming, and application usage. Early mobile internet usage and data plans were often expensive and limited, but they paved the way for the future expansion of mobile data services and applications.
Early Smartphone Operating Systems
The initial operating systems for smartphones were diverse, reflecting the varied approaches of different manufacturers. Symbian, used by Nokia’s early smartphones, offered a platform for developers to create applications. BlackBerry’s operating system focused on email and messaging, while Palm OS, used in devices like the Palm Treo, emphasized personal organization. These systems laid the foundation for the modern operating systems we see today.
- Symbian OS, developed by Symbian Ltd., was one of the earliest operating systems for smartphones. It provided a platform for developers to create applications, but it also faced challenges in terms of memory management and performance, particularly as the demands of applications grew.
- BlackBerry OS, developed by Research In Motion (RIM), focused on email and messaging. Its strength was in its robust email capabilities, which made it popular with business users. The physical keyboard was a key part of its initial design.
- Palm OS, used in devices like the Palm Treo, was known for its focus on personal organization. It offered a unique interface that focused on task management and calendar functionality.
Key Milestones and Innovations
The smartphone journey isn’t just about incremental improvements; it’s a series of groundbreaking leaps forward. From the initial concept of a pocket-sized computer to the sophisticated devices we use today, each milestone represents a significant advancement in technology and design. These pivotal moments have not only reshaped communication but also profoundly influenced how we live, work, and interact with the world around us.The evolution of smartphones is a tapestry woven from technological breakthroughs and market responses.
The adoption of specific features, such as touchscreens, app stores, and high-resolution cameras, has been driven by consumer demand and the need to address existing limitations in mobile technology. This dynamic interplay between innovation and consumer expectation is crucial in understanding the smartphone’s trajectory.
Touchscreen Technology
The transition from physical buttons to touchscreens marked a turning point in smartphone design. Early touchscreen devices, while functional, often suffered from limited responsiveness and accuracy. However, advancements in display technology, including capacitive touchscreens, dramatically improved the user experience. This shift allowed for more intuitive interaction, paving the way for a wider range of applications and functions.
The introduction of multi-touch gestures further refined user control and fluidity, making smartphones more user-friendly.
App Stores and the Rise of Software
The introduction of dedicated app stores revolutionized the smartphone experience. No longer limited to pre-installed applications, users gained access to a vast and diverse ecosystem of software, catering to various needs and interests. This democratization of software access spurred innovation and creativity, creating an environment where developers could build and monetize their creations. The app store model also incentivized companies to develop user-friendly interfaces and robust software platforms to support the growing number of apps.
High-Resolution Cameras
The integration of high-resolution cameras into smartphones fundamentally changed how we capture and share moments. Early mobile cameras, while usable, often produced images of lower quality compared to dedicated cameras. The rapid advancement in sensor technology and image processing algorithms has enabled smartphones to capture stunning photographs and videos, blurring the lines between dedicated cameras and mobile devices.
This trend reflects a growing consumer demand for convenience and portability in capturing and sharing visual content.
Operating System Evolution
Smartphone operating systems have undergone significant evolution, shaping the market landscape and user experiences. Early mobile operating systems, like Symbian and Palm OS, were foundational to the smartphone industry, setting the stage for future developments. However, the rise of iOS and Android has dramatically reshaped the market. The competition between these platforms has driven innovation, resulting in advanced features and a rich ecosystem of applications.
The market share dynamics of these operating systems have shifted over time, reflecting consumer preferences and technological advancements.
Key Hardware Innovations
The performance and functionality of smartphones have been significantly impacted by advancements in hardware components. These advancements include faster processors, higher resolution displays, and improved battery technology. More powerful processors enable smoother multitasking and more demanding applications. Higher-resolution displays provide a richer visual experience, while improved battery technology extends the lifespan of devices between charges. These advancements demonstrate a relentless pursuit of performance and efficiency in smartphone hardware.
Design and Adoption
Specific design choices have played a significant role in shaping smartphone adoption rates. The balance between form factor, functionality, and usability has driven the evolution of smartphone design. Features like slimmer profiles, ergonomic shapes, and improved durability have contributed to a greater sense of user comfort and convenience. The influence of these design choices has been substantial, impacting the overall appeal and desirability of smartphones in the marketplace.
Cultural and Societal Impact
The smartphone’s pervasive influence has fundamentally reshaped how we live, work, and interact. From revolutionizing communication to transforming industries, its impact is profound and multifaceted. This transformation is not simply technological; it’s a societal shift, impacting our daily routines and shaping our future.The smartphone has become an indispensable tool, seamlessly integrating into nearly every facet of modern life.
This integration has profound effects on communication patterns, social interactions, work-life balance, and the very structure of businesses and industries. The once-separate worlds of personal and professional life have blurred, creating new opportunities and challenges.
Transformation of Communication Patterns and Social Interactions
Smartphones have dramatically altered how we communicate. Instant messaging, social media, and video calls have become the norm, fostering a culture of constant connectivity. While this connectivity has undeniable benefits, it also raises concerns about social isolation, cyberbullying, and the potential for addiction. The immediacy of communication often leads to shorter attention spans and a less nuanced approach to interpersonal relationships.
Ever wondered how smartphones evolved? A cool infographic on the history of smartphones really highlights the tech leaps. It’s fascinating how far we’ve come, and the progression is quite evident. It’s also interesting to note that someone like Eric Lempel, senior vice president of marketing and head of PlayStation Network , is a key player in shaping the marketing strategies behind today’s tech giants.
Ultimately, the infographic gives a great overview of the smartphone journey.
Effects on Work and Personal Life
The smartphone has blurred the lines between work and personal life, creating a constant state of accessibility. This can lead to increased productivity, but also to burnout and reduced work-life balance. The constant stream of notifications and emails can create a feeling of being “always on,” impacting personal time and well-being.
Emergence of Mobile-First Businesses and Industries
The smartphone’s ubiquity has spurred the emergence of mobile-first businesses and industries. Companies are recognizing the importance of a seamless mobile experience, adapting their products and services to fit the needs of users. This shift has led to the rise of apps for virtually every aspect of daily life, from ordering food to managing finances. Mobile commerce has exploded, and businesses are constantly innovating to meet the demands of this evolving market.
Changes in Daily Life
The table below illustrates how smartphones have transformed various aspects of daily life. The impact on entertainment, news consumption, and shopping is readily apparent, but the effect on other aspects, such as banking and healthcare, is equally significant.
| Aspect of Daily Life | Before Smartphones | With Smartphones | Impact Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Entertainment | Limited to physical media (CDs, DVDs, etc.), local events, and occasional TV/radio | Streaming services, mobile games, social media engagement | Entertainment has become highly personalized and readily available anytime, anywhere. |
| News Consumption | Reliant on newspapers, radio, and television broadcasts | Real-time updates via news apps, social media, and personalized feeds | News consumption has become immediate and tailored to individual preferences. |
| Shopping | Limited to physical stores and mail-order catalogs | Online shopping via mobile apps, e-commerce platforms, and targeted ads | Shopping has become highly convenient and accessible, offering a vast selection of products. |
| Banking and Finance | In-person transactions at banks, ATM use, and limited online banking | Mobile banking apps, online transfers, and payment systems like Apple Pay | Financial transactions are now incredibly convenient and accessible on the go. |
| Healthcare | Appointments, prescriptions, and medical records managed through physical interactions | Telemedicine, mobile health apps, and wearable devices for monitoring health | Healthcare access and management have become more accessible and convenient through remote tools and technologies. |
Technological Advancements
The smartphone’s journey isn’t just about evolving form factors and user interfaces; it’s a relentless race to improve underlying technologies. From processing power to connectivity, advancements have been instrumental in shaping the modern mobile experience. This evolution has been driven by the insatiable demand for faster performance, greater capabilities, and seamless integration with our lives.The relentless pursuit of performance has pushed the boundaries of what’s possible in a pocket-sized device.
The evolution of mobile hardware has dramatically impacted the functionality and capabilities of smartphones, making them far more than just communication tools.
Mobile Processors
Mobile processors have undergone a remarkable transformation. Early smartphones relied on relatively basic processors, limiting their capabilities. The progression has been characterized by a dramatic increase in clock speeds, core counts, and integrated graphics processing units (GPUs). This has allowed for more complex tasks, smoother user interfaces, and the execution of demanding applications. Modern processors can handle sophisticated gaming, video editing, and augmented reality experiences, a stark contrast to the limitations of earlier generations.
Memory and Storage
Memory and storage capacities have also dramatically increased. Early smartphones often struggled with limited RAM, leading to performance issues and application instability. The surge in memory and storage has enabled multitasking, smoother transitions between applications, and the ability to store vast amounts of data, including high-resolution photos, videos, and large files. Today, gigabytes of RAM and terabytes of storage are commonplace, reflecting the ever-growing demands of users.
Mobile Connectivity
Mobile connectivity has been a key driver of smartphone evolution. The shift from 2G to 3G, 4G, and 5G has profoundly impacted how we interact with our devices and the world around us. The ever-increasing data speeds have enabled high-definition video streaming, cloud gaming, and real-time communication, creating a more interconnected and immersive experience. 5G promises to further enhance these capabilities with unprecedented speeds and lower latency, potentially revolutionizing various sectors, from entertainment to healthcare.
Emerging Technologies
Several emerging technologies are poised to reshape the smartphone landscape. Foldable displays offer new form factors and interactive possibilities. Artificial intelligence (AI) integration is enabling more intelligent assistants, personalized recommendations, and enhanced image processing. These advancements will likely lead to devices that are not only more powerful but also more intuitive and seamlessly integrated into our daily lives.
The emergence of foldable displays, for example, is transforming the way we interact with our phones, blurring the lines between a phone and a tablet.
Technical Specifications Over Time
| Year | Processor | RAM (GB) | Storage (GB) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2007 | ARM 11 | 128 MB | 8-16 GB |
| 2012 | Dual-core ARM Cortex-A9 | 1-2 GB | 16-32 GB |
| 2017 | Octa-core ARM Cortex-A73 | 2-4 GB | 32-64 GB |
| 2022 | Octa-core ARM Cortex-X2 | 6-8 GB | 128-512 GB |
The Future of Smartphones
The smartphone, once a novelty, has become an indispensable tool in modern life. Its evolution has been rapid and transformative, and the future promises even more profound changes. This journey into tomorrow’s smartphones will explore the emerging trends shaping design, new functionalities, and the impact of disruptive technologies.The relentless pursuit of innovation in the smartphone industry fuels a constant evolution.
From improved processing power and battery life to groundbreaking design elements, the devices are becoming more integrated into our daily routines, altering the way we interact with the world.
Ever wondered how the smartphone evolved? A great infographic on the history of the smartphone is a fantastic way to visualize this journey. It’s fascinating to see how far we’ve come, from the first clunky models to the sleek devices we use daily. Knowing about the innovative leadership in the digital world, like Andrea Mallard, CMO of Pinterest, Andrea Mallard cmo pinterest , gives insight into how brands adapt to the evolving tech landscape.
Ultimately, studying these historical shifts in mobile technology provides context for the incredible smartphone journey we’ve all experienced.
Major Trends Shaping Future Smartphone Design
The future of smartphone design is characterized by a confluence of factors, from materials science advancements to a renewed focus on user experience. Manufacturers are exploring new materials and fabrication techniques to create lighter, more durable, and aesthetically pleasing devices. Sustainability is also playing an increasingly important role, with a push towards eco-friendly materials and responsible manufacturing practices.
- Foldable and flexible displays: Foldable smartphones, like the Samsung Galaxy Z Fold series, are already showing promise. Future iterations are expected to have even more robust and durable displays, with a wider range of sizes and functionality. This trend promises greater screen real estate and new form factors.
- Enhanced camera systems: Camera technology continues to advance, leading to improvements in image quality, low-light performance, and the incorporation of innovative features like advanced image processing and augmented reality integration.
- Integration of advanced sensors: Smartphones will incorporate more sensors for advanced functionalities like biometrics, environmental monitoring, and health tracking. This integration will further blur the lines between smartphones and personal health and fitness trackers.
- Improved battery technology: Battery life is a persistent concern for smartphone users. Ongoing research and development aim to deliver significantly longer battery life with more efficient charging methods.
Potential New Functionalities and Applications
The smartphone’s potential is far from exhausted. New functionalities and applications are constantly emerging, extending beyond basic communication and information access.
- Personalized healthcare: Smartphones can provide more comprehensive health monitoring through sophisticated sensors and AI-powered diagnostics. This trend will likely continue to blur the line between consumer devices and medical tools.
- Immersive experiences: AR and VR technologies will integrate more deeply into smartphones, creating more engaging and interactive experiences. Imagine games and entertainment applications that transport you to different worlds or provide real-world overlays for navigation or product information.
- Smart home integration: Smartphones will act as central hubs for controlling smart home devices, enabling users to manage lighting, temperature, security, and other systems remotely.
- Financial transactions: The smartphone’s role in financial transactions is expanding. Future models may incorporate advanced security features and biometric authentication to enhance security and streamline the payment process.
Impact of Emerging Technologies on Smartphones
Emerging technologies are profoundly impacting the smartphone landscape. The convergence of these technologies is leading to exciting possibilities for the future of smartphones.
- Internet of Things (IoT): Smartphones will play a central role in connecting and controlling various IoT devices, offering a unified platform for managing smart homes, wearables, and other connected gadgets. This will enhance efficiency and convenience.
- Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR): AR and VR applications are expected to become more integrated into smartphones, enhancing gaming, entertainment, and even education through immersive experiences.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): AI will continue to shape smartphone experiences by improving features like voice assistants, image recognition, and personalized recommendations. AI will power more intelligent and intuitive interactions with the device.
Projected Technological Advancements
The next decade promises a surge in technological advancements within the smartphone industry. This infographic visually represents projected advancements in various categories.
That cool infographic on the history of the smartphone is fascinating, right? It’s amazing how far we’ve come! Understanding how these devices evolved is key to grasping the need for strategies like cross channel marketing, like the ones detailed in this insightful article about 6 ways to connect Google and Facebook audiences cross channel marketing 6 ways connect google facebook audiences.
Ultimately, the infographic’s historical context highlights the importance of adapting marketing techniques to keep pace with technological advancements.
| Category | Advancement | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Display Technology | Flexible, foldable, and high-resolution displays with advanced touch interfaces | Enhanced user experience and new form factors |
| Processing Power | More efficient and powerful processors with improved energy efficiency | Faster performance and longer battery life |
| Camera Technology | High-resolution sensors, advanced image processing, and AR integration | Enhanced image quality and interactive experiences |
| Connectivity | 5G and beyond with enhanced speeds and reliability | Faster data transfer and seamless connectivity |
Case Studies of Landmark Devices
The smartphone revolution wasn’t a single event; it was a series of iterations, each building on the successes and shortcomings of its predecessors. Understanding the key features, design philosophies, and market impacts of landmark devices like the iPhone and various Android models provides crucial insight into the evolution of the mobile computing landscape. This section delves into the specific characteristics of influential models, showcasing how they shaped the industry and user expectations.
Key Features of the iPhone
The iPhone, introduced in 2007, revolutionized mobile technology with its intuitive touch interface, integrated multimedia capabilities, and elegant design. Its initial release focused on a user-friendly experience, moving away from the complex menu systems of previous mobile phones. This simplified approach, coupled with a high-quality display and intuitive touch controls, made the iPhone a game-changer. The iPhone’s App Store, introduced later, solidified its position as a platform for developers and users alike, opening up a world of possibilities beyond basic calling and messaging.
This pioneering app ecosystem continues to influence mobile platforms today.
Key Features of Android
The Android platform, initially introduced in 2008, offered a contrasting approach to the iPhone. Its open-source nature allowed for diverse customization and a broader range of hardware partners, leading to a more fragmented but ultimately more competitive market. Early Android phones often prioritized affordability and a wider range of form factors, catering to diverse user needs and budgets. The flexibility of the Android OS allowed developers to create apps targeting specific user groups and device types.
This open-source philosophy, though, also contributed to a greater variety of quality and performance across different Android devices.
Evolution of Device Features
The evolution of key features across various models reflects the dynamic interplay between technological advancements, market demands, and user expectations. This evolution often follows a pattern of gradual improvement and innovation, with iterative refinements and additions over time. The advancements in processing power, camera technology, and battery life are particularly noticeable.
| Feature | iPhone 2G (2007) | iPhone 14 Pro (2023) | Nexus One (2010) | Pixel 7 Pro (2023) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Processor | ARM 11 processor | Apple A16 Bionic chip | Qualcomm MSM7250 | Google Tensor G2 |
| Display | 3.5-inch LCD | 6.7-inch Super Retina XDR display | 3.7-inch AMOLED | 6.7-inch LTPO AMOLED |
| Camera | 2-megapixel camera | 48-megapixel main camera | 5-megapixel camera | 50-megapixel main camera |
| Operating System | iOS 1.0 | iOS 16 | Android 1.0 | Android 13 |
Illustrative Examples of Smartphone Infographics
Infographics are powerful tools for visualizing complex information, and the history of smartphones is no exception. A well-designed infographic can condense decades of technological advancements into a digestible format, making it easier to grasp the evolution of these ubiquitous devices. They often highlight key milestones, innovations, and the cultural impact smartphones have had on our lives.Effective smartphone history infographics utilize various visual elements to engage the viewer and convey information clearly.
This includes the strategic use of timelines, charts, icons, and color palettes to illustrate significant periods and key developments. By employing these tools, infographics can transform potentially dry historical data into captivating narratives.
Examples of Well-Designed Infographics
Many excellent infographics illustrate the journey of smartphones. One effective approach uses a timeline format, visually representing the chronological progression of key events and inventions. Another effective method uses a branching tree diagram, showing how different technologies and concepts intersected and led to the smartphone as we know it. For example, a compelling infographic might start with the invention of the transistor and trace its impact on miniaturization, leading to mobile phones and ultimately, smartphones.
Visual Elements in Effective Infographics
A well-constructed infographic employs a variety of visual elements. Timelines, for instance, effectively depict the chronological progression of events, visually showcasing the sequential development of smartphone features. Charts can illustrate data like market share, sales figures, or technological improvements over time, offering a concise overview of significant growth trends. Icons and symbols can represent specific technologies, companies, or concepts, enhancing visual understanding and memorability.
Data Visualization in Smartphone Development
Infographics use data visualization to present information about smartphone development. A pie chart, for instance, could illustrate the market share of different smartphone operating systems over time. Bar graphs might show the increasing processing power or memory capacity of smartphones across different generations. Such visualizations transform complex numerical data into easily comprehensible visual representations. The comparison of processor speeds across different models over the years could be illustrated with a bar graph, enabling viewers to easily perceive the exponential growth.
Color Palettes and Fonts for Enhanced Understanding
Color palettes and fonts significantly impact the overall aesthetic and comprehensibility of an infographic. A consistent color scheme can represent different eras or categories of smartphones, making it easier for the viewer to identify and distinguish between various generations. The use of color-coded icons or symbols can further enhance the clarity and visual appeal. Font choices should be legible and visually appealing, aligning with the overall tone and message of the infographic.
Using a hierarchy of fonts can guide the viewer’s eye to crucial information. A bold, easily readable font for major milestones and a smaller, supporting font for additional details would enhance the visual hierarchy.
End of Discussion
In conclusion, the history of the smartphone infographic offers a compelling visual narrative of how a simple idea evolved into a ubiquitous technology. It’s a story of innovation, ingenuity, and societal transformation. The infographic highlights not just the technological advancements but also the profound impact smartphones have had on our daily lives, from communication to entertainment to commerce.
This infographic serves as a valuable resource for anyone looking to understand the complete journey of the smartphone.
