Amazon FBA vs FBM Your Ultimate Guide
Amazon FBA vs FBM: This guide delves into the complexities of fulfillment options on Amazon, exploring the pros and cons of Fulfillment by Amazon (FBA) and Fulfillment by Merchant (FBM). We’ll examine inventory management, shipping logistics, customer service, and ultimately, how these factors impact your bottom line and business scalability. Ready to make the best decision for your Amazon business?
Understanding the nuances of FBA and FBM is crucial for any seller aiming to thrive on the Amazon marketplace. This comprehensive comparison will provide a clear picture of each model, enabling you to choose the option that aligns best with your specific needs and goals. From initial setup to long-term profitability, we’ll cover every aspect, empowering you to make an informed choice.
Introduction to Amazon FBA and FBM

Amazon offers two primary fulfillment options for sellers: Fulfillment by Amazon (FBA) and Fulfillment by Merchant (FBM). Understanding the nuances of each model is crucial for optimizing your Amazon business strategy. Choosing the right model depends on your specific needs, resources, and long-term goals.FBA and FBM differ significantly in how inventory is managed, shipped, and handled. FBA empowers Amazon to manage the entire process, from warehousing to shipping, while FBM places the full responsibility on the seller.
This difference impacts everything from your overhead costs to your customer service response time.
Amazon FBA (Fulfillment by Amazon)
FBA leverages Amazon’s extensive network of warehouses and logistics infrastructure. Sellers ship their products to Amazon fulfillment centers. Amazon then handles warehousing, packaging, shipping, and customer service for those products. This often leads to faster shipping times and enhanced customer satisfaction. Amazon’s customer service and returns processes are integrated into the FBA system.
Thinking about selling on Amazon? Choosing between FBA (Fulfillment by Amazon) and FBM (Fulfillment by Merchant) can be tricky. Ultimately, the best option depends on your specific business needs. A fascinating example of someone navigating these complexities is John Sheldon, CMO of SmileDirectClub. John Sheldon, CMO of SmileDirectClub likely had to weigh the pros and cons of each method, considering inventory management, shipping, and customer service.
Understanding these factors is key to success, no matter which path you choose in the Amazon FBA vs FBM debate.
Inventory Management in FBA
Amazon takes on the responsibility of storing and managing your inventory within their fulfillment centers. This frees you from the need to maintain your own warehousing space and associated costs. You only need to focus on product listings and sales.
Shipping in FBA
Amazon handles all shipping aspects, from packaging to delivery. This simplifies the logistics process and can potentially lead to cost savings and efficiency. Amazon’s vast network of delivery hubs ensures timely delivery to customers.
Customer Service in FBA
Amazon handles customer service interactions for orders fulfilled through FBA. This means addressing customer inquiries, handling returns, and managing any potential issues. Sellers are responsible for handling any issues arising from the product itself, rather than the fulfillment process.
Seller Setup Process for FBA
The setup process involves creating an FBA account, shipping products to designated Amazon fulfillment centers, and ensuring product listings are compliant with Amazon’s policies. This usually includes detailed product information, accurate inventory data, and necessary compliance documents.
Amazon FBM (Fulfillment by Merchant)
With FBM, sellers are entirely responsible for managing every aspect of the fulfillment process. This includes warehousing, packaging, shipping, and customer service. This option offers greater control and flexibility, but also entails higher operational costs and responsibilities.
Inventory Management in FBM
Sellers are responsible for storing and managing their inventory. This requires significant investment in warehousing space, staffing, and logistics infrastructure. Potential issues include managing inventory levels, tracking shipments, and ensuring prompt order fulfillment.
Shipping in FBM
Sellers are responsible for all shipping arrangements, from labeling and shipping to handling tracking information. This necessitates the use of a shipping carrier and careful management of shipping costs.
Customer Service in FBM
Sellers are responsible for addressing all customer service inquiries, handling returns, and resolving any issues. This requires a dedicated customer service team or a well-structured process to handle inquiries and returns efficiently.
Seller Setup Process for FBM
Setting up an FBM account involves creating a seller account, handling inventory, setting up shipping procedures, and handling customer service directly. This process often requires significant upfront investment in infrastructure and staffing.
Cost Analysis and Pricing Strategies
Pricing strategies are crucial for success on Amazon. Understanding the costs associated with each fulfillment method—Amazon FBA (Fulfillment by Amazon) and FBM (Fulfillment by Merchant)—is essential for determining competitive pricing and maximizing profitability. This section delves into the cost breakdowns, pricing strategies, and product category advantages for each model.Analyzing costs and developing effective pricing strategies is paramount to achieving profitability in the Amazon marketplace.
A comprehensive understanding of the financial implications of each fulfillment model is key to making informed decisions.
Cost Breakdown for FBA and FBM
Understanding the different costs associated with FBA and FBM is fundamental to creating a sustainable business model. This includes storage fees, shipping costs, and potential penalties. These costs can significantly impact the profitability of your products.
- FBA Costs: FBA involves Amazon handling the warehousing, packaging, and shipping of your products. This typically incurs storage fees, which are based on the size and type of inventory stored. Shipping costs are often lower for FBA as Amazon handles the shipping logistics. However, potential penalties may arise from issues like product damage, incorrect labeling, or insufficient inventory.
The overall cost of FBA depends on these variables.
- FBM Costs: FBM requires you to handle all fulfillment tasks yourself. This means you’re responsible for warehousing, packaging, shipping, and customer service. You’ll need to factor in the costs of storage, packaging materials, shipping, and potential returns. FBM can potentially offer lower costs if you have significant economies of scale and efficient fulfillment operations. Potential issues with order accuracy and shipping time can also affect sales and reputation.
Pricing Strategies for FBA and FBM
Developing a comprehensive pricing strategy is critical to maximize profit margins for both FBA and FBM. This involves considering factors like product costs, shipping costs, and competition. Proper pricing allows you to cover all associated costs and maintain a competitive edge.
- FBA Pricing: Amazon FBA pricing often involves calculating the cost per unit (product cost + FBA fees + shipping costs) and adding a markup to reach the selling price. It’s important to thoroughly understand Amazon’s FBA fees for accurate cost calculations. Consider factors like product demand, competition, and potential sales volume when determining the markup percentage.
- FBM Pricing: FBM pricing requires careful calculation of all fulfillment costs, including packaging, shipping, and potential return handling. You need to calculate the total cost per unit and add a markup that accounts for these costs and desired profit margin. Consider factors like shipping rates, storage costs, and the need for a wider profit margin to compensate for handling the logistics yourself.
Product Categories Favoring FBA
Certain product categories benefit significantly from FBA’s streamlined fulfillment process. This model can help improve order fulfillment efficiency, which can positively impact customer satisfaction and order volume.
- Heavy or Bulky Items: Products that are large, heavy, or fragile often benefit from FBA. Amazon’s vast network of fulfillment centers handles the logistics of shipping these items more efficiently than individual sellers. This is particularly true for products that have a higher risk of damage during shipping.
- High-Volume Products: Products with high sales volume often see better cost-effectiveness with FBA. Amazon’s scale and efficiency in processing large quantities of orders can lead to cost savings compared to handling them independently. This model is advantageous when sales volume is significant.
- Products Requiring Specialized Handling: Certain products, like perishable items or those needing specific temperature controls, might be better served by FBA. Amazon’s infrastructure is often better equipped to handle these specialized requirements.
Determining Optimal Pricing for FBA and FBM
Accurate pricing is essential to achieve profitability and competitiveness in both FBA and FBM models. This requires careful analysis of costs, competitor pricing, and market demand.
- Cost Analysis: Determine the total cost per unit for each fulfillment method, including product cost, fulfillment fees (FBA or FBM), shipping, and potential returns. Accurate cost calculations are essential for establishing profitable pricing.
- Market Research: Analyze competitor pricing, market trends, and customer demand to identify a competitive and profitable pricing strategy. Monitoring competitor pricing and understanding market dynamics are crucial for staying competitive.
- Profit Margin Calculation: Determine the desired profit margin for each product and incorporate it into the pricing strategy. A clear profit margin ensures financial sustainability and growth. Calculate the markup needed to achieve the desired profit margin, considering all associated costs.
Inventory Management and Storage
Managing inventory effectively is crucial for success in any e-commerce business, especially on Amazon. Understanding the nuances of inventory management for both Fulfillment by Amazon (FBA) and Fulfillment by Merchant (FBM) is key to optimizing your operations and minimizing costs. This section delves into the specifics of inventory management and storage within each model, focusing on seller responsibilities, storage conditions, and the implications of inventory costs.The inventory management process varies significantly between FBA and FBM.
FBA entrusts Amazon with the warehousing and shipping of products, while FBM requires the seller to handle all aspects of inventory, from storage to shipping. This difference in responsibility translates into distinct costs, control, and potential risks. Comprehending these distinctions is critical for making informed decisions about which fulfillment method aligns best with your business strategy.
Inventory Management Process for FBA
Amazon handles the storage, picking, packing, and shipping of your products when using FBA. This means you are responsible for providing Amazon with properly labeled and packaged items, meeting their quality and safety standards. Your responsibilities are primarily focused on maintaining inventory accuracy within your Amazon account. Amazon manages the storage, handling, and distribution of your inventory.
This includes tracking inventory levels, managing potential damages, and coordinating shipments.
Inventory Management Process for FBM
In FBM, you are responsible for every aspect of inventory management. This encompasses warehousing, storage, picking, packing, and shipping your products. You need to source, manage, and store inventory. This involves securing appropriate warehouse space, employing staff for handling and shipping, and managing inventory levels. You are also accountable for maintaining quality control, handling potential damage, and ensuring timely delivery.
Storage Space and Conditions Offered by Amazon (FBA)
Amazon offers various storage options for FBA, tailored to different product types and sizes. These options include general-purpose storage, climate-controlled environments, and specialized storage for fragile or temperature-sensitive items. The specific storage space and conditions depend on the product’s characteristics and the seller’s chosen storage options. For example, books might be stored in general-purpose storage, while electronics might require a climate-controlled environment to prevent damage.
This customization enables sellers to optimize storage based on their products’ needs. Amazon generally maintains high standards for temperature and humidity control, ensuring product safety and longevity.
Implications of Inventory Storage Costs and Handling
Storage costs for FBA are based on factors like the size and type of storage used, along with the volume of inventory stored. FBM, on the other hand, requires you to cover all storage costs and labor expenses. For FBA, Amazon handles the storage costs, but there are fees associated with FBA services, such as monthly storage fees, and potential damage fees.
These costs should be factored into your pricing strategy and financial projections. Calculating the cost of storage and handling for both FBA and FBM is essential for accurate pricing and profitability.
Level of Control Over Inventory
FBA offers limited control over inventory management. You are not directly involved in the day-to-day handling and storage of your products, but your control over the inventory is limited to your Amazon seller account. You have less direct oversight over inventory locations and the specific conditions under which it is stored. In FBM, you maintain full control over your inventory.
You are responsible for everything, from storage location to handling and shipping. You can choose the most suitable warehousing solutions based on your specific requirements.
Shipping and Delivery
Shipping and delivery are critical aspects of any e-commerce business, particularly when considering Amazon’s fulfillment options. Understanding the nuances of how products are shipped, delivered, and tracked is essential for maximizing sales and customer satisfaction. This section dives into the details of shipping and delivery processes for both Fulfillment by Amazon (FBA) and Fulfillment by Merchant (FBM), examining the differences and highlighting Amazon’s role in the FBA model.
Shipping Processes for FBA and FBM
The shipping processes for FBA and FBM differ significantly. In FBA, Amazon takes on the responsibility for storing, packing, and shipping products to customers, while FBM requires merchants to handle these tasks themselves. This difference impacts the speed, reliability, and cost of delivery, along with the customer experience.
Types of Shipping Options, Amazon fba vs fbm
FBA offers a range of shipping options, leveraging Amazon’s extensive network and logistics infrastructure. Merchants have the advantage of selecting shipping services like Amazon Prime, which often entails faster delivery times and customer loyalty. For FBM, merchants must independently select carriers and shipping services, potentially offering a broader spectrum of options but often at a higher cost and with less control over the customer experience.
- FBA typically utilizes Amazon’s own delivery network, providing a variety of shipping options, such as Standard, Expedited, and Prime. These services are tailored to meet different customer needs and budgets.
- FBM offers a wider array of shipping options, potentially including services from UPS, FedEx, USPS, or other carriers. This allows merchants more control over shipping costs and delivery times but requires more direct management.
Speed and Reliability Comparison
Generally, FBA offers faster and more reliable delivery services compared to FBM. Amazon’s optimized logistics infrastructure and vast network of delivery centers contribute to quicker transit times. For FBM, delivery speed and reliability heavily depend on the chosen shipping carrier and the merchant’s management of the shipping process. This can lead to variability in delivery times and potential issues with tracking and customer service.
Amazon’s Role in the FBA Shipping Process
Amazon plays a critical role in the FBA shipping process, taking on the responsibility of warehousing, packing, and shipping products. This includes:
- Warehousing and Inventory Management: Amazon handles the storage and management of inventory, reducing the logistical burden for merchants.
- Picking and Packing: Amazon’s fulfillment centers handle the picking and packing of orders, ensuring accurate and efficient order processing.
- Shipping and Tracking: Amazon utilizes its extensive delivery network and shipping partners to dispatch orders and provide customers with tracking information.
This streamlined process reduces operational overhead for merchants, focusing their efforts on product sourcing and marketing.
Shipping Options Comparison Table
| Shipping Option | FBA | FBM |
|---|---|---|
| Amazon Prime | Yes, various Prime shipping options available | Potentially available through carrier partnerships, but not always guaranteed |
| Standard Shipping | Yes, with varying delivery times | Yes, through selected carriers |
| Expedited Shipping | Yes, with faster delivery times | Yes, through selected carriers |
| Shipping Costs | Usually competitive, but subject to product weight and dimensions | Highly variable, depending on carrier, weight, and distance |
| Delivery Time | Generally faster and more consistent, especially with Prime | Can vary significantly depending on carrier and merchant’s shipping process |
| Tracking | Comprehensive tracking available via Amazon | Tracking available through the carrier’s system |
Customer Service and Returns
Customer service is a critical component of any successful e-commerce business, especially on Amazon. Whether you’re fulfilling orders yourself (FBM) or utilizing Amazon’s fulfillment network (FBA), a strong customer service strategy is essential for building positive reviews, repeat business, and ultimately, boosting sales. This section dives into the nuances of customer service procedures and return handling for both FBA and FBM, highlighting seller and Amazon responsibilities.
Customer Service Procedures for FBA
Amazon handles customer service interactions, returns, and complaints for FBA sellers. This means Amazon is the first point of contact for customer issues. Sellers receive notifications and have access to customer information, enabling proactive communication and resolution. Amazon’s comprehensive system streamlines return processing, providing clear guidelines and tools for sellers to manage returns effectively.
Seller Responsibilities in FBA
While Amazon handles the majority of customer service interactions, sellers still have crucial responsibilities. Sellers are expected to provide accurate product information and descriptions. This includes providing detailed product specifications, dimensions, and material information, to avoid misunderstandings or customer dissatisfaction. Sellers must also comply with Amazon’s policies on product quality and customer service. If a customer has a legitimate complaint or return, the seller needs to collaborate with Amazon to ensure a fair resolution.
Customer Service Procedures for FBM
For FBM sellers, the entire customer service process, including returns and complaints, falls squarely on the seller’s shoulders. Sellers must have a clear return policy, readily available customer support channels, and efficient procedures for handling returns and addressing customer concerns. The seller is responsible for responding to customer inquiries, handling returns, and providing replacements or refunds.
Seller Responsibilities in FBM
In FBM, sellers are fully accountable for managing the entire customer service process. This includes promptly addressing customer inquiries, resolving issues, and ensuring a positive customer experience. A well-defined return policy, easily accessible contact information, and a clear process for processing returns are crucial for effective FBM customer service. Sellers must adhere to Amazon’s policies on returns and refunds.
This includes clearly stating return policies in their listings, and having a readily available and responsive customer service team.
Amazon’s Role in FBM
While Amazon doesn’t directly handle customer service interactions in FBM, they still provide resources and tools to assist sellers. Amazon’s Seller Central platform offers guidelines, templates, and resources to help sellers manage customer service effectively.
Comparing Customer Experiences
The customer experience varies significantly between FBA and FBM. FBA offers a more streamlined return process, with Amazon handling many aspects. FBM requires sellers to manage the entire process, potentially leading to a less smooth experience for customers if not well-managed. The perception of reliability and trust can vary depending on how well the seller handles the process.
Return Handling Steps (Table)
| Fulfillment Model | Steps in Handling a Return |
|---|---|
| FBA |
|
| FBM |
|
Profitability and Scalability
Choosing between Fulfillment by Amazon (FBA) and Fulfillment by Merchant (FBM) hinges on a crucial balance between profitability and scalability. Understanding the factors influencing each model’s success is vital for making an informed decision. This section delves into the key aspects that impact profitability and how each model impacts business growth potential.
Deciding between Amazon FBA (Fulfillment by Amazon) and FBM (Fulfillment by Merchant) for your online store can be tricky. A crucial step in this process is understanding your strengths and weaknesses, opportunities and threats. A solid SWOT analysis, like the one detailed in the right way conduct swot analysis , will help you weigh the pros and cons of each model, ensuring you choose the option best suited to your business goals and resources.
Ultimately, the right approach for your Amazon strategy hinges on a thorough understanding of your own capabilities and the market landscape.
Factors Influencing FBA and FBM Profitability
Profitability in both models is deeply intertwined with sales volume and pricing strategies. High sales volume often leads to economies of scale, reducing per-unit costs and boosting overall profit margins. Pricing strategies must align with product costs, market competition, and desired profit margins. Pricing too low can erode profits, while pricing too high may deter sales. Accurate cost analysis, including shipping, storage, and potential returns, is crucial for optimizing pricing decisions.
Impact on Scalability
The scalability of a business is significantly affected by the chosen fulfillment method. FBA’s infrastructure allows for faster scaling. Amazon’s vast network of fulfillment centers facilitates increased order volume without significant upfront investment in warehousing and logistics. FBM, on the other hand, demands more direct control over inventory management and logistics, potentially limiting the speed of expansion.
As a business grows, the infrastructure required for FBM can become a bottleneck, making it harder to scale efficiently.
Figuring out Amazon FBA vs FBM can be tricky, right? It’s a common dilemma for sellers. You’re constantly weighing the pros and cons of fulfillment. Fortunately, exploring a multi service case study, like the one detailed in this multi service case study , can provide valuable insight. It really helps you understand how different approaches work in practice, ultimately helping you choose the best option for your Amazon business model and product.
Measuring Profitability of FBA vs. FBM
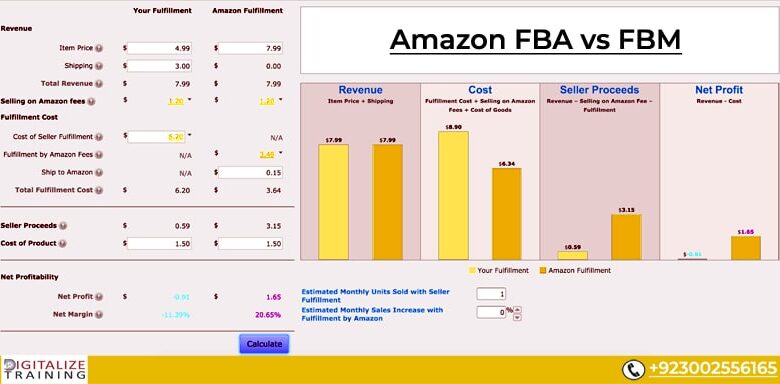
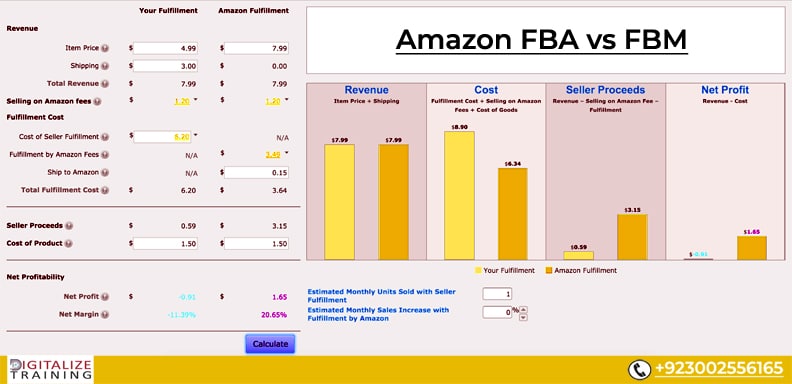
Profitability is measured by comparing revenue to total costs. For FBA, the calculation involves understanding Amazon’s fees (storage, processing, etc.), as well as the cost of goods sold. The profit margin is calculated by subtracting total costs from revenue. For FBM, the calculation includes costs like warehousing, shipping, and personnel, in addition to the cost of goods sold.
| Metric | FBA | FBM |
|---|---|---|
| Revenue | Sales generated from orders fulfilled by Amazon | Sales generated from orders fulfilled by the merchant |
| Cost of Goods Sold (COGS) | Cost of the product itself | Cost of the product itself |
| Amazon Fees | Storage, processing, and other fees charged by Amazon | Shipping, warehousing, and personnel costs |
| Other Costs (FBM) | N/A | Inventory management, customer service, and potential returns |
| Profit Margin | (Revenue – COGS – Amazon Fees) / Revenue | (Revenue – COGS – Other Costs) / Revenue |
Case Studies of Successful Businesses
Numerous businesses have successfully leveraged both models. For instance, a company selling high-demand electronics might benefit from FBA’s scalability, allowing rapid growth and market penetration. A company specializing in niche products with high profit margins might choose FBM to retain tighter control over pricing and logistics. Analyzing the specific characteristics of the product and target market is essential to determining the optimal model.
Thorough research into market trends and competitor strategies is crucial.
Pricing Strategies for Optimal Profitability
Pricing strategies directly impact profitability. A detailed analysis of cost of goods, shipping costs, and fulfillment fees is crucial for creating effective pricing strategies. Competitor analysis helps determine the optimal price point while maintaining profitability. Implementing dynamic pricing based on demand fluctuations can also enhance profitability.
Choosing the Right Model
Deciding between Fulfillment by Amazon (FBA) and Fulfillment by Merchant (FBM) is a crucial step in launching or scaling your Amazon business. It’s not a one-size-fits-all decision; the optimal choice hinges on various factors unique to your product, target audience, and business goals. Understanding the strengths and weaknesses of each model is paramount for making an informed and profitable decision.
Comparative Analysis of FBA and FBM
This table provides a concise overview of the key differences between FBA and FBM. A clear understanding of these contrasts is essential for a successful decision.
| Feature | FBA | FBM |
|---|---|---|
| Inventory Management | Amazon manages inventory, storage, and picking/packing. | You manage inventory, storage, and shipping. |
| Shipping Costs | Amazon handles shipping costs to customers, often at competitive rates. | You are responsible for all shipping costs, including potential higher shipping costs for larger orders. |
| Customer Service | Amazon handles customer service and returns. | You handle all customer service and returns. |
| Storage Costs | You pay storage fees based on product size and type. | No storage fees on Amazon, but you need warehouse or storage space. |
| Product Visibility | Amazon’s fulfillment network enhances product visibility. | You need to ensure your product is easily discoverable on Amazon. |
| Potential for Profit | Can lead to higher profit margins due to lower shipping costs and Amazon’s customer service. | Higher potential profit due to lower storage costs and greater control over pricing. |
| Time Commitment | Requires less time management for shipping and customer service. | Requires more time management for shipping, customer service, and inventory. |
Key Considerations for Choosing a Fulfillment Model
Several factors significantly influence the best fulfillment model for your product. A thorough evaluation of these considerations is crucial for optimal results.
- Product Characteristics: Product size, weight, and fragility significantly impact fulfillment costs. Bulky or fragile items might benefit from FBA’s robust handling capabilities, while lighter, smaller items might be more cost-effective to fulfill using FBM.
- Shipping Costs: Evaluate the cost of shipping your products to Amazon’s fulfillment centers. Compare these costs to the storage fees you will pay with FBA and the shipping costs associated with FBM. This will help you understand the true cost of each model.
- Inventory Management: FBA eliminates the burden of inventory management, storage, and shipping. This can be beneficial for businesses lacking the infrastructure or resources to handle these processes. Conversely, FBM gives you greater control over your inventory and allows you to manage it according to your business strategy.
- Customer Service and Returns: Amazon’s robust customer service and return handling capabilities can improve customer satisfaction. However, handling customer service and returns yourself gives you greater control over the customer experience. This control is crucial for building customer loyalty and a strong brand image.
- Scalability: Consider how your business might scale in the future. FBA provides scalability through Amazon’s vast fulfillment network, allowing you to handle increasing order volumes easily. FBM allows for scalability by adding more resources to your fulfillment infrastructure.
- Profitability: Calculate the potential profit margins for both models. Analyze your predicted sales volume and consider the costs associated with each fulfillment method. Factor in potential revenue gains from enhanced visibility through FBA.
Examples of When to Choose FBA or FBM
- FBA Preferred: High-volume sellers of fragile or oversized items, sellers seeking to benefit from Amazon’s customer service and brand recognition, and sellers aiming for broader market reach, would likely benefit from FBA. It’s a good option for products that benefit from Amazon’s logistics and expertise in handling returns.
- FBM Preferred: Low-volume sellers, sellers with limited resources or infrastructure, or sellers who want complete control over pricing and customer service, might favor FBM. This is a good option for products that can be easily shipped or that benefit from customized customer service strategies.
Advanced Strategies and Best Practices
Optimizing your Amazon FBA and FBM strategies requires more than just basic setup. Advanced techniques leverage Amazon’s tools and seller central features to enhance visibility, improve customer satisfaction, and ultimately drive higher sales and profitability. This section delves into crucial strategies for success in both fulfillment models.Advanced strategies involve a multifaceted approach, considering not only the product itself but also the marketplace dynamics, customer behavior, and Amazon’s algorithms.
Understanding these factors is key to maximizing your chances of success.
Optimizing Listings for Enhanced Visibility
Amazon’s search algorithm is complex and constantly evolving. To ensure your products are discoverable, optimizing listings is critical. A well-optimized listing attracts more organic traffic, which directly translates to more sales. This involves meticulous attention to product descriptions, high-quality images, and relevant s.
- Research and Implementation: Thorough research is essential to understand the terms customers use when searching for your product. Tools like Helium 10, MerchantWords, or even Amazon’s own search suggestions can provide valuable insights. Incorporate these s strategically into product titles, bullet points, and descriptions. Examples include long-tail s (e.g., “high-quality leather laptop sleeve for MacBook Pro 16”) and related terms.
Use a mix of broad, mid-tail, and long-tail s to target a wider range of potential customers.
- High-Quality Product Images: Visual appeal is paramount. Use professional-quality images that showcase the product from various angles and in different contexts. Clear, well-lit images, showcasing key features, are essential to attract customer attention. Include lifestyle images that demonstrate how the product is used. Avoid blurry, low-resolution, or misleading images.
- Compelling Product Descriptions: Detailed descriptions highlighting the product’s unique selling points are critical. Provide specific details about materials, features, benefits, and care instructions. Use clear, concise language that is easy for customers to understand. Focus on addressing customer needs and pain points.
Leveraging Amazon’s Tools for Enhanced Performance
Amazon offers a plethora of tools to assist sellers in optimizing their listings and improving performance. Utilizing these tools effectively can significantly impact sales and profitability.
- Amazon A+ Content: These custom templates allow sellers to create visually engaging content, showcasing product features and benefits in a more comprehensive manner. They can enhance the appearance of listings and increase customer engagement.
- Amazon Seller Central Reports: Seller Central provides detailed reports on sales, inventory, customer reviews, and other crucial metrics. Analyzing these reports allows sellers to identify trends, areas for improvement, and potential issues. For example, analyzing customer reviews can reveal common complaints or positive feedback, which can then be used to improve product offerings or marketing strategies.
- Amazon Advertising (Sponsored Products): Advertising campaigns can boost product visibility and drive targeted traffic to listings. This approach allows sellers to reach specific customer segments based on their search queries or browsing history. Careful budget management and targeted ad copy are crucial for success.
Setting Up FBA and FBM Listings for Optimal Results
Implementing a well-structured approach is critical for success in both FBA and FBM. This structured approach includes clear guidelines for listing optimization, inventory management, and customer service.
- Listing Optimization: Carefully research s, create compelling descriptions, and utilize high-quality images. Implement A+ content for a more compelling presentation.
- Inventory Management: Establish a robust inventory management system to track stock levels for both FBA and FBM. This ensures products are readily available and avoids stockouts.
- Customer Service Excellence: Prioritize responsive and helpful customer service, regardless of the fulfillment model. Promptly address customer inquiries and concerns to build trust and encourage repeat business.
Outcome Summary: Amazon Fba Vs Fbm
Ultimately, the choice between FBA and FBM depends heavily on your individual circumstances, product type, and business goals. Consider your current inventory, shipping capacity, customer service capabilities, and long-term scalability when making your decision. This in-depth comparison provides the necessary tools to navigate the Amazon fulfillment landscape with confidence and optimize your Amazon sales strategy.
