What is Customer Journey Mapping A Beginners Guide
What is customer journey mapping a beginners guide? This guide dives deep into the world of customer journey mapping, a powerful tool for understanding and improving customer experiences. We’ll explore the key stages of a typical customer journey, from initial awareness to post-purchase, and discover how it differs from other customer-centric approaches. We’ll also learn how to identify different customer segments and map their unique journeys, creating a visual representation to pinpoint areas for improvement.
From defining your customers and collecting data to creating a map, analyzing results, and taking actionable steps, this guide will equip you with the knowledge to master customer journey mapping. This journey begins with a concise explanation of the process and its benefits, and culminates in practical strategies for improving your customer experience.
Introduction to Customer Journey Mapping
Customer journey mapping is a powerful tool for understanding how customers interact with your business from initial awareness to post-purchase. It’s more than just a list of steps; it’s a visual representation of the entire customer experience, allowing businesses to identify pain points, optimize touchpoints, and ultimately enhance customer satisfaction and loyalty. By mapping the journey, businesses can gain valuable insights into how customers perceive their brand and what motivates their decisions.This deep dive into customer behavior helps companies tailor their strategies to meet evolving customer needs and expectations.
It’s a crucial exercise in customer-centricity, guiding businesses towards providing seamless and satisfying experiences.
Key Stages of a Customer Journey
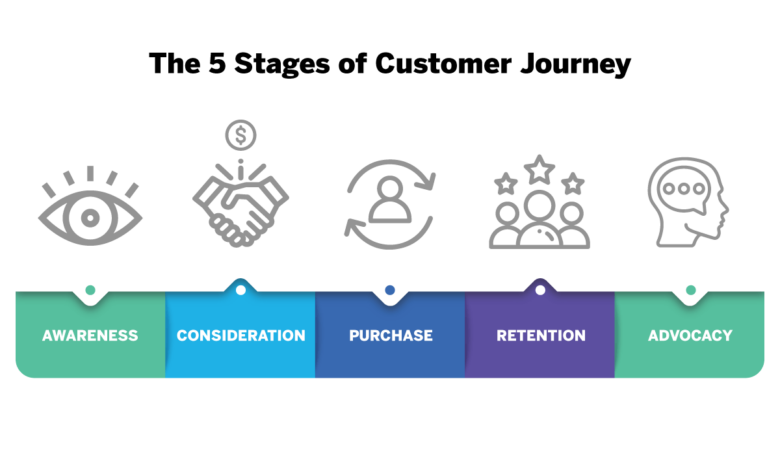
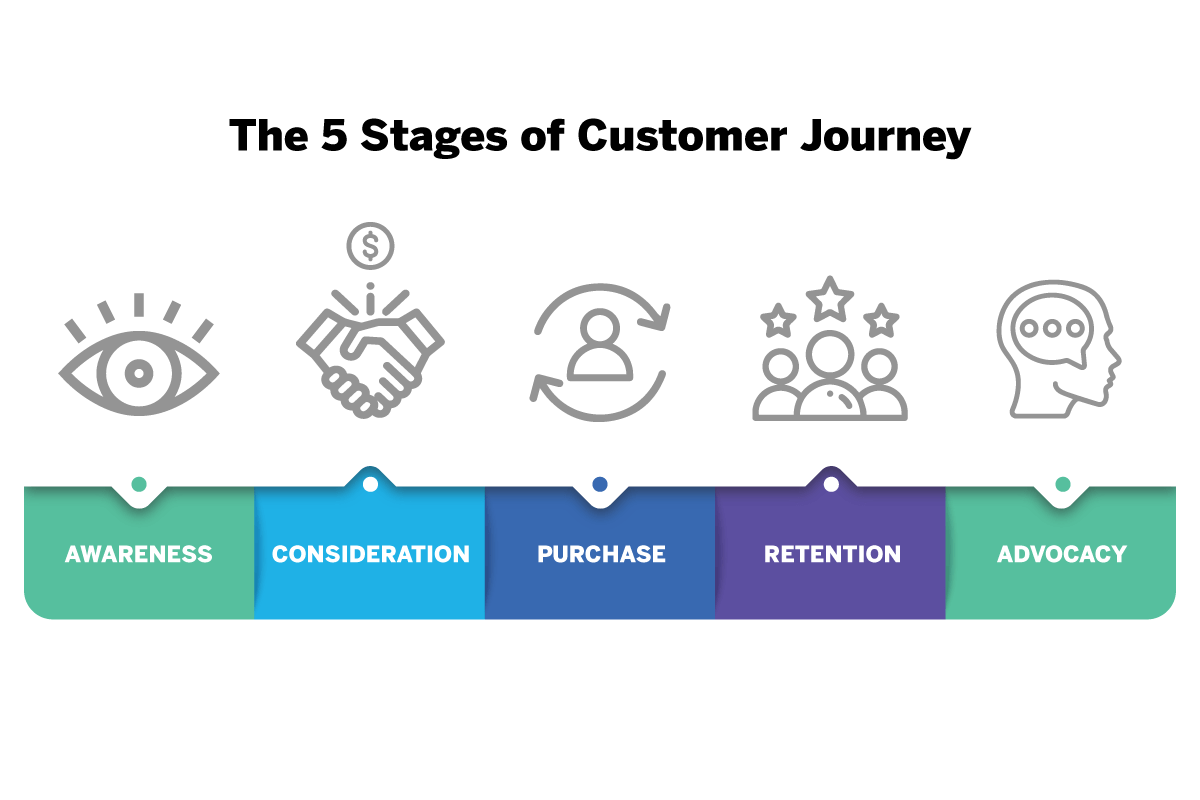
Understanding the different stages of a customer’s journey is essential for effective mapping. This journey typically unfolds in distinct phases, starting with awareness and culminating in post-purchase interactions.
- Awareness: This initial stage involves the customer becoming aware of your product or service. This can be through various channels, such as social media, search engine results, or word-of-mouth. Understanding how a customer becomes aware of your business is critical in crafting targeted marketing campaigns.
- Consideration: Once aware, the customer researches and considers different options. This phase involves evaluating your product or service against competitors and understanding what factors influence their decision-making process. It’s crucial to identify the information sources the customer uses during this stage to ensure they find the information they need.
- Decision: This stage involves the customer making a purchase decision. Understanding the factors that lead to a purchase decision, like price, reviews, and perceived value, is vital to optimizing the customer experience and overcoming any obstacles.
- Action: The customer interacts with your product or service. This includes the purchase process, the delivery, and the initial use of the product or service. Analyzing the experience at this stage will reveal potential pain points and opportunities for improvement.
- Post-Purchase: This final stage includes customer feedback, loyalty, and advocacy. It is important to follow up with customers after purchase to gather feedback and ensure they are satisfied with the product or service. Building long-term customer relationships is a key goal in this phase.
Customer Journey Mapping vs. Other Approaches
Customer journey mapping is distinct from other customer-centric approaches. While concepts like customer personas and customer feedback provide valuable insights, journey mapping offers a holistic view of the entire customer experience. Customer personas focus on defining the ideal customer profile, while customer feedback only captures a snapshot of the experience. Journey mapping provides a dynamic representation of the entire customer interaction.
| Approach | Focus |
|---|---|
| Customer Persona | Defining the ideal customer profile |
| Customer Feedback | Capturing a snapshot of the customer experience |
| Customer Journey Mapping | Providing a holistic view of the entire customer experience |
Visual Representation of a Customer Journey Map
A simple visual representation of a customer journey map can use basic shapes and text to illustrate the flow of a customer’s interaction. This visual representation helps to easily identify key touchpoints and potential areas for improvement.
“A customer journey map is a visual tool that helps businesses understand the complete customer experience.”
Imagine a horizontal line representing the customer journey, broken into distinct stages like awareness, consideration, decision, action, and post-purchase. Rectangles can represent different touchpoints (website, phone call, social media interaction). Circles can depict customer emotions or pain points. Arrows connecting these elements illustrate the flow and highlight specific actions. Adding color-coded text can further emphasize different aspects of the journey, such as customer sentiment.
Brief History of Customer Journey Mapping
Customer journey mapping has evolved significantly over time. Its origins can be traced to the development of marketing and customer service strategies. Initially, businesses focused on individual touchpoints, but a holistic view of the entire customer experience gradually emerged. As technology advanced, tools and methodologies for mapping customer journeys became more sophisticated, allowing for more detailed and nuanced insights.
Today, customer journey mapping is a standard practice for many businesses, offering a structured approach to understanding and optimizing the customer experience.
Defining the Customer: What Is Customer Journey Mapping A Beginners Guide
Understanding your customer is the cornerstone of effective customer journey mapping. Without a clear picture of who your customers are, their needs, and their motivations, your journey map will lack the crucial context to truly represent their experience. This section delves into the crucial steps of defining your customer base.Defining your customer isn’t just about identifying demographics; it’s about uncovering the motivations and pain points that drive their choices.
By understanding these intricacies, you can tailor your strategies to resonate with your audience and ultimately enhance their journey.
Customer Segmentation
Effective customer journey mapping requires a deep understanding of different customer segments. Simply put, your customer base is likely not monolithic. Instead, it’s comprised of diverse groups with unique needs and motivations. Understanding these segments allows you to tailor your messaging and experiences to resonate with each group.
So, you’re diving into customer journey mapping? It’s all about understanding how your customers interact with your brand, from initial awareness to post-purchase. Knowing this helps you tailor your marketing strategies. To visually represent this journey, consider using some cool video editing apps like the best video editing apps for Instagram free paid apps to create engaging visuals that highlight key touchpoints and pain points.
Ultimately, mapping out the customer journey is about creating a better customer experience, which leads to increased loyalty and sales.
- Demographic Segmentation: This involves categorizing customers based on observable characteristics like age, gender, location, income, and education level. This provides a foundational understanding of your customer base. For instance, a company selling luxury handbags might find a strong market among affluent women in major metropolitan areas.
- Psychographic Segmentation: This dives deeper, focusing on customers’ lifestyles, values, interests, and personalities. It reveals the “why” behind their choices. For example, a company selling eco-friendly clothing might target customers who prioritize sustainability and environmental consciousness.
- Behavioral Segmentation: This analyzes customer actions and interactions with your brand. This includes purchase history, website activity, customer service interactions, and frequency of engagement. A company selling online courses might segment customers based on their completion rates and engagement with course materials.
Customer Personas
Creating customer personas is a vital step in the journey mapping process. These are fictional, yet representative, characters that embody the key characteristics of your target customer segments. They provide a human face to the data, making it easier to understand and empathize with your audience.
- Defining Characteristics: A well-defined persona goes beyond basic demographics. It should encompass details like their goals, frustrations, pain points, motivations, and tech savviness. For instance, a persona for an online grocery store might be a busy professional who values convenience and fresh, healthy options.
- Examples: Imagine “Emily,” a young professional in her 20s. She’s a tech-savvy social media enthusiast, values convenience, and is concerned about the environment. This persona can inform the design of a user-friendly website and app for an eco-conscious clothing retailer.
Data Collection for Mapping
Gathering the necessary data for your journey map is crucial. The methods you use will depend on the specific aspects of the customer journey you’re focusing on. This might include surveys, interviews, focus groups, customer feedback, website analytics, and sales data.
- Surveys and Interviews: Surveys can help quantify customer experiences, while interviews provide in-depth qualitative insights. Combining both approaches provides a richer understanding.
- Customer Feedback Mechanisms: Actively soliciting feedback through various channels, such as online reviews, feedback forms, and social media monitoring, provides real-time insights into customer experiences.
- Data Analysis Techniques: Analyzing collected data using appropriate methods, such as trend identification and pattern recognition, helps extract actionable insights for the journey map.
Organizing Customer Journey Mapping Data
Organizing data in a user-friendly format is vital for analysis. A well-structured table or a visual representation, like a flowchart, will greatly aid in understanding the customer’s journey.
| Customer Segment | Key Motivations | Pain Points | Desired Outcomes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Eco-conscious shopper | Sustainability, ethical production | Limited eco-friendly options, high prices | Transparency, traceability, affordable options |
Mapping the Journey
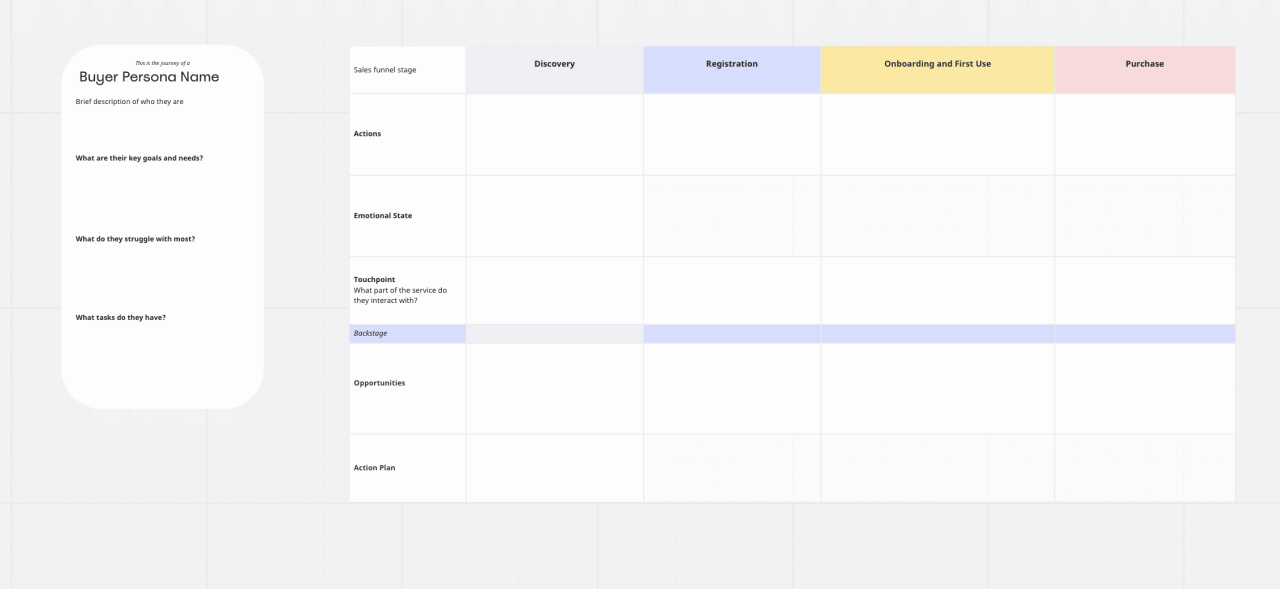
Now that we’ve established the importance of understanding our customers, let’s dive into the heart of customer journey mapping: visualizing the entire customer experience. This crucial step allows us to identify pain points, optimize touchpoints, and ultimately, improve customer satisfaction and loyalty. By mapping the journey, we move beyond theoretical understanding and gain actionable insights.
Effective journey mapping goes beyond simply listing touchpoints. It’s about understanding the customer’s emotional state, motivations, and expectations at each stage. We’ll explore different methods for gathering this data, creating a detailed template, and using visualization to uncover hidden opportunities for improvement.
Methods for Creating a Customer Journey Map
Several methods can be used to collect the necessary data for creating a comprehensive customer journey map. Combining multiple approaches provides a richer and more nuanced understanding of the customer experience.
- User Interviews: Directly engaging with customers through interviews provides valuable insights into their motivations, frustrations, and overall experience. These conversations allow for in-depth exploration of specific touchpoints and can uncover hidden pain points that might not be apparent through other methods.
- Surveys: Surveys are a powerful tool for gathering quantitative data on customer experiences. They can efficiently collect feedback from a large number of customers, providing a broader perspective on the journey. Use a mix of open-ended and multiple-choice questions to gain a balanced understanding.
- Existing Data Analysis: Leveraging existing data sources like website analytics, CRM data, and support ticket logs is crucial. Analyzing this data reveals patterns and trends in customer behavior and pain points, providing a valuable baseline for the journey map.
Creating a Customer Journey Map Template
A well-structured template is essential for effectively visualizing the customer journey. This template should encompass key elements that capture the complete experience.
| Element | Description |
|---|---|
| Touchpoints: | These are the specific interactions a customer has with your business. Examples include website visits, social media interactions, phone calls, and in-store experiences. |
| Emotions: | At each touchpoint, consider the customer’s emotional state. Are they excited, frustrated, confused, or satisfied? Mapping emotions helps identify potential areas for improvement. |
| Pain Points: | Identify areas where the customer experience is less than ideal. These could be delays, unclear instructions, or a lack of helpful support. Understanding pain points is critical for improvement. |
| Customer Goals: | Defining the customer’s goals and motivations at each stage helps you understand their actions. For example, a customer looking to purchase a new phone might be motivated by a need for faster internet or a better camera. |
Visualizing Customer Interactions
Visualizing customer interactions at each touchpoint is crucial for understanding the complete experience. A simple timeline is often sufficient, showcasing the sequence of events. You can use different colors or symbols to represent different touchpoints and highlight emotional states or pain points. This visual representation allows for easy identification of potential areas for improvement.
Empathy and Customer Perspectives
Throughout the journey mapping process, it’s essential to maintain empathy and strive to understand the customer’s perspective. Imagine yourself in their shoes, considering their motivations, frustrations, and expectations. This perspective helps identify areas needing improvement.
Identifying Customer Touchpoints
Systematic identification of touchpoints is crucial for creating an accurate journey map. Start by brainstorming all potential interactions a customer might have with your business. This could include online interactions, phone calls, in-person visits, and marketing communications. Consider every point of contact, from initial awareness to post-purchase support.
Key Elements of a Journey Map
A customer journey map is more than just a timeline of events. It’s a visual representation of the entire customer experience, revealing insights into their thoughts, feelings, and actions at each touchpoint. Understanding these key elements allows businesses to empathize with their customers and identify areas for improvement. This deep dive into the key elements will equip you with the tools to create effective journey maps that drive meaningful change.This section delves into the critical components of a customer journey map, demonstrating how to incorporate emotions, motivations, and pain points to gain a holistic view of the customer experience.
Understanding customer journey mapping is all about tracing a customer’s experience with your brand. It’s like creating a roadmap for their interactions, from initial awareness to post-purchase. A crucial step in this process is to perform a SWOT analysis, evaluating your strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats. This allows for a strategic approach and helps you to pinpoint areas for improvement.
Checking out the right way conduct swot analysis can help you understand the best practices for creating a thorough and impactful analysis, which ultimately fuels a better customer journey map. Ultimately, this will help you to create a more personalized and satisfying experience for your customers.
We’ll also show how to analyze interactions and utilize customer feedback to refine the map and enhance strategies.
Touchpoints and Channels
Understanding the various touchpoints and channels through which customers interact with your brand is fundamental. A touchpoint is any instance where a customer interacts with your company, whether it’s visiting your website, talking to customer service, or reading a review. Channels are the specific methods used for these interactions, such as email, social media, or phone calls. Identifying and documenting these touchpoints and channels provides a comprehensive view of the customer’s journey.
- Website visits: A customer might browse products, read blog posts, or check out shipping options. These interactions should be noted and categorized.
- Phone calls: Tracking calls allows businesses to understand customer support interactions, order inquiries, or complaints. Categorizing these interactions (e.g., successful order placement, issue resolution, unresolved issues) is crucial.
- Social media interactions: A customer might post reviews, ask questions, or engage with your brand’s content on social media platforms. These interactions are essential to understanding customer sentiment.
- Email communications: Email touchpoints like newsletters, promotional offers, or order confirmations should be documented and analyzed for their effectiveness.
Emotions and Motivations, What is customer journey mapping a beginners guide
Customer emotions and motivations play a significant role in shaping their experience. By understanding what drives customers and how they feel at each touchpoint, you can tailor your interactions to better meet their needs. Mapping emotions like excitement, frustration, or indifference provides a deeper understanding of the customer journey.
- Customer motivations: A customer might be motivated by saving money, convenience, or a desire for a specific product feature. Identifying these motivations helps understand their decisions and anticipate their needs.
- Emotional triggers: Understanding emotional responses at each touchpoint, such as feelings of anxiety when facing a complicated order process, is crucial. Identifying these triggers helps businesses proactively address potential issues and enhance the customer experience.
- Empathy mapping: Empathy mapping techniques, including detailed descriptions of customer feelings and needs at each stage of the journey, help to create a strong connection between the company and its customers.
Pain Points, Obstacles, and Frustrations
Pinpointing customer pain points, obstacles, and frustrations is vital for improvement. Analyzing these issues helps identify areas where the customer experience can be enhanced.
- Categorizing pain points: Pain points can be categorized by the customer’s needs, such as difficulty navigating the website, long wait times, or unclear return policies. This systematic approach aids in prioritizing areas for improvement.
- Analyzing interactions: Analyzing interactions, such as website browsing behavior or customer service calls, allows for identification of obstacles and frustrations, providing a clear picture of where the customer experience falters.
- Example: If a customer frequently abandons their online shopping cart, this indicates a potential pain point. Analyzing the reasons behind this behavior, such as a complex checkout process or lack of clear product information, helps businesses address the issue.
Incorporating Customer Feedback
Customer feedback is invaluable in refining journey maps. Collecting and analyzing feedback provides insights into customer experiences and helps businesses understand how to improve their offerings.
- Surveys and questionnaires: Surveys and questionnaires can collect feedback on various aspects of the customer journey. They can identify specific pain points or areas where customers feel frustrated.
- Review analysis: Analyzing online reviews and feedback from social media interactions helps identify recurring themes and common frustrations, providing concrete examples for improvement.
- Customer interviews: In-depth interviews with customers can provide valuable insights into their experiences and perspectives. Understanding their motivations and pain points allows for a tailored solution.
Analysis and Insights
Turning raw customer journey data into actionable insights is the ultimate goal of customer journey mapping. It’s not enough to simply understand the steps a customer takes; we need to understandwhy* they take those steps and what their motivations are. This analysis phase helps uncover pain points, opportunities for improvement, and ultimately, a more satisfying customer experience.The analysis of customer journey data reveals patterns and trends that are often hidden in disparate sources of information.
By synthesizing these insights, businesses can gain a holistic view of the customer experience and identify areas for optimization. This approach is crucial for building customer loyalty and driving business growth.
Methods for Analyzing Customer Journey Data
Understanding how to analyze the data collected during customer journey mapping is critical. Various methods can be employed to effectively extract meaningful insights. Qualitative data analysis, such as thematic analysis of customer feedback, and quantitative analysis of website analytics, are key techniques.
- Qualitative Analysis: This method focuses on understanding the “why” behind customer actions. Techniques include reviewing customer feedback (surveys, interviews, reviews), observing customer interactions (focus groups, shadowing), and analyzing open-ended responses to understand underlying emotions and motivations. By examining the nuances in customer narratives, businesses can gain a deeper understanding of the customer experience and identify subtle pain points.
- Quantitative Analysis: This approach uses numerical data to identify patterns and trends. Website analytics (page views, bounce rates, conversion rates), CRM data (customer interactions, purchase history), and sales data can be analyzed to pinpoint areas of high engagement or disengagement. This data-driven approach allows for measurable improvements to the customer journey.
- Combining Qualitative and Quantitative Methods: The most effective analysis often involves combining qualitative and quantitative methods. For example, quantitative data can show high bounce rates on a specific page, while qualitative data (customer feedback) might reveal that the page is difficult to navigate. By combining these methods, a comprehensive understanding of the problem and potential solutions emerges.
Identifying Patterns and Trends in Customer Behavior
Analyzing customer journey data reveals patterns and trends in customer behavior. By examining the frequency and timing of customer interactions, businesses can identify recurring themes and optimize their processes accordingly.
- Frequency of Interactions: High frequency of interactions on certain pages or at specific points in the journey might indicate areas of strong customer engagement or confusion. This can reveal opportunities to enhance these areas or address potential pain points.
- Timing of Interactions: Examining the timing of interactions across different touchpoints provides insights into customer flow and the optimal placement of resources. Delays or inconsistencies in the journey might indicate bottlenecks that can be improved.
- Clustering Interactions: Clustering similar customer behaviors can reveal patterns in their needs and preferences. This knowledge allows businesses to personalize their offerings and tailor the customer experience to specific segments.
Pinpointing Areas for Improvement in the Customer Experience
Once patterns and trends are identified, pinpoint areas requiring improvement. These areas may include friction points in the journey, unmet customer needs, or inadequate communication channels.
- Friction Points: Identify points where customers experience difficulty or frustration. These might include complicated forms, long wait times, or confusing instructions. Focusing on these friction points can lead to immediate improvements in the customer experience.
- Unmet Needs: Analyze customer feedback to uncover areas where customer needs are not being met. This might involve a lack of specific information, inadequate support, or missing features in a product. Addressing these unmet needs can significantly improve customer satisfaction.
- Communication Gaps: Assess the effectiveness of communication channels. Ensure clear, consistent, and timely communication across all touchpoints. A lack of clarity or responsiveness can lead to customer frustration. Improving communication channels strengthens the customer experience.
Prioritizing Improvement Efforts
Prioritizing improvement efforts based on the insights gained from the journey map is crucial. A clear prioritization strategy focuses resources on the most impactful areas.
- Impact Assessment: Assess the impact of each identified improvement opportunity. Consider the potential increase in customer satisfaction, efficiency gains, or revenue generation.
- Feasibility Analysis: Evaluate the feasibility of each improvement effort. Consider the resources, time, and expertise required to implement the change. Realistic timelines and achievable goals are critical.
- Risk Assessment: Evaluate the potential risks associated with each improvement effort. This ensures that any implementation process is carefully considered, and potential roadblocks are anticipated.
Identifying Opportunities for Enhancing the Customer Experience
Customer journey mapping can reveal opportunities to enhance the customer experience at various touchpoints. These opportunities can be identified by analyzing customer interactions and feedback.
- Personalized Experiences: Utilize data to personalize the customer experience, providing tailored interactions and offerings. This approach enhances customer satisfaction and loyalty.
- Streamlined Processes: Identify and eliminate unnecessary steps in the customer journey, creating a more efficient and user-friendly experience. This can significantly reduce friction points.
- Proactive Support: Anticipate customer needs and proactively offer support before problems arise. This proactive approach enhances customer satisfaction and reduces negative experiences.
Actionable Steps and Improvement
Turning customer journey map insights into tangible improvements is crucial for enhancing the customer experience. A well-crafted map reveals pain points, opportunities, and areas where your business can shine. This section delves into translating those insights into actionable steps, offering specific examples, and showing how to measure success.Effective improvement hinges on a deep understanding of customer needs and behaviors as revealed by the journey map.
A beginner’s guide to customer journey mapping helps you understand how your customers interact with your brand. Knowing this is crucial for improving your products and services. Understanding how search engine optimization works, particularly dynamic rendering, is also important. For example, learning about dynamic rendering SEO details you need to know will help you ensure your site is easily discoverable.
Ultimately, a strong customer journey map will guide your strategies for better conversions and satisfaction.
It’s not just about fixing problems; it’s about proactively creating a positive and seamless experience from start to finish.
Translating Insights into Actionable Steps
Identifying specific pain points and opportunities from the journey map is the first step. For instance, if the map shows customers struggling with a complex checkout process, this suggests a need for streamlining the steps. Identifying these specific points of friction empowers you to focus your efforts and resources on tangible improvements. The focus should be on solving real problems, not just adding features.
Examples of Specific Improvements
To illustrate, imagine a company discovers customers are abandoning their online shopping carts due to long loading times. A solution could be optimizing website performance through image compression or upgrading server infrastructure. Another example: if the customer journey map reveals frustration with lengthy customer service hold times, a solution could be implementing a live chat option or providing self-service resources like FAQs.
These examples highlight the direct link between map insights and actionable steps.
Tracking the Impact of Improvements and Measuring Success
Tracking the impact of improvements is crucial to demonstrating the value of journey mapping. Implementing A/B testing can be a powerful tool for evaluating different solutions. For instance, comparing conversion rates before and after implementing a simplified checkout process can offer quantifiable evidence of success. This data-driven approach provides evidence to support the validity of the customer journey mapping efforts.
Ongoing Monitoring and Refinement of the Customer Journey
The customer journey is dynamic. Customer needs evolve, and market conditions change. Therefore, regular monitoring and refinement of the customer journey are essential for maintaining a competitive edge. Continuous improvement through monitoring feedback and adapting to changing conditions ensures the customer journey remains relevant and effective. Using customer feedback channels and analyzing website analytics are key for maintaining this ongoing monitoring.
A Table of Improvement Steps at Each Touchpoint
This table Artikels the steps required for improvement at each touchpoint identified in the customer journey map.
| Touchpoint | Pain Point | Actionable Step | Metrics to Track |
|---|---|---|---|
| Website Landing Page | Poor user experience | Improve website design, add clear call-to-actions | Conversion rate, bounce rate, time on page |
| Product Page | Lack of product information | Add detailed product descriptions, high-quality images | Average order value, product views |
| Checkout Process | Complex and confusing steps | Simplify the checkout process, offer multiple payment options | Cart abandonment rate, checkout completion rate |
| Customer Service | Long hold times | Implement live chat, provide self-service options | Customer satisfaction score, average resolution time |
Visualizing the Customer Journey
Bringing your customer journey map to life involves more than just words and descriptions. Visualizations are crucial for effectively communicating the customer experience and identifying key pain points and opportunities. They transform abstract data into tangible insights, making the journey easier to understand and act upon. A well-designed visualization helps stakeholders grasp the entire customer experience at a glance, leading to better collaboration and faster decision-making.Visualizations allow you to quickly identify patterns, trends, and potential problems in the customer journey.
They’re a powerful tool for gaining a holistic understanding of the customer’s experience and making data-driven improvements.
Visual Representation Types
Visual representations of the customer journey can significantly enhance understanding and analysis. Different visual formats offer unique advantages, each highlighting specific aspects of the journey.
| Visual Representation | Purpose | Use Cases | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Flowchart | Illustrates the step-by-step process of the customer journey, highlighting sequential actions. | Ideal for depicting linear processes like online ordering, onboarding, or a product return. | A flowchart showing the steps involved in booking a flight online, from searching for flights to completing the payment. |
| Timeline | Highlights the duration and sequence of events in the customer journey, showing how long each step takes. | Useful for visualizing the entire customer journey from initial contact to post-purchase follow-up. Shows the time spent at each stage. | A timeline depicting the entire process of a customer purchasing a new car, from initial inquiry to the final delivery. |
| Customer Journey Map (with different styles) | Provides a comprehensive overview of the customer’s experience across different touchpoints. Various styles emphasize different aspects. | Excellent for understanding the emotional and psychological aspects of the journey, including customer frustrations and satisfaction levels. | A customer journey map focusing on the emotional experience of a customer returning a defective product, highlighting frustration and the desire for quick resolution. |
| Kanban Board | Visually tracks progress through stages of the customer journey. | Effective for showing how a customer moves through different stages of the sales process. Useful for tracking customer support tickets. | A Kanban board showing the progress of a customer’s support ticket, from initial submission to resolution. |
Color and Symbol Representation
Using color and symbols effectively can significantly enhance the clarity and impact of your customer journey map. Consistent use of color and symbols ensures the map is easily understood.For instance, use different colors to represent different customer segments (e.g., new customers, returning customers). Green might represent positive experiences, yellow could indicate neutral points, and red could represent areas of friction.
Symbols can represent specific touchpoints, such as a shopping cart for online purchases, a phone icon for customer service calls, or a speech bubble for feedback.
Effective Stakeholder Communication
Presenting the customer journey map to stakeholders requires a clear and concise approach. Focus on key insights and actionable recommendations, ensuring everyone understands the value of the map.Use clear and concise language to explain the map’s key findings. Highlight the most significant pain points and opportunities for improvement. Prepare a summary of the findings, highlighting actionable recommendations.
Incorporate visuals to simplify complex information and make it easy for stakeholders to grasp the essence of the journey.
Comprehensive Customer Journey Map Example
A comprehensive customer journey map integrates various visual tools and techniques. For instance, it could combine a timeline with a flowchart, illustrating the sequence of events and the duration spent at each touchpoint. A customer journey map can include various customer segments, demonstrating how different customer types interact with the product or service.Imagine a customer journey map for a software company.
It could showcase the steps a new user takes to install and start using the software, highlighting potential problems at each stage. The map could use a timeline to show the duration of each step and a flowchart to visualize the flow of events. Different colors could represent different user types (e.g., free trial users, paying subscribers), helping to identify specific pain points for each group.
Closure
In conclusion, customer journey mapping is a vital tool for businesses seeking to enhance customer satisfaction and loyalty. By understanding the customer’s perspective, businesses can identify pain points, optimize touchpoints, and ultimately create a seamless and positive experience. The insights gained from mapping the customer journey lead to actionable strategies for improvement, driving growth and fostering stronger customer relationships.