Guide to relalternate for Mobile Subdomain Optimization
Guide to relalternate for mobile subdomain optimization dives deep into optimizing your mobile site for search engines. This comprehensive guide covers everything from understanding mobile subdomains and rel=”alternate” tags to implementing them correctly and measuring their impact. We’ll explore best practices, technical considerations, and content strategies to ensure your mobile site performs optimally in today’s mobile-first world.
Mobile subdomains are crucial for in today’s mobile-first world. This guide will help you understand how to use rel=”alternate” tags effectively to direct search engines to your mobile content. We’ll cover technical implementation, mobile-first indexing, and crucial troubleshooting tips to ensure a smooth transition to a mobile-optimized website. Learn how to create a seamless experience for mobile users and enhance your search engine rankings.
Introduction to Mobile Subdomain Optimization
Mobile subdomain optimization is a strategy that involves creating a separate domain for mobile devices. This dedicated mobile site often improves the user experience by providing a tailored design, faster loading times, and optimized content for smaller screens. This approach contrasts with a responsive design, which adapts the same website code for all devices.This dedicated mobile experience, often accomplished through a mobile subdomain, is crucial for delivering a superior user experience.
Users expect quick loading times and a seamless browsing experience on their mobile devices. By having a dedicated mobile subdomain, developers can optimize the website specifically for mobile users.
Mobile Subdomain Strategies
Mobile subdomain optimization strategies are aimed at enhancing the mobile user experience. A mobile subdomain helps to improve site performance and accessibility on various devices. The strategy hinges on creating a separate domain or subdirectory for mobile devices. This approach allows for targeted optimization, including tailored design, specific content, and improved loading speeds.
Benefits of Mobile Subdomains for
Mobile subdomains can offer several advantages for search engine optimization. A dedicated mobile site can result in better mobile search rankings. Search engines, like Google, recognize and prioritize mobile-friendly websites, often rewarding them with higher rankings in mobile search results. This improved ranking can lead to increased visibility and organic traffic.
Optimizing your mobile subdomain with rel=alternate is crucial for search engine visibility. But did you know that a significant portion of potential customers leave items in their carts? Understanding abandoned cart marketing strategies, like those explored in abandoned cart marketing explained , can help you recover those lost sales. This means focusing on your rel=alternate tags for mobile subdomains is key for keeping your mobile site visible and your overall website traffic strong.
Role of rel=”alternate” Tags
The `rel=”alternate”` tag is a crucial component of mobile subdomain optimization. It allows search engines to understand the relationship between the mobile and desktop versions of a website. This tag is essential for proper indexing and ranking, ensuring search engines recognize both versions as part of the same site. By using `rel=”alternate”` tags, search engines can crawl both the desktop and mobile versions, preventing duplicate content penalties and effectively linking the mobile and desktop versions for optimal indexing.
Reasons for Using Mobile Subdomains
| Reason | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Improved User Experience | A dedicated mobile site can be optimized for touchscreens, smaller screens, and mobile-specific features, leading to a smoother browsing experience. |
| Enhanced Performance | Optimizing for mobile can reduce loading times and improve site responsiveness, which positively impacts user engagement and search engine rankings. |
| Content Optimization | A mobile-specific site allows for tailoring content, such as images and text, to better suit the smaller screens and navigation patterns of mobile devices. |
| Better Search Engine Crawling | `rel=”alternate”` tags help search engines differentiate between the desktop and mobile versions of a website, preventing duplicate content issues and improving the crawl process. |
| Separate Optimization Opportunities | A dedicated mobile site provides separate opportunities for optimizing images, code, and content for mobile-specific characteristics, leading to improved mobile performance. |
Understanding rel=”alternate” for Mobile: Guide To Relalternate For Mobile Subdomain Optimization
The `rel=”alternate”` link element is a crucial part of web optimization, particularly for mobile-first indexing. It allows webmasters to explicitly inform search engines about alternative versions of a page, such as mobile-specific content. This is essential for mobile subdomain optimization because it helps search engines understand which version of a page is intended for mobile users. Proper implementation ensures that search engines correctly index and serve the appropriate content to users, regardless of the device they are using.The `rel=”alternate”` tag acts as a bridge between different versions of a page, specifically designed for mobile users, and the main, desktop version.
This connection facilitates the delivery of the most suitable content to users based on their device. Correctly implementing `rel=”alternate”` helps search engines avoid indexing discrepancies and deliver the best user experience.
Technical Specifications of rel=”alternate”
The `rel=”alternate”` attribute, used within a ` ` tag, signifies that a given URL is an alternative version of another. This tag isn’t just about serving different content; it’s about guiding search engines toward the most appropriate version for a specific context. This is fundamental to delivering a consistent and optimized experience across various devices.
Attributes Relevant for Mobile Subdomain Optimization
Several attributes within the `rel=”alternate”` tag are particularly important for mobile subdomain optimization. These attributes help define the relationship between the main (often desktop) page and its mobile counterpart.
- `href`: This attribute specifies the URL of the alternative resource. Crucially, for mobile optimization, this would point to the mobile subdomain version of the page.
- `hreflang`: This attribute is vital for specifying the language and region targeted by the alternative resource. While not strictly required for mobile optimization, it’s good practice to use it to ensure correct interpretation by search engines.
- `media`: This attribute allows you to specify the media type or device for which the alternative resource is intended. For mobile optimization, you’d use a value such as `screen` and potentially a specific `width` and `height` value for device-specific targeting.
How rel=”alternate” Helps Search Engines Understand Mobile-Specific Content, Guide to relalternate for mobile subdomain optimization
By using the `rel=”alternate”` tag, you inform search engines that a mobile-specific version of the content exists. This tells search engines which version is tailored for mobile devices. Search engines leverage this information to deliver the appropriate page based on the user’s device. This direct communication ensures that search engines are aware of the dedicated mobile version, enhancing the user experience and mobile .
Table of rel=”alternate” Tag Implementations
The table below demonstrates different `rel=”alternate”` tag implementations for mobile subdomain optimization, showcasing various attributes and their impact.
| Scenario | HTML Implementation | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| Desktop page linking to a mobile subdomain | This example links the desktop page to the mobile subdomain, targeting English (US) users with a maximum width of 768 pixels. | |
| Handling different screen sizes | Two separate links for different screen sizes, providing tailored content for smaller and larger screens. | |
| Handling different languages | Separate links for English (US) and Spanish (Spain) versions, crucial for multilingual sites. |
Implementing rel=”alternate” for Mobile Subdomains
Implementing `rel=”alternate”` for mobile subdomains is crucial for search engine optimization. This technique signals to search engines that your mobile site is a distinct but related version of your desktop site, ensuring proper indexing and avoiding duplicate content penalties. This approach is particularly important for websites with significant differences between their desktop and mobile versions, as it helps search engines understand and appropriately rank both versions.The proper implementation of `rel=”alternate”` allows search engines to understand the relationship between the desktop and mobile versions, promoting a better user experience and higher search rankings for both.
This is crucial for mobile-first indexing, where Google prioritizes mobile versions of websites in search results.
Best Practices for Implementation
Correct implementation of `rel=”alternate”` tags involves several key practices. These ensure search engines accurately interpret the relationship between your desktop and mobile versions, avoiding confusion and potential penalties. Adhering to these best practices is vital for maintaining a positive presence.
Optimizing your mobile subdomain with rel=alternate is crucial for a positive user experience and search engine visibility. Understanding how this affects your overall SEO score is key. A higher SEO score, as explained in this helpful resource what is an seo score , can lead to better rankings. Ultimately, implementing a robust rel=alternate strategy ensures your mobile site is effectively indexed and easily accessible, maximizing your chances of a strong search engine presence.
- Use the correct URL format: The `href` attribute of the `link` tag must accurately point to the mobile subdomain’s URL. For example, if your desktop site is `www.example.com` and your mobile site is `m.example.com`, the `href` value should be `m.example.com`. Incorrect URLs can lead to misinterpretation and hinder the intended relationship between the sites.
- Specify the `rel=”alternate”` attribute: This attribute explicitly tells search engines that the linked URL is an alternative version of the current page. This attribute is crucial for conveying the relationship between the desktop and mobile versions to search engines.
- Include `hreflang` attribute if applicable: For mobile versions that serve specific regions, the `hreflang` attribute helps to specify the target audience for the alternative version. For example, a mobile version tailored for a specific country would use a `hreflang` attribute to signal that to the search engine.
Various Implementation Methods
Implementing `rel=”alternate”` tags can be done in several ways within your website’s HTML code. Each method serves the same purpose of signaling the relationship between the desktop and mobile versions to search engines.
- Using the `` section: The most common and straightforward approach involves embedding the `link` tag with the `rel=”alternate”` attribute within the ` ` section of your HTML pages. This ensures the tag is readily available for the browser and search engines to process.
- Using a separate `` tag for each page: For greater control, you can use a separate `link` tag for each page. This allows for more tailored configurations depending on the content, ensuring appropriate handling for different pages within the website.
Examples of Correct and Incorrect Implementations
Correct Implementation (Example):
<link rel="alternate" href="m.example.com/page1" hreflang="en-US" media="only screen and (max-width: 768px)" />
Incorrect Implementation (Example):
<link rel="alternate" href="https://example.com/mobile/page1" />
The correct example above clearly specifies the mobile URL and, importantly, uses the `hreflang` attribute for targeted regional mobile pages and a `media` attribute. The incorrect example lacks crucial elements, potentially leading to misinterpretation by search engines.
Setting Up a Mobile Subdomain with rel=”alternate”
A Comprehensive Guide:
- Identify your mobile subdomain: Determine the specific URL for your mobile site (e.g., `m.example.com`).
- Create the mobile version of your pages: Ensure that each page on your mobile subdomain corresponds to a page on your desktop site. Content should be tailored for mobile viewing, but the overall message should remain consistent with the desktop version.
- Add the rel=”alternate” tag: In the ` ` section of each corresponding desktop page, include the `link` tag with the `rel=”alternate”` attribute, linking to the equivalent mobile page.
- Test your implementation: Use developer tools and checkers to verify that the `rel=”alternate”` tags are correctly implemented and functioning as intended.
Mobile-First Indexing and rel=”alternate”
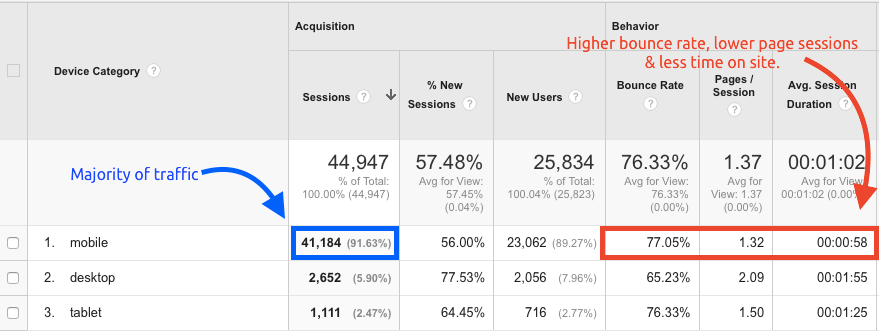
Mobile-first indexing is a significant shift in how search engines crawl and index websites. It prioritizes the mobile version of a website over the desktop version, meaning Google now primarily uses the mobile site’s content to understand and rank pages. This change has profound implications for website optimization, particularly for mobile subdomains.
Understanding how mobile-first indexing interacts with the `rel=”alternate”` tag is crucial for maintaining a positive user experience and achieving high search rankings. The `rel=”alternate”` tag helps search engines understand the relationship between different versions of a website, especially important in the mobile-first world.
Mobile-First Indexing Impact on rel=”alternate”
Mobile-first indexing fundamentally alters how search engines interpret `rel=”alternate”` tags used for mobile subdomains. Previously, search engines could index and rank both mobile and desktop versions, potentially leading to duplicate content issues. Now, the mobile version is the primary source, and `rel=”alternate”` tags become vital for directing search engines to the correct mobile content when different versions exist.
Significance of rel=”alternate” for Mobile-First Indexing
The `rel=”alternate”` tag acts as a clear signal to search engines, specifically Google, about the relationship between the mobile and desktop versions of a website. This ensures that Google understands which version is the canonical, or primary, version for indexing. Without proper `rel=”alternate”` implementation, search engines might misinterpret the relationship between the different versions, potentially resulting in indexing errors and ranking inconsistencies.
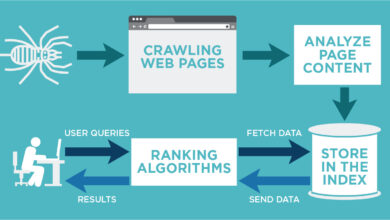
How Search Engines Use rel=”alternate” for Mobile-First Indexing
Search engines use the `rel=”alternate”` tag to determine the correct mobile version to index for a particular search query. This involves several key steps:
- Crawling and Parsing: Search engines crawl both the mobile and desktop versions of a website. They parse the HTML code to identify `rel=”alternate”` tags.
- Identifying Canonical Version: The `rel=”alternate”` tag, combined with the `hreflang` attribute (if present) and the URL structure, helps determine the canonical mobile version. This version is treated as the primary version for indexing.
- Indexing Mobile Content: The search engine indexes the content of the identified canonical mobile version, creating an index entry for the mobile site. It ignores the desktop version unless it’s properly linked and marked with appropriate `rel=”alternate”` and `hreflang` attributes.
- Ranking Based on Mobile Experience: Search engines then use the indexed mobile content to rank the website in search results. The ranking algorithm considers factors such as page speed, mobile usability, and overall user experience of the mobile site.
Correctly implementing `rel=”alternate”` tags is crucial for mobile-first indexing. Inaccurate or missing `rel=”alternate”` tags can confuse search engines, leading to improper indexing and reduced rankings. This is especially true when a mobile subdomain is used. For example, if the mobile site is not properly linked with the desktop site via `rel=”alternate”`, search engines might incorrectly perceive the mobile site as a separate, independent entity, leading to reduced visibility in search results.
Therefore, careful consideration of `rel=”alternate”` tags is essential for successful mobile-first optimization.
Technical Considerations for Mobile Subdomains
Setting up a mobile subdomain isn’t just about creating a separate URL; it’s about crafting a seamless user experience optimized for mobile devices. This involves more than just redirecting traffic; it’s a meticulous process requiring careful technical consideration. Proper implementation ensures your mobile site performs at optimal speed and efficiency, leading to better user engagement and improved search rankings.
The technical aspects of mobile subdomains, particularly the configuration of servers and the implementation of rel=”alternate” tags, are crucial for successful mobile-first indexing. Careful attention to website speed and responsiveness directly impacts user satisfaction and search engine rankings. This section will delve into the technical requirements, configuration strategies, and performance considerations involved in establishing a robust and effective mobile subdomain setup.
Server Configuration for Mobile Subdomains
To effectively manage traffic and ensure optimal performance, you need to configure your server to handle requests from both the desktop and mobile versions of your website. This typically involves setting up a separate server block or virtual host for the mobile subdomain. This allows for customized caching, compression, and other performance-enhancing strategies. For example, you might use a Content Delivery Network (CDN) to serve static assets from a geographically closer server to the user, significantly reducing load times.
Implementing rel=”alternate” Tags
The `rel=”alternate”` tag is crucial for guiding search engines to the correct mobile version of your website. Proper implementation ensures that search engines can easily identify and understand the relationship between your desktop and mobile sites. The `rel=”alternate”` tag must be correctly structured and linked from both the desktop and mobile versions.
Website Speed and Responsiveness
A slow-loading mobile website is a significant barrier to user engagement. Optimize your mobile site for speed through techniques like image optimization, browser caching, and leveraging a CDN. Furthermore, ensure your website is responsive, adapting seamlessly to different screen sizes and orientations. This responsiveness is paramount for providing a consistent and engaging user experience across various devices.
Comparison of Mobile Subdomain Technologies
| Technology | Advantages | Disadvantages | Considerations |
|—|—|—|—|
| Apache Virtual Host | Simple configuration, widely available | Limited scalability, potential performance bottlenecks for high traffic | Suitable for smaller websites or those with predictable traffic |
| Nginx | High performance, excellent scalability | Steeper learning curve for some users | Ideal for large-scale deployments or websites with significant traffic |
| Cloud Hosting Services (e.g., AWS, Google Cloud) | Scalability, reliability, managed infrastructure | Cost considerations, dependence on cloud providers | Appropriate for complex applications and websites with high traffic volume |
Content Strategy for Mobile Subdomains
Optimizing for mobile is no longer a nice-to-have, but a must-have. A significant portion of your website traffic likely originates from mobile devices. A dedicated mobile subdomain, combined with a well-defined content strategy, allows you to tailor the user experience for a seamless and efficient browsing experience.
Mobile subdomains are crucial for providing an optimal experience. They not only improve performance but also cater to the specific needs and constraints of mobile users, such as smaller screens, limited bandwidth, and different interaction patterns.
Creating Mobile-Specific Content
Mobile users often have different information needs than desktop users. They may be looking for quick answers, product details, or directions. The content on your mobile subdomain should reflect these needs. Avoid lengthy articles or complex layouts that don’t translate well to smaller screens.
Tailoring Content to Mobile Needs
Mobile users typically seek concise and easily digestible information. Short, scannable paragraphs, clear headings, and bulleted lists are effective for mobile content. Images should be optimized for mobile devices, ensuring they load quickly and display correctly. Consider using responsive design principles to ensure content adapts seamlessly to various screen sizes.
Mobile-Friendly Design and Layout
Mobile-friendly design is essential for a positive user experience. Use a clean, uncluttered layout with large, easy-to-read text. Prioritize essential information, making it easily accessible to users. Avoid using complex navigation structures that are difficult to use on a small screen. Consider using a mobile-first design approach.
Example of a Webpage with Mobile Subdomain and rel=”alternate”
Let’s imagine a clothing retailer, “FashionForward.” They have a primary website (www.fashionforward.com) and a mobile subdomain (m.fashionforward.com). The following example demonstrates how rel=”alternate” tags are used to signal the relationship between the desktop and mobile versions.
Optimizing your mobile subdomain with rel=alternate is crucial for SEO. Understanding how drip campaign marketing explained works can help you build a more effective strategy for user engagement. For example, if you use a different mobile subdomain, using rel=alternate tags ensures that search engines know which version of your site is the best for mobile users. This detailed guide to relalternate for mobile subdomain optimization is key to keeping your mobile site optimized and performing well.
| Desktop Page (www.fashionforward.com/products/dress1) | Mobile Page (m.fashionforward.com/products/dress1) |
|---|---|
|
Detailed description of the dress, including fabric, color options, and size charts. Large images of the dress from multiple angles. Customer reviews and ratings. Extensive FAQs. |
Concise description of the dress, focusing on key features and benefits. Optimized images, suitable for smaller screens. Customer ratings, but reduced detail. Quick links to relevant FAQs. |
The mobile page (m.fashionforward.com/products/dress1) would include the following rel="alternate" tag:
<link rel="alternate" href="http://www.fashionforward.com/products/dress1" hreflang="en" media="(min-width: 768px)" />
This tag indicates that the desktop page (www.fashionforward.com/products/dress1) is the alternate version for larger screens. This example clearly demonstrates how rel=”alternate” tags can assist search engines in understanding the relationship between the desktop and mobile versions of a page.
Troubleshooting rel=”alternate” Implementation
The `rel=”alternate”` tag is crucial for mobile subdomain optimization, ensuring search engines correctly identify and index your mobile content. However, implementation errors can hinder this process. This section details common issues and provides troubleshooting steps.Proper implementation of the `rel=”alternate”` tag is vital for search engines to understand the relationship between your desktop and mobile versions of a page. Errors can lead to indexing issues, impacting your mobile site’s visibility and overall performance.
Common Implementation Errors
Incorrect `rel=”alternate”` tag attributes or values can lead to problems. Missing or mismatched attributes, incorrect URLs, or inconsistencies in the tag’s usage across your site are frequent issues.
Troubleshooting Tips and Solutions
Thorough testing and meticulous checking are key to identifying and resolving `rel=”alternate”` implementation problems. Here are some actionable steps:
- Validate the HTML Structure: Use a validator like the W3C Markup Validation Service to ensure the `rel=”alternate”` tag is properly embedded within the HTML code. This ensures correct syntax and proper attribute values, preventing errors caused by incorrect HTML structure.
- Verify URL Accuracy: Double-check the URLs referenced in the `rel=”alternate”` tag. Ensure they are accurate and point to the intended mobile subdomain versions of your pages. Mistakes in URLs are a frequent source of errors.
- Ensure Correct Attribute Values: Confirm that the `hreflang` attribute (if used) is correctly specifying the language and region for each alternate version. Incorrect `hreflang` values can confuse search engines, making them unable to identify the appropriate mobile page. Make sure the `hreflang` attribute is correctly targeted to mobile users in the appropriate region and language.
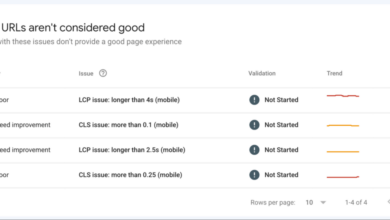
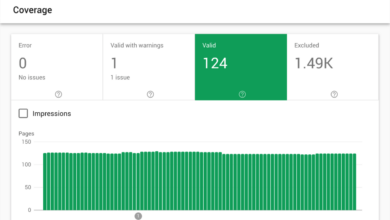
- Cross-check with Search Console Data: Use Google Search Console to identify any indexing issues related to your mobile subdomain. Review crawl errors and indexing status to pinpoint problems with `rel=”alternate”` implementation.
- Test Across Different Browsers and Devices: Verify the `rel=”alternate”` tag works correctly across various browsers (Chrome, Firefox, Safari) and mobile devices (iOS, Android). This helps in identifying any browser-specific issues or inconsistencies.
Examples of Errors and Fixes
- Error: Incorrect URL in `href` attribute of the `rel=”alternate”` tag. For example, the tag might point to a desktop page instead of the mobile version.
Fix: Correct the `href` attribute to point to the appropriate mobile subdomain URL. Example: Replace `https://www.example.com/page` with `https://m.example.com/page`.
- Error: Missing or incorrectly formatted `rel=”alternate”` tag.
Fix: Ensure the tag is properly formatted within the `
` section of the HTML document, containing the correct `href` attribute and other required attributes.
Table of Common Errors and Fixes
| Error | Description | Fix |
|---|---|---|
Incorrect URL in href attribute |
The href attribute points to the wrong URL (e.g., desktop instead of mobile). |
Correct the href attribute to point to the correct mobile subdomain URL. |
Missing rel="alternate" tag |
The tag is absent from the HTML. | Add the rel="alternate" tag to the `` section of the HTML document. |
Incorrect hreflang attribute value |
The hreflang attribute is incorrect, not specifying the correct language or region. |
Correct the hreflang attribute value to match the language and region of the mobile version. |
Measuring the Impact of rel=”alternate”
Tracking the effectiveness of your mobile subdomain optimization, particularly with `rel=”alternate”` implementation, hinges on meticulous monitoring and analysis. Understanding how users interact with your mobile site and how search engines perceive it is crucial. By implementing robust tracking mechanisms, you can identify areas for improvement and quantify the benefits of your efforts.A key element in assessing the impact of `rel=”alternate”` is recognizing that success isn’t solely measured by a single metric.
A holistic approach that combines various performance indicators provides a more comprehensive picture of your mobile subdomain’s health and effectiveness.
Tracking Mobile Subdomain Performance
Monitoring mobile subdomain performance requires a multi-faceted approach. You should track not only the direct impact on search engine rankings but also how users engage with the content. Comprehensive tracking tools and data analysis are essential to understanding the full picture.
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
Several key metrics offer insights into the success of your mobile subdomain optimization.
- Search Engine Rankings: Monitoring the ranking position of your mobile subdomain for targeted s is crucial. Changes in rankings directly correlate with the effectiveness of your `rel=”alternate”` implementation and efforts. Tools like Google Search Console provide valuable data in this area.
- Mobile Traffic: Analyze the volume of mobile traffic directed to your subdomain. An increase in traffic could indicate that users are finding and engaging with your mobile site more easily. Tracking tools such as Google Analytics offer detailed traffic data.
- Conversion Rates: Monitor conversion rates on your mobile subdomain. If your mobile site is optimized for conversions (e.g., online purchases, form submissions), an increase in conversion rates indicates success. This data should be analyzed in relation to traffic data to get a clearer picture of engagement.
- Bounce Rate: The bounce rate indicates how quickly visitors leave your mobile site. A low bounce rate suggests users find your mobile site engaging and informative, while a high bounce rate could indicate issues with the site’s design or content relevance. Compare bounce rates with desktop site data.
- Average Session Duration: This metric reveals how long users spend on your mobile site. A longer average session duration often suggests high user engagement and satisfaction with the content. Analyzing this metric alongside other user behavior metrics will help understand the reasons for increased session duration.
Analyzing Data to Assess Effectiveness
Data analysis involves comparing the performance metrics of your mobile subdomain before and after the `rel=”alternate”` implementation. A clear understanding of trends is key to identifying the true impact.
- Baseline Performance: Establish a baseline for your mobile subdomain’s performance before implementing `rel=”alternate”`. This data serves as a benchmark for comparison and assessing the improvements that result from the implementation.
- Post-Implementation Analysis: Collect and analyze data for a period after implementing `rel=”alternate”`. Compare the key performance indicators (KPIs) with the baseline to assess the effectiveness of the implementation. Identify areas that are improving and areas where additional optimization is needed.
- Correlation Analysis: Identify correlations between specific changes in your `rel=”alternate”` implementation and changes in user behavior or search engine rankings. If a particular change in the implementation coincides with an improvement in a metric, it provides evidence of its effectiveness.
Sample Dashboard
A sample dashboard for a mobile subdomain might display:
| Metric | Data (e.g., Jan 2024) | Data (e.g., Feb 2024) | Change |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mobile Traffic (unique visitors) | 10,000 | 12,500 | +25% |
| Conversion Rate (e-commerce) | 2% | 2.5% | +25% |
| Average Session Duration | 1 minute 30 seconds | 2 minutes | +40 seconds |
| Search Console Mobile Index Coverage | 95% | 98% | +3% |
This table provides a snapshot of how data from various sources can be combined to track the effectiveness of the `rel=”alternate”` implementation. Note that actual data will vary depending on the specific website and implementation.
Last Word
In conclusion, optimizing your mobile site with rel=”alternate” tags is vital for success in today’s mobile-first world. By understanding the technical aspects, implementing best practices, and monitoring your results, you can significantly improve your mobile and user experience. This guide provides a roadmap for achieving a seamless transition to mobile-first optimization.